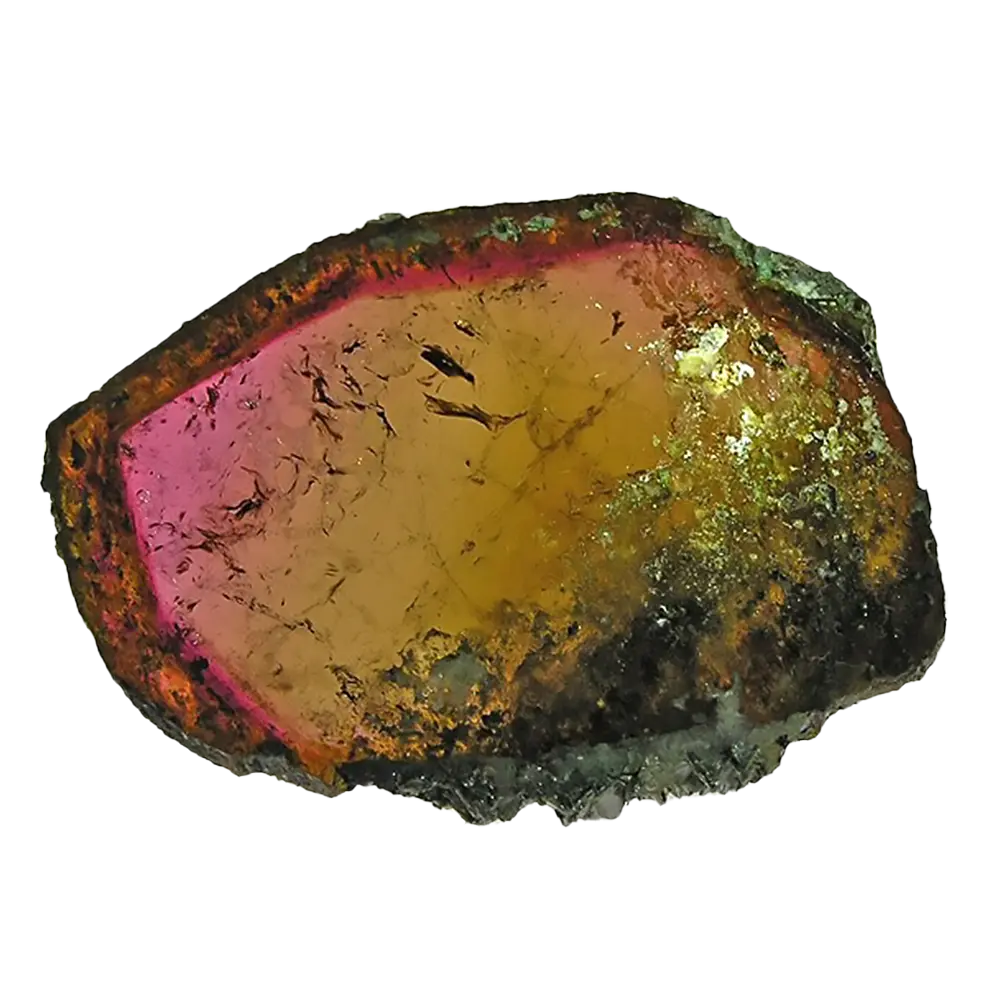
Fact Sheet:
– Chemical Composition: A group of silicate minerals with the general formula X₃Y₂(SiO₄)₃, where X can be Ca, Mg, Fe, or Mn, and Y can be Al, Fe, or Cr
– Hardness: 6.5 to 7.5 on the Mohs scale
– Crystal System: Isometric
