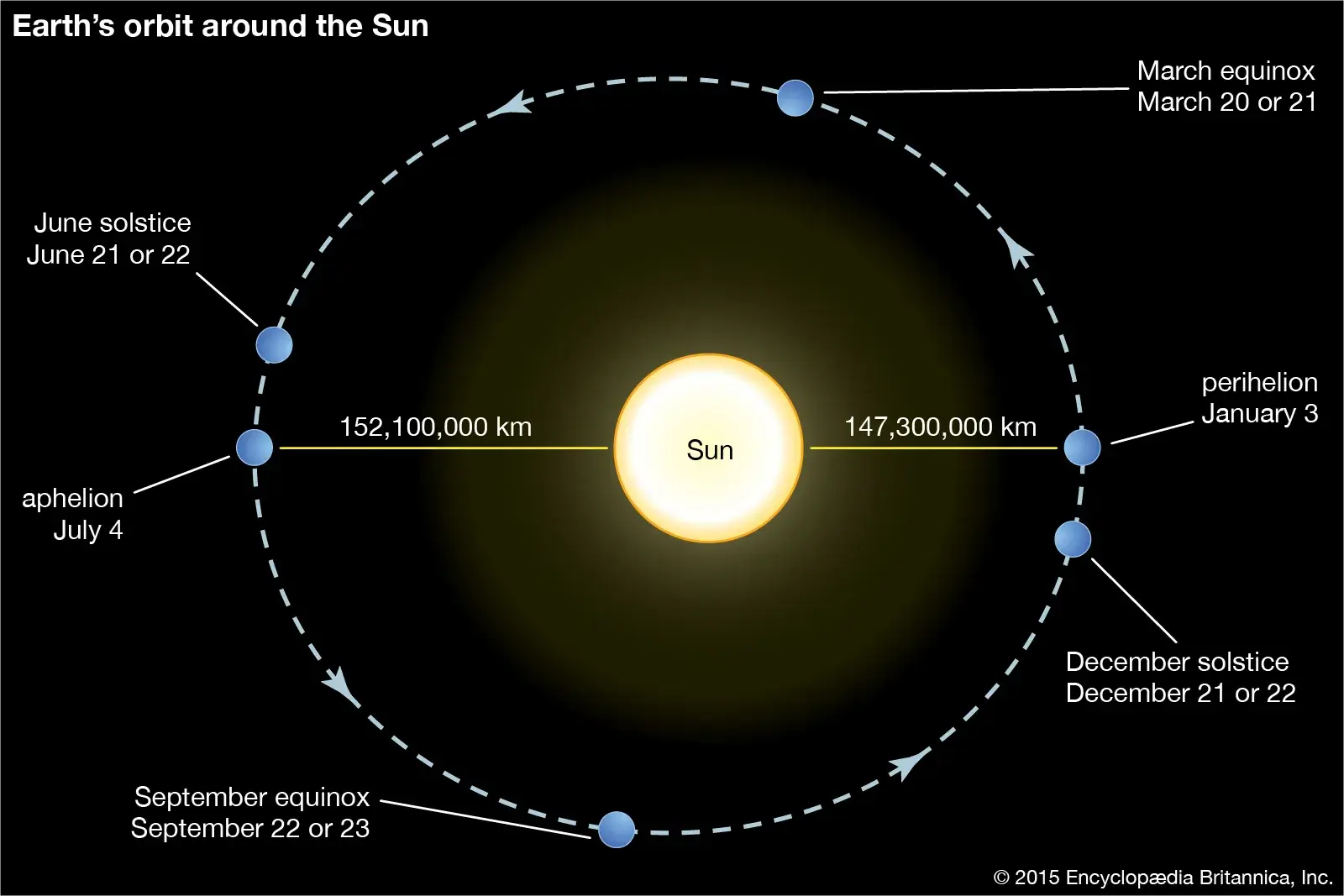
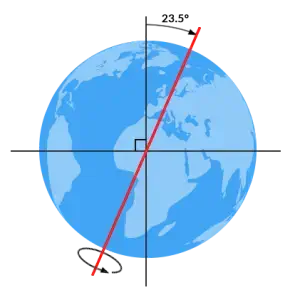
Aphelion is the point in the orbit of a planet, asteroid, or comet where it is farthest from the Sun. For Earth, this occurs in early July. The concept of aphelion is important in understanding the variations in solar energy received by a planet, which can influence seasonal climate patterns. The difference in distance between aphelion and perihelion (the closest point) contributes to the Earth’s elliptical orbit.
Reference: Laskar, J., Robutel, P., Joutel, F., Gastineau, M., Correia, A. C. M., & Levrard, B. (2004). “A Long-Term Numerical Solution for the Insolation Quantities of the Earth.” Astronomy & Astrophysics, 428(1), 261-285.