Fact Sheet:
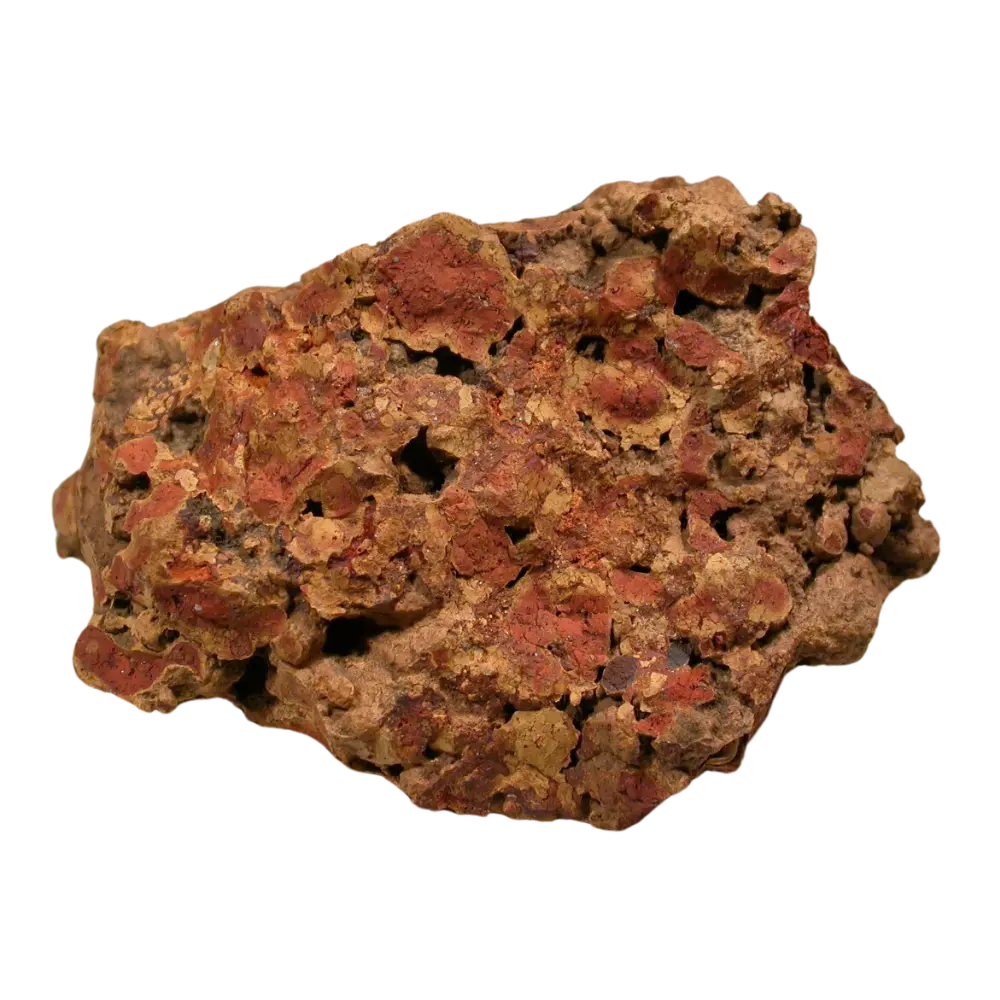
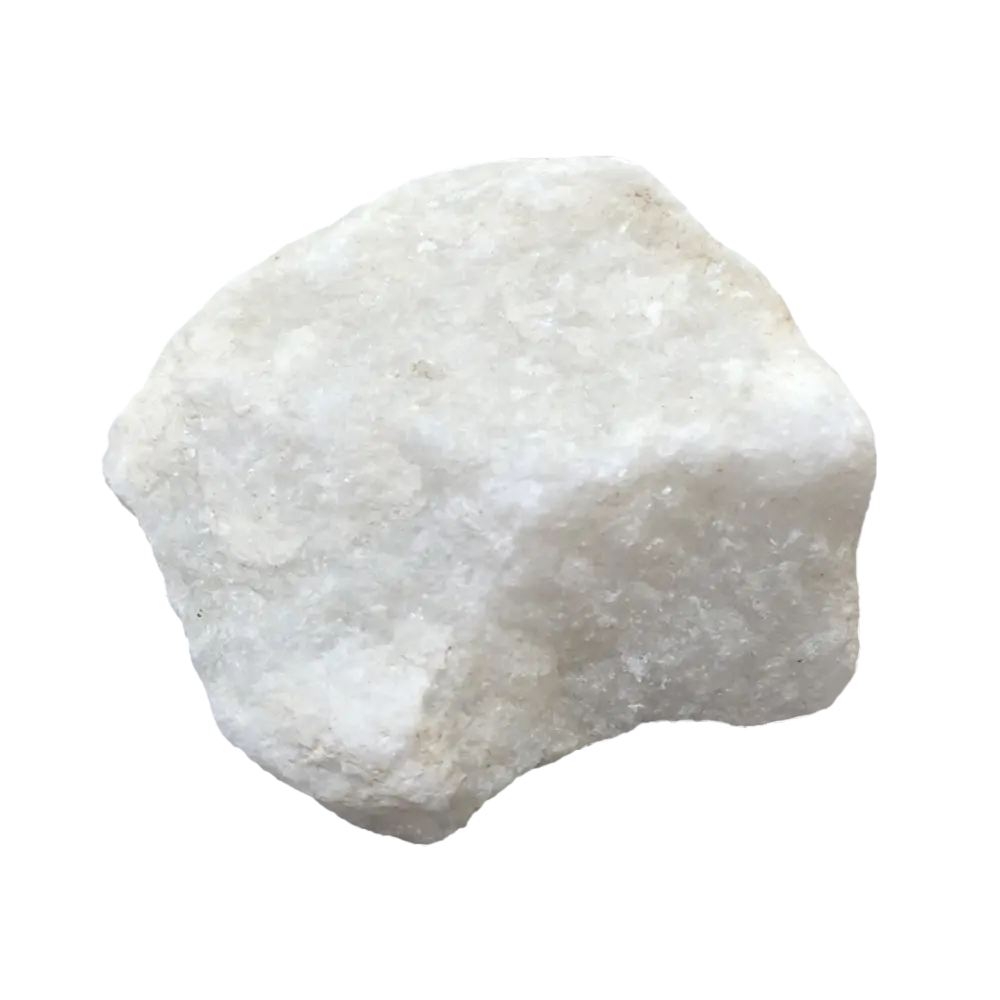
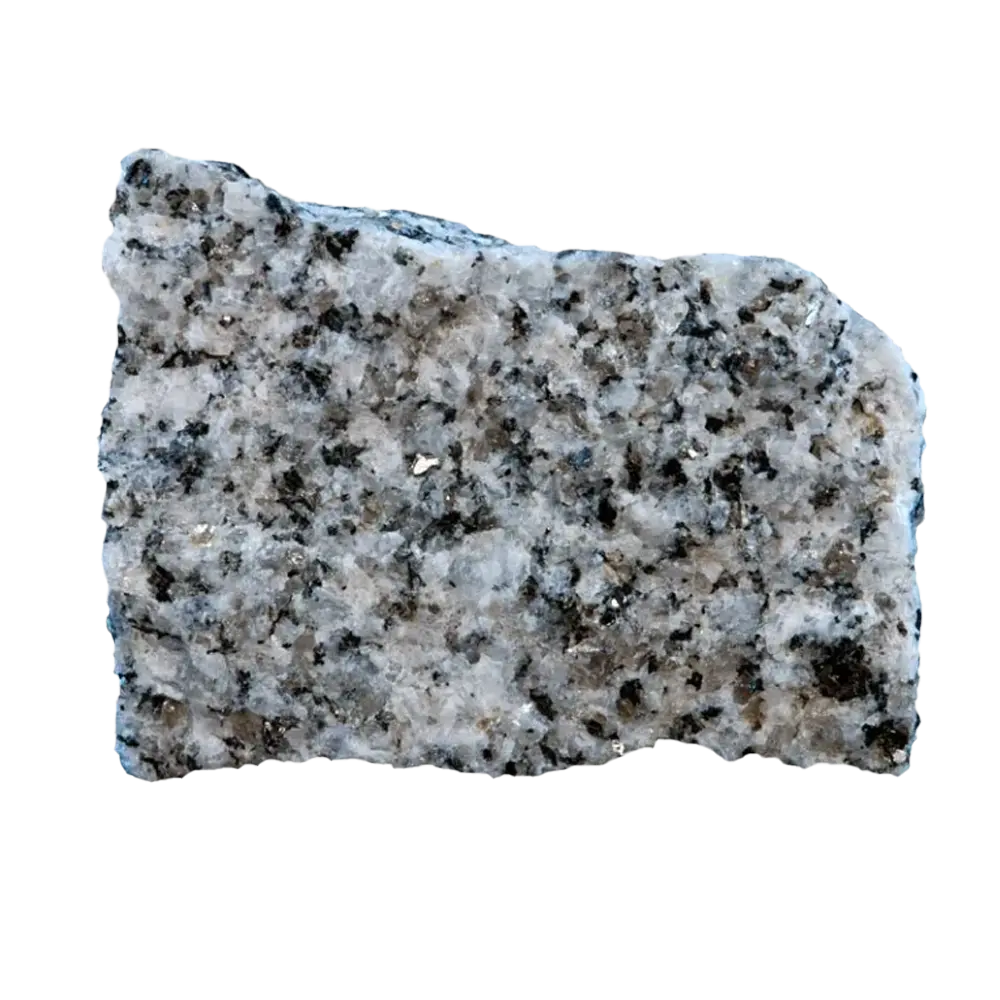
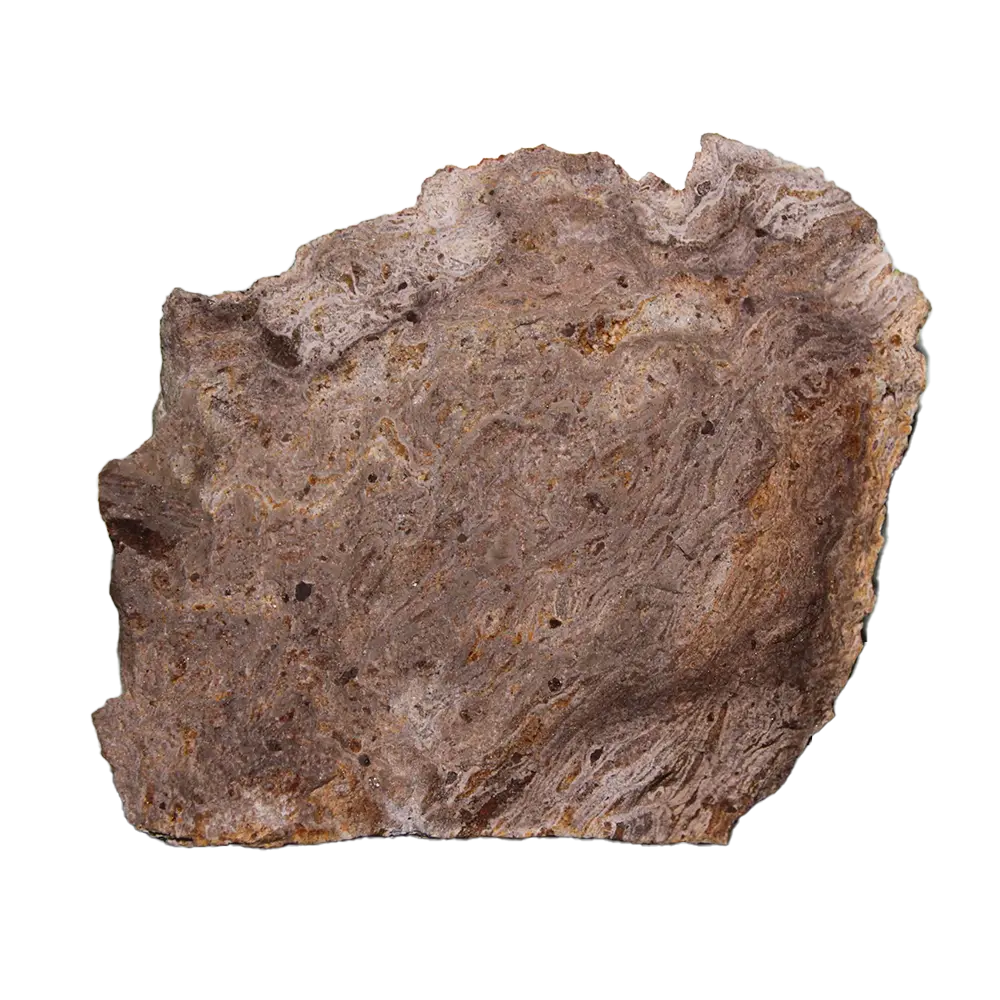
– Chemical Composition: A mixture of aluminum hydroxides, predominantly gibbsite (Al(OH)₃), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH))
– Hardness: 1 to 3 on the Mohs scale
– Crystal System: Amorphous (typically not crystalline)
– Color Varieties: White, gray, yellow, orange, red, brown
– Major Localities: Australia, Guinea, Brazil, and Jamaica
– Common Uses: Primary source of aluminum, refractory materials, abrasives, and in cement production
Introduction: Bauxite is the world’s primary source of aluminum, a metal critically important for modern life. This mineral was named after the village of