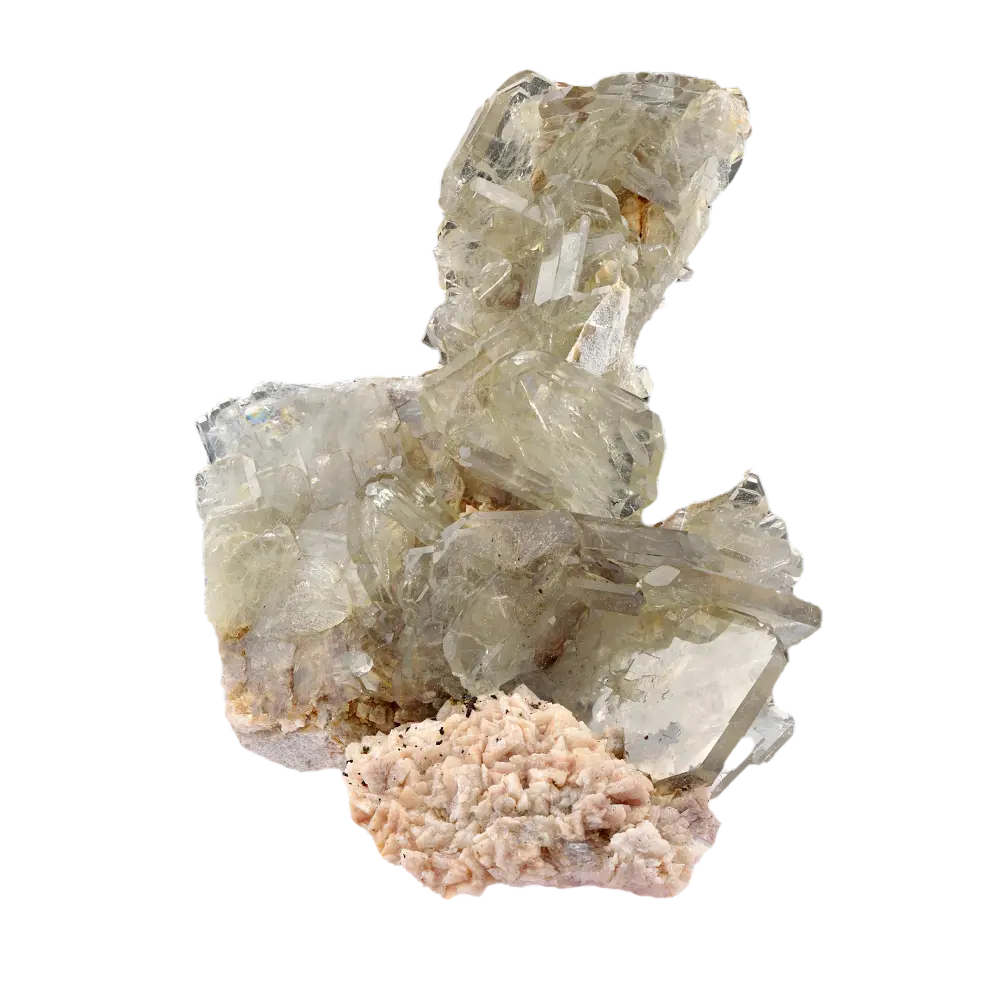
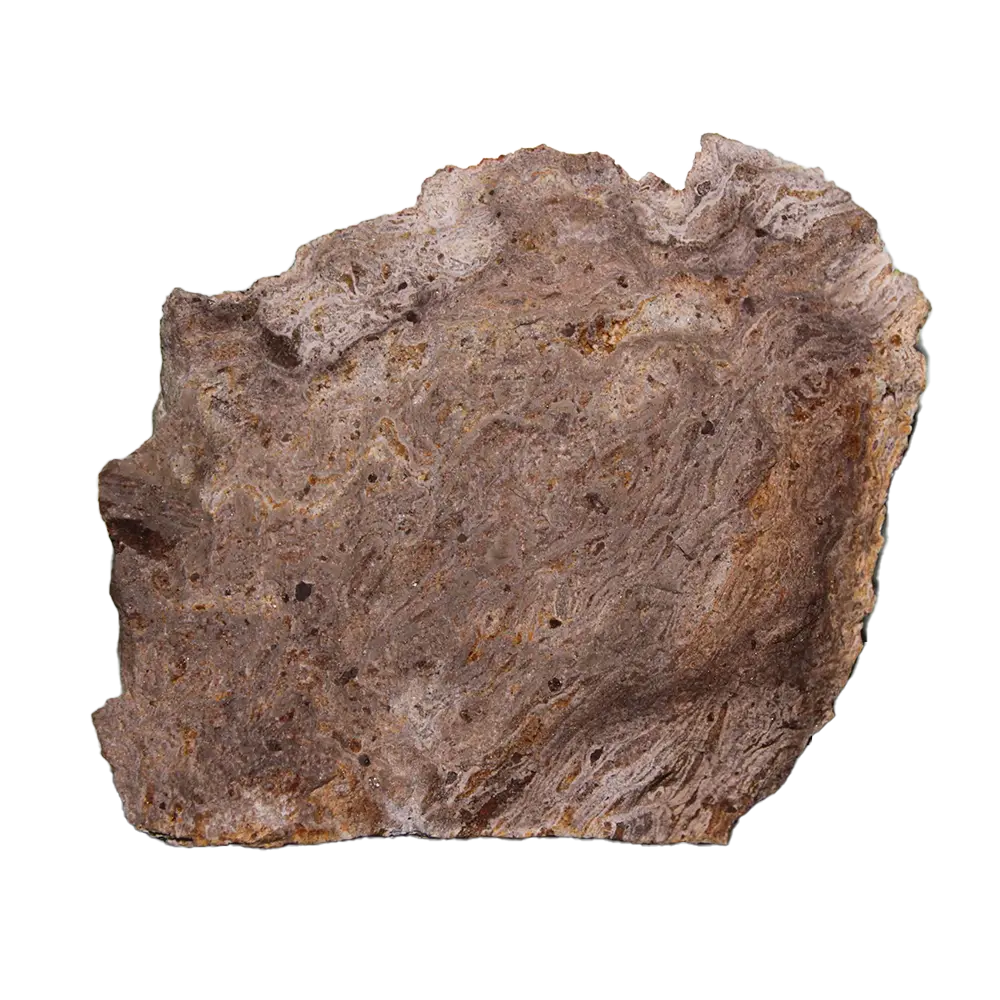
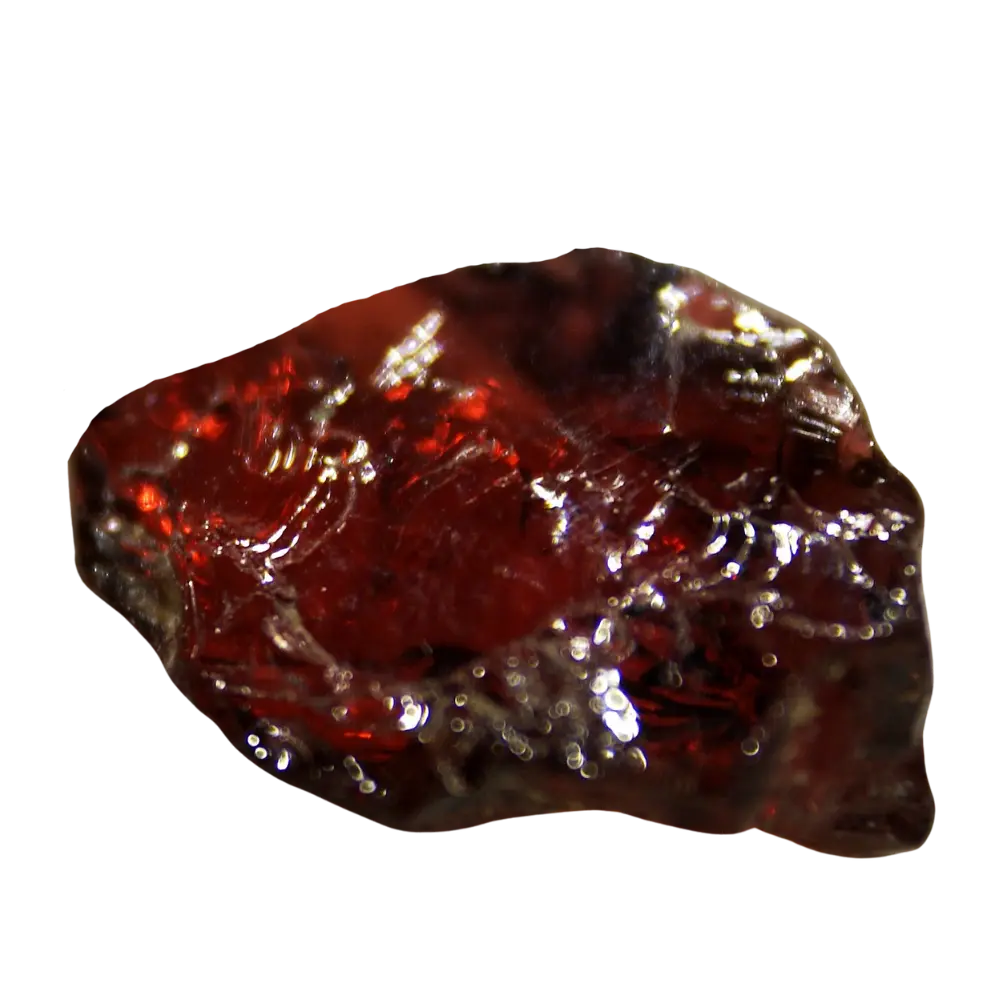
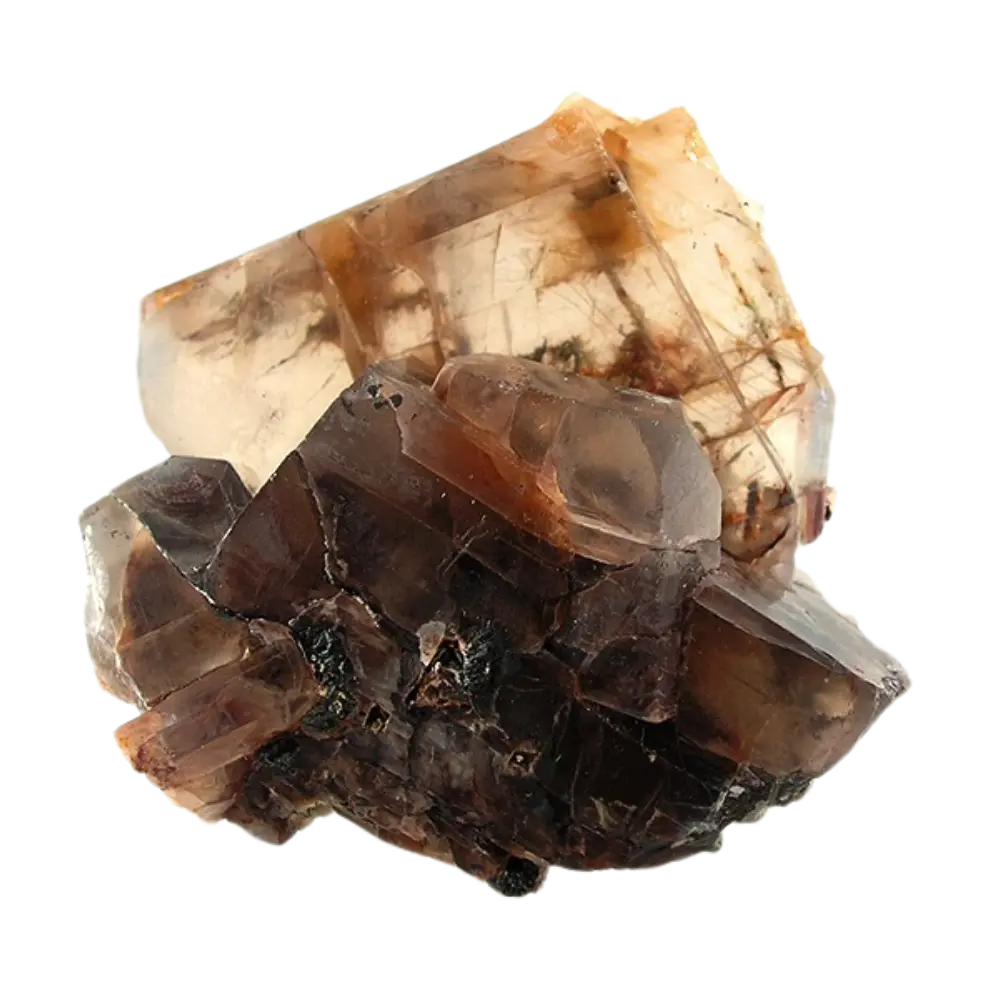
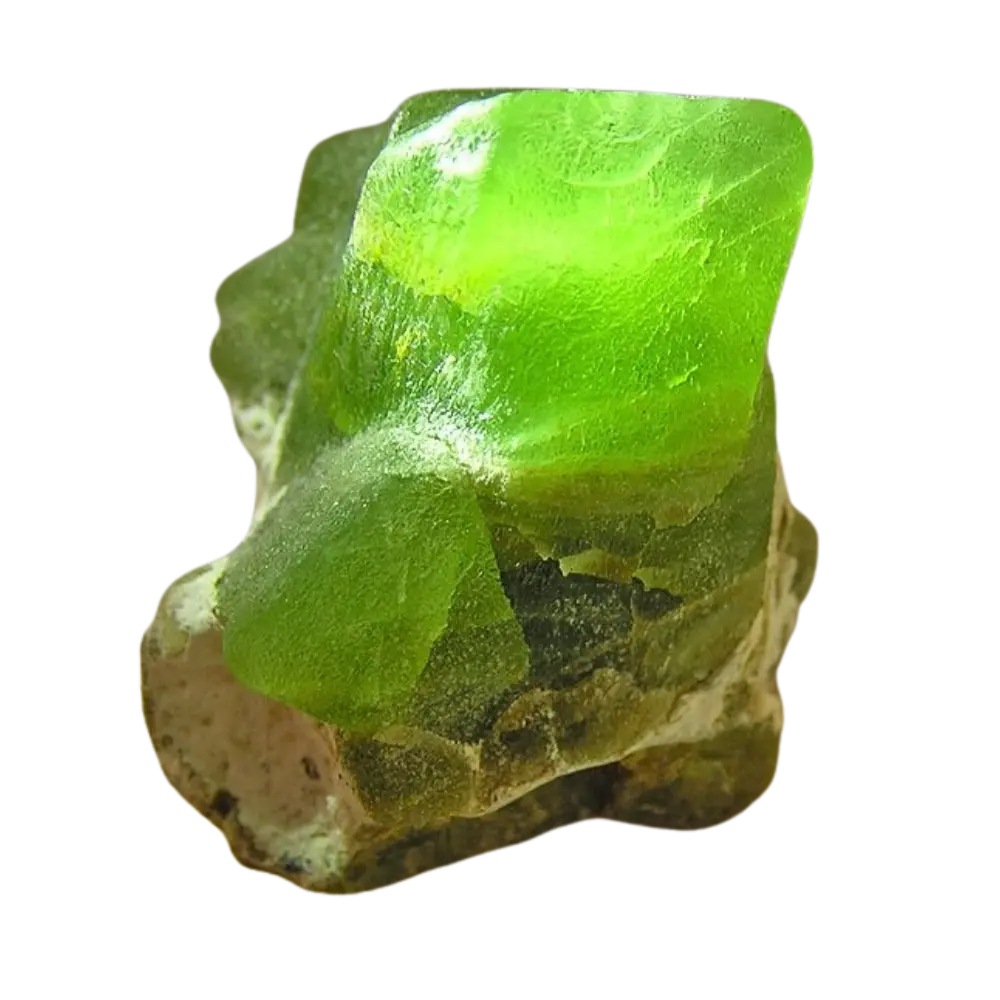
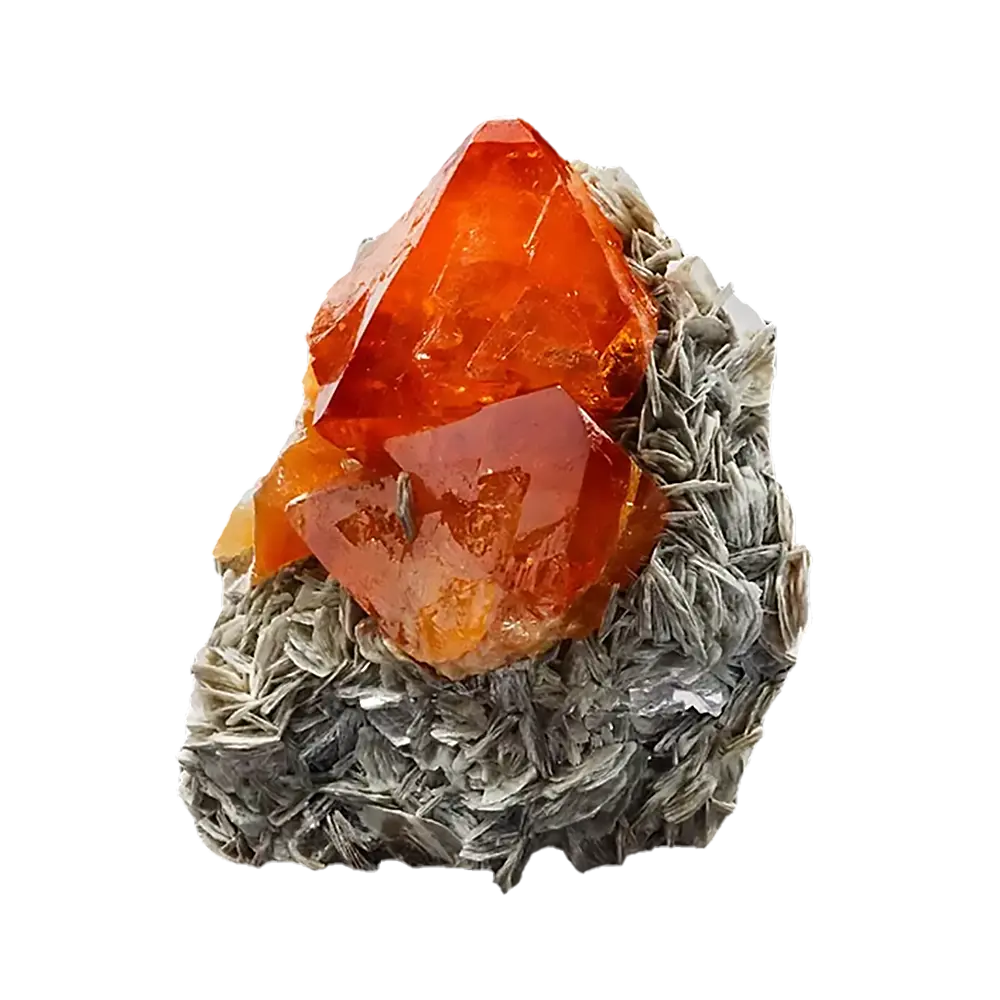
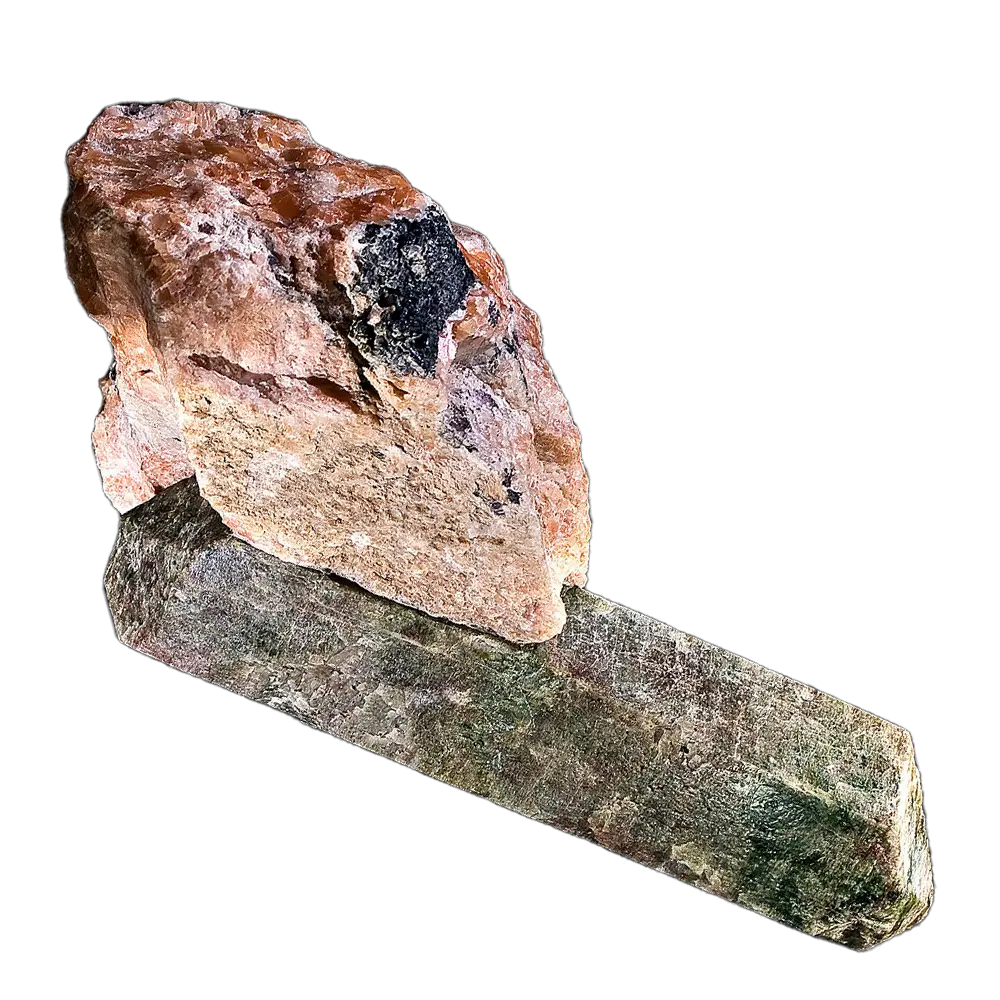
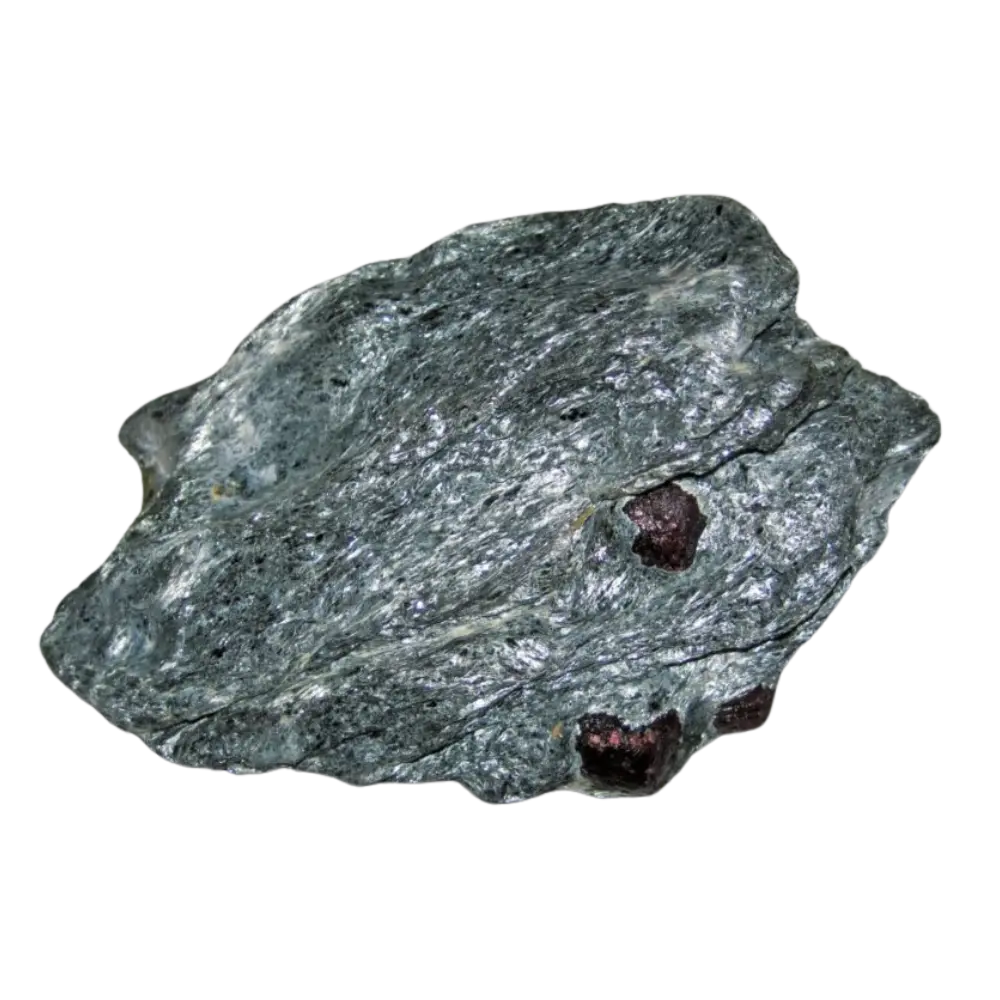
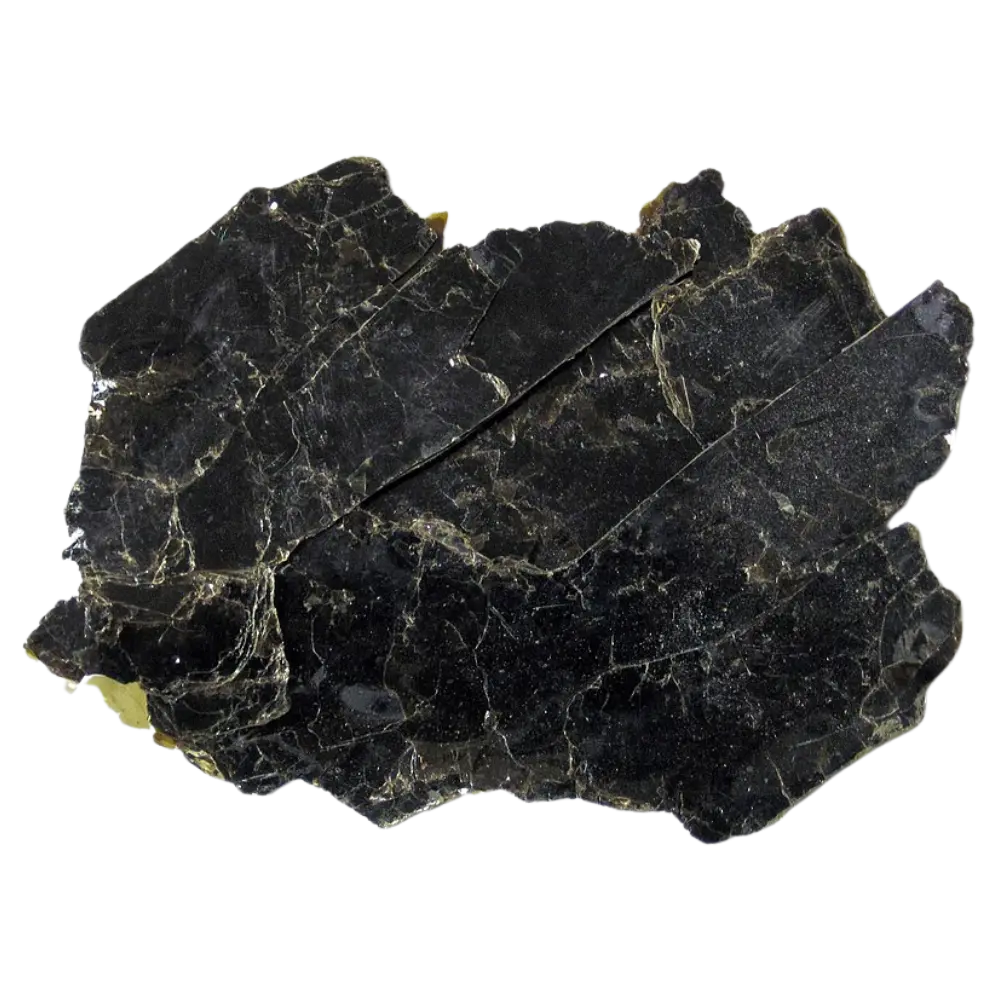
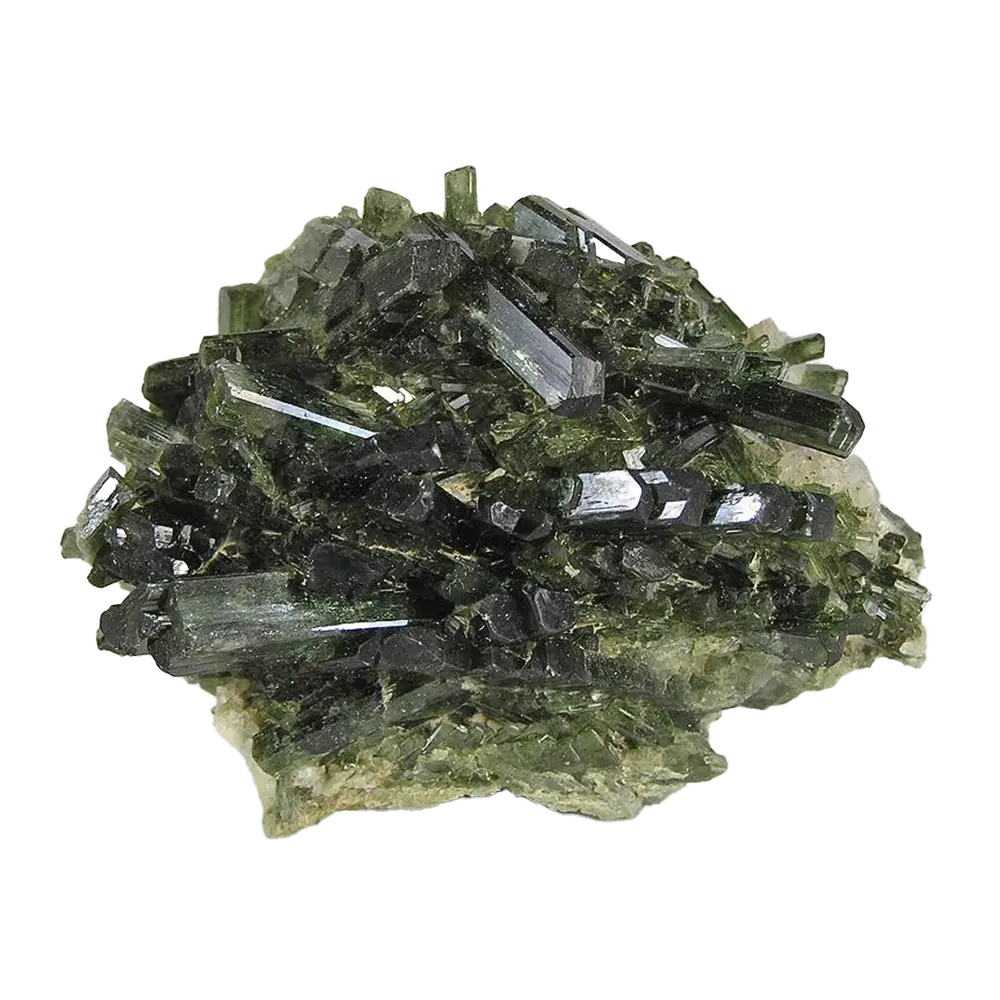
Fact Sheet:
- Chemical Composition: Ca₅(PO₄)₃(F, Cl, OH) (Calcium Phosphate)
- Hardness: 5 on the Mohs scale
- Crystal System: Hexagonal
- Color Varieties: Green, blue, yellow, purple, brown, pink, and colorless
- Major Localities: Canada, Brazil, Russia, Mexico, and the United States
- Common Uses: Source of phosphate for fertilizer, gemstones, and industrial applications
Introduction: Apatite is a widely occurring mineral, essential for both biological processes and industrial applications. Its name is derived from the Greek word “apate,” meaning “deceit,” due to its similarity to other minerals, which led to confusion in its early identification. Apatite is the primary source of phosphorus, a key nutrient for plant growth and a crucial component of fertilizers.
Formation: Apatite forms in a variety of geological environments, including igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. It is most commonly found in phosphate-rich igneous rocks such as pegmatites, carbonatites, and hydrothermal veins. Apatite can also form through biological processes, particularly in the bones and teeth of animals, including humans.
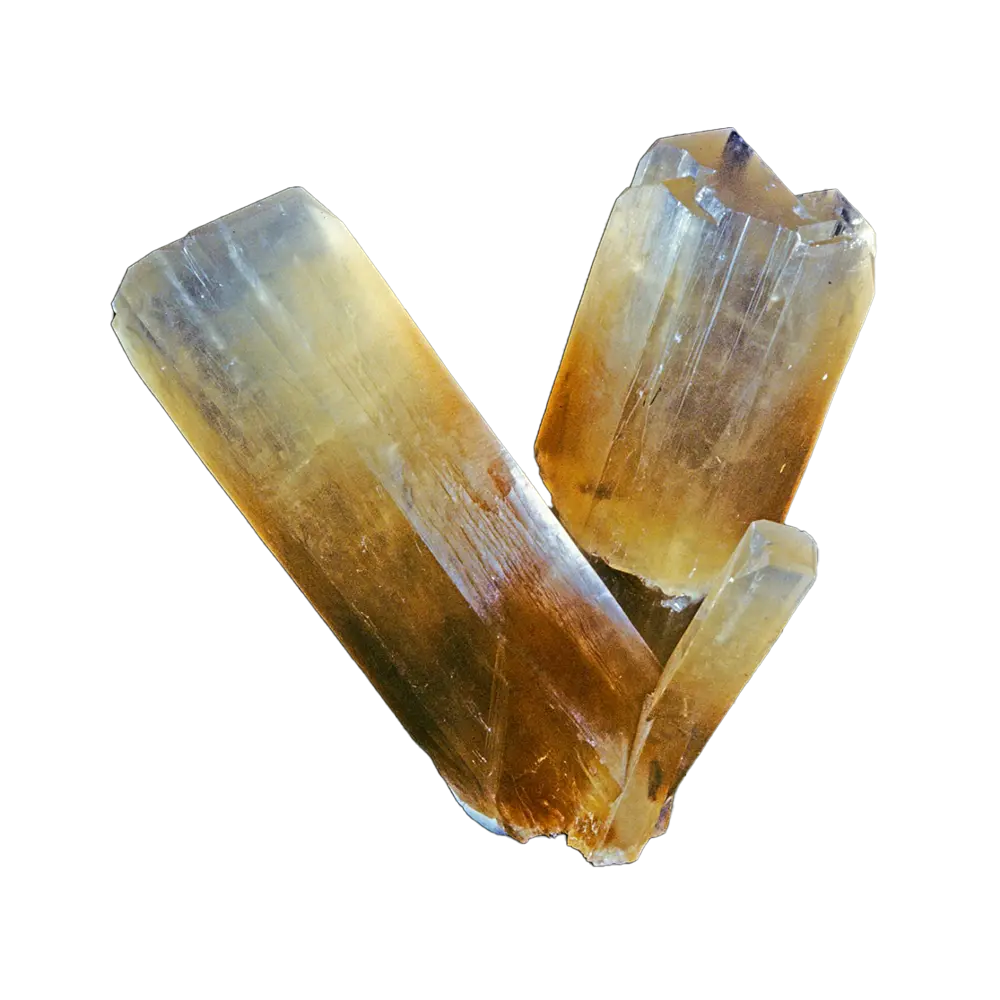
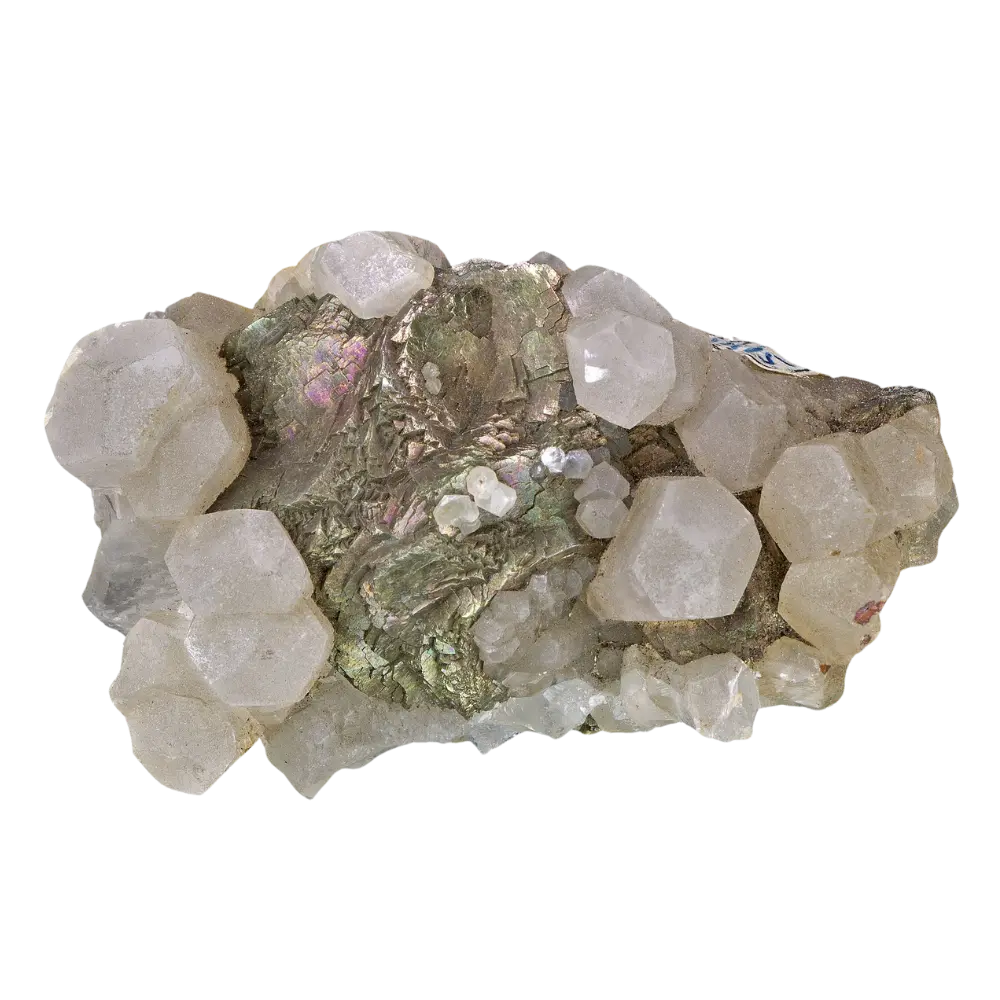
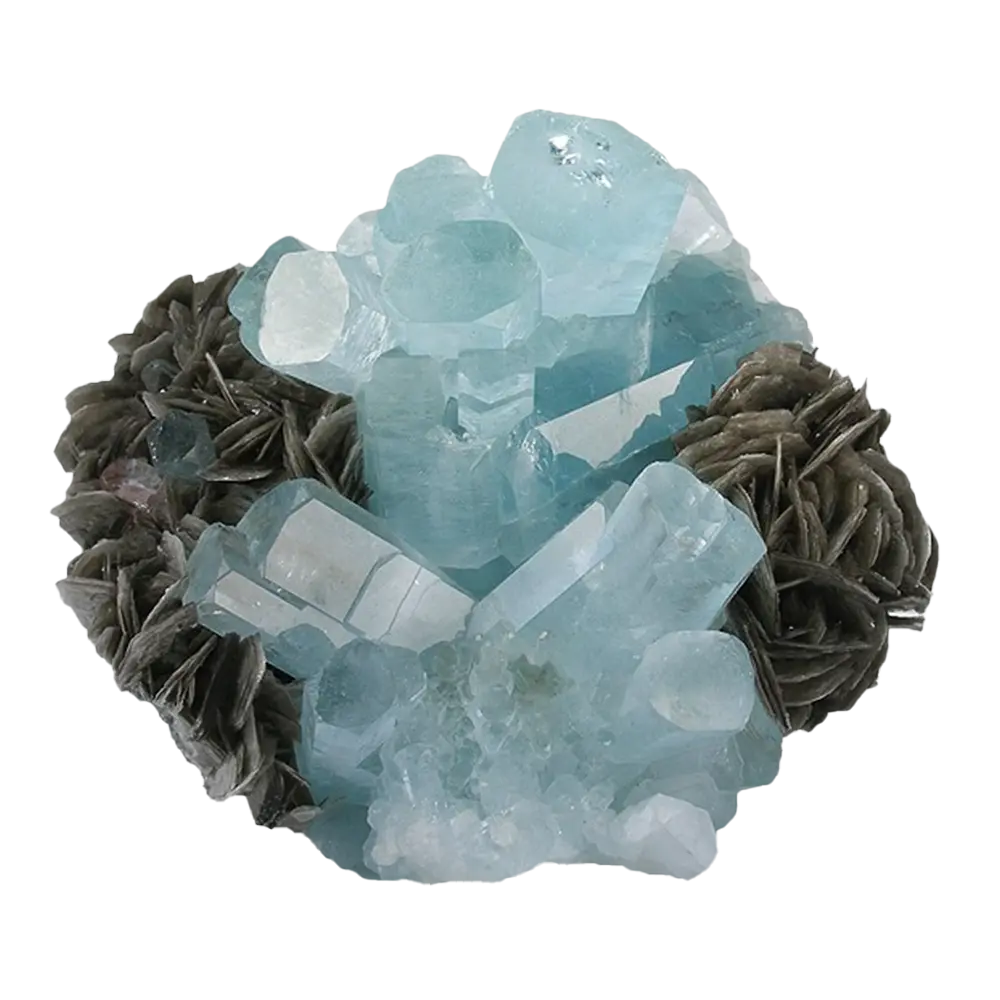