Les Baux in southern France, where it was first discovered in 1821 by geologist Pierre Berthier. Aluminum, extracted from bauxite, is used extensively in industries ranging from aerospace to packaging due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Formation: Bauxite forms through the weathering of aluminum-rich rocks under tropical or subtropical climates. This weathering process involves the leaching of silica and other soluble materials, leaving behind a residue enriched in aluminum hydroxides. Bauxite deposits are typically found near the surface and can vary greatly in depth and size.
Types and Colors:
– Gibbsite Bauxite: Predominantly composed of gibbsite, this type is usually soft and white to gray in color.
– Boehmite Bauxite: Contains boehmite and is typically harder with colors ranging from yellow to brown.
– Diaspore Bauxite: Contains diaspore and can be found in shades of white, gray, or brown.
Localities and Mining: Significant bauxite deposits are found in Australia (the largest producer), Guinea, Brazil, and Jamaica. These countries have large, high-quality deposits that are mined using open-pit methods. The extracted bauxite is then refined into alumina, which is further processed to produce aluminum.
Applications: Bauxite is primarily used for aluminum production. The refining process involves crushing the bauxite and treating it with sodium hydroxide to extract alumina. This alumina is then subjected to electrolysis to produce aluminum metal. Bauxite is also used in the production of refractory materials, abrasives, and cement.