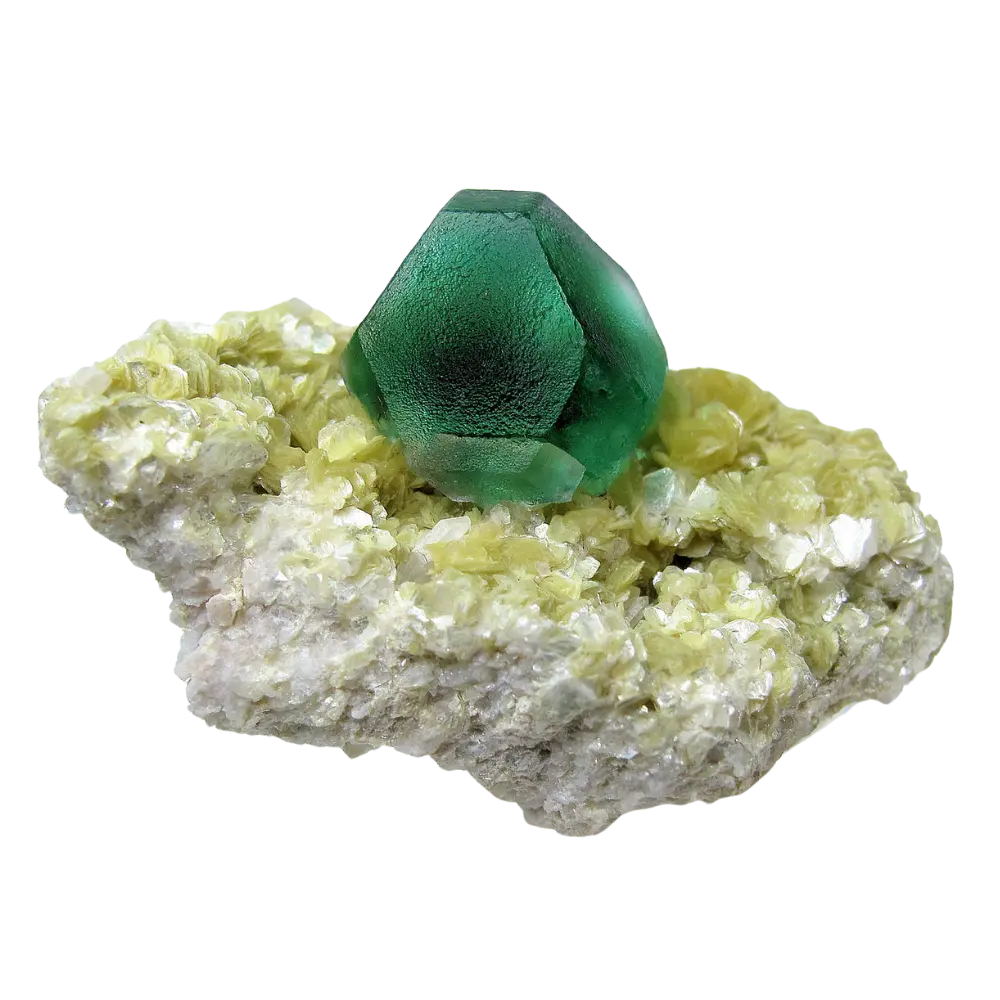
Types and Colors: Apatite comes in a variety of colors, influenced by trace impurities:
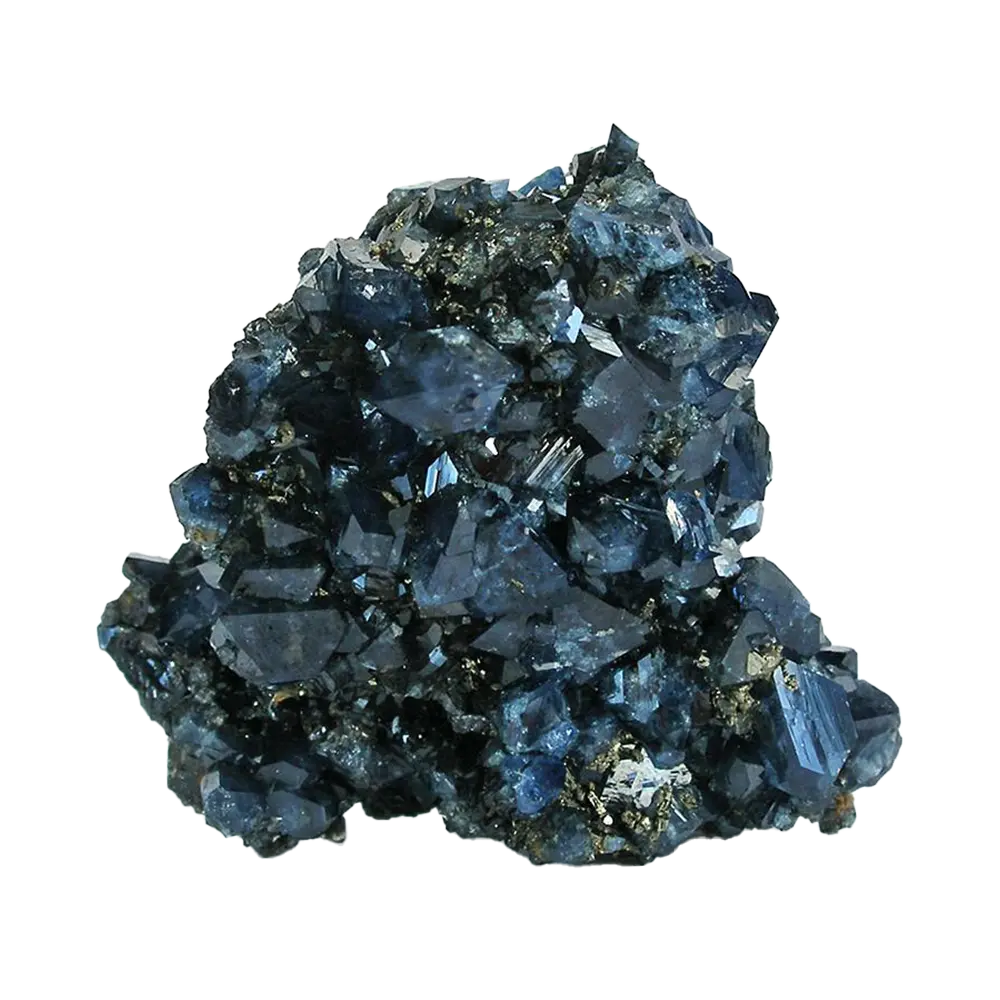
- Green Apatite: The most common color, often found in pegmatites and hydrothermal veins.
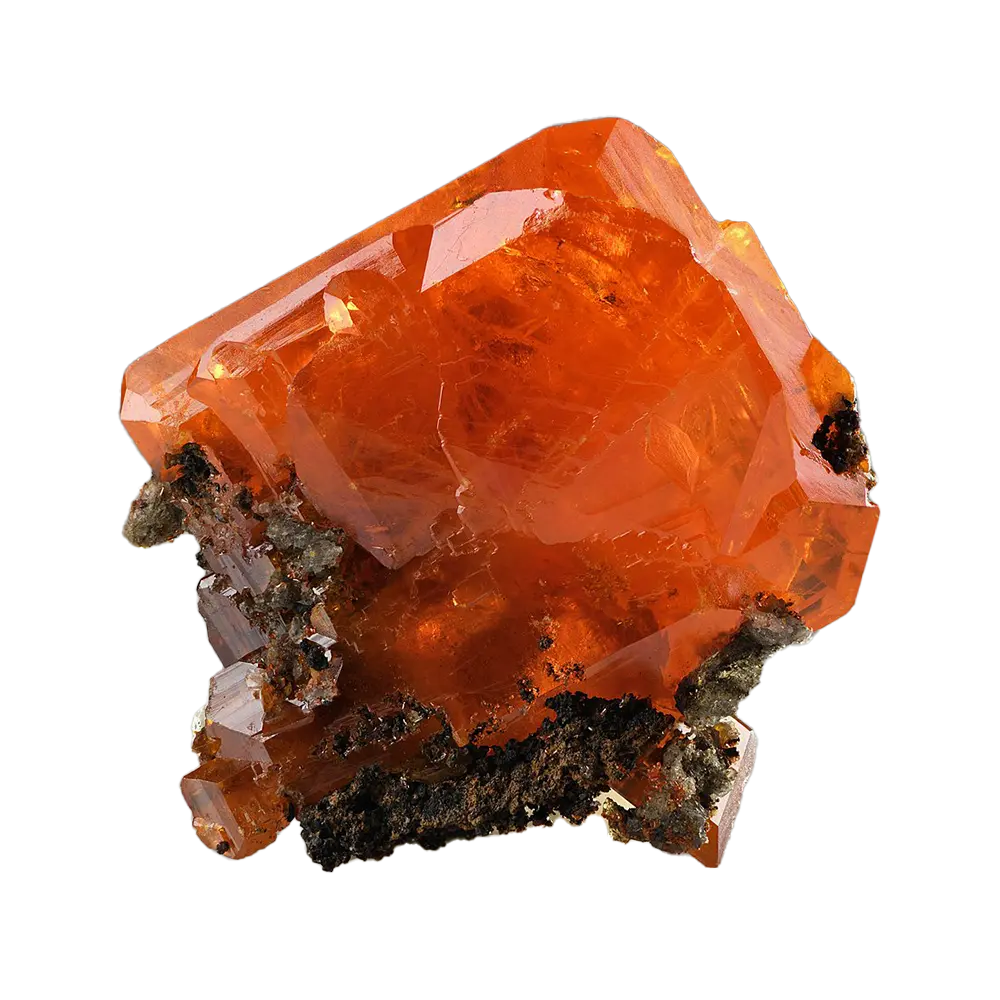
- Blue Apatite: Highly prized as a gemstone, known for its vivid blue color, often from Brazil.
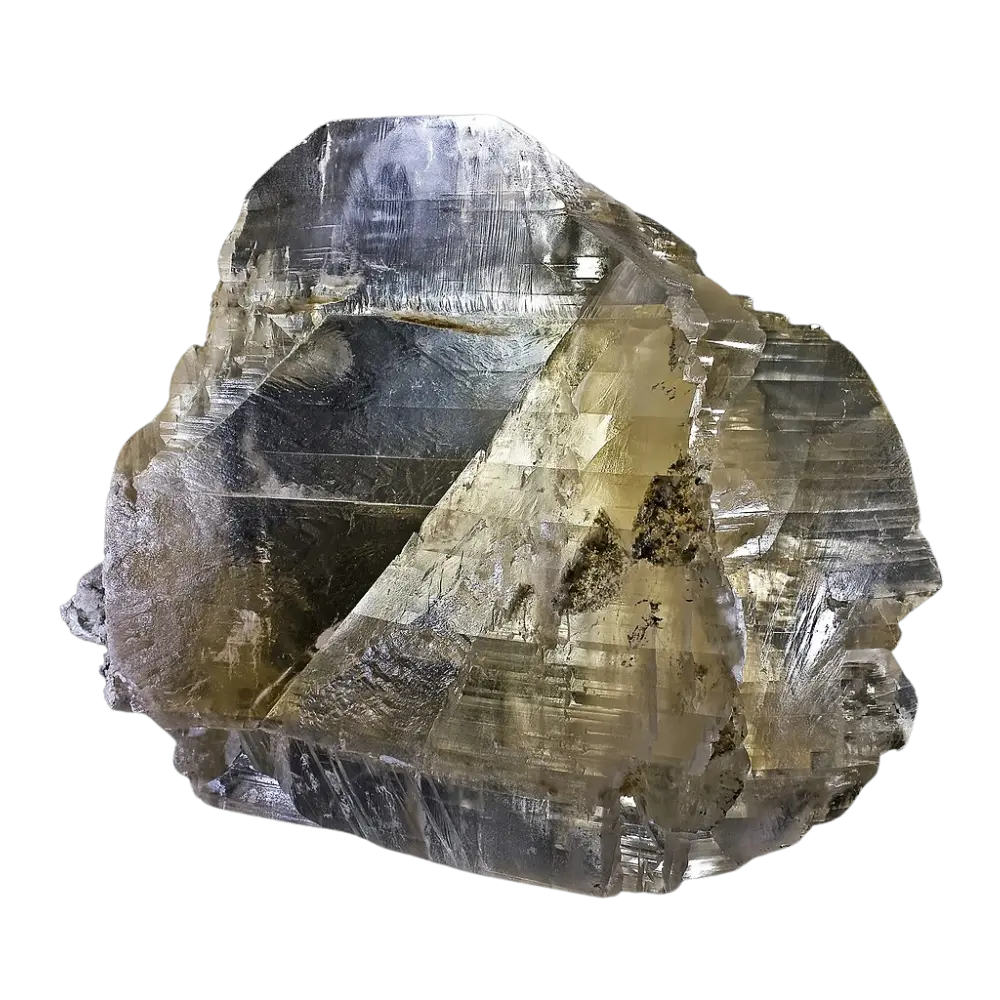
- Yellow Apatite: Also known as “asparagus stone,” found in metamorphic rocks.
- Purple Apatite: Less common but highly sought after in jewelry markets.
- Colorless Apatite: Rare and found in some igneous and metamorphic rocks.
Localities and Mining: Significant apatite deposits are found in Canada (particularly Quebec), Brazil, Russia, Mexico, and the United States. Apatite is mined primarily for its phosphate content, which is used in fertilizers. In places like Brazil, gem-quality blue and green apatite crystals are mined and cut for use in jewelry.
Applications: Apatite is an essential mineral with several important applications:
- Fertilizer Production: Apatite is the primary source of phosphorus used in the production of fertilizers, which are critical for agriculture worldwide.
- Gemstones: Brightly colored varieties of apatite, especially blue and green, are used in jewelry.
- Industrial Uses: Apatite is used in the production of phosphoric acid, phosphates for chemicals, and various industrial processes.
- Biological Role: Apatite forms the mineral component of bones and teeth in animals and humans, known as hydroxylapatite.
Sources and further reading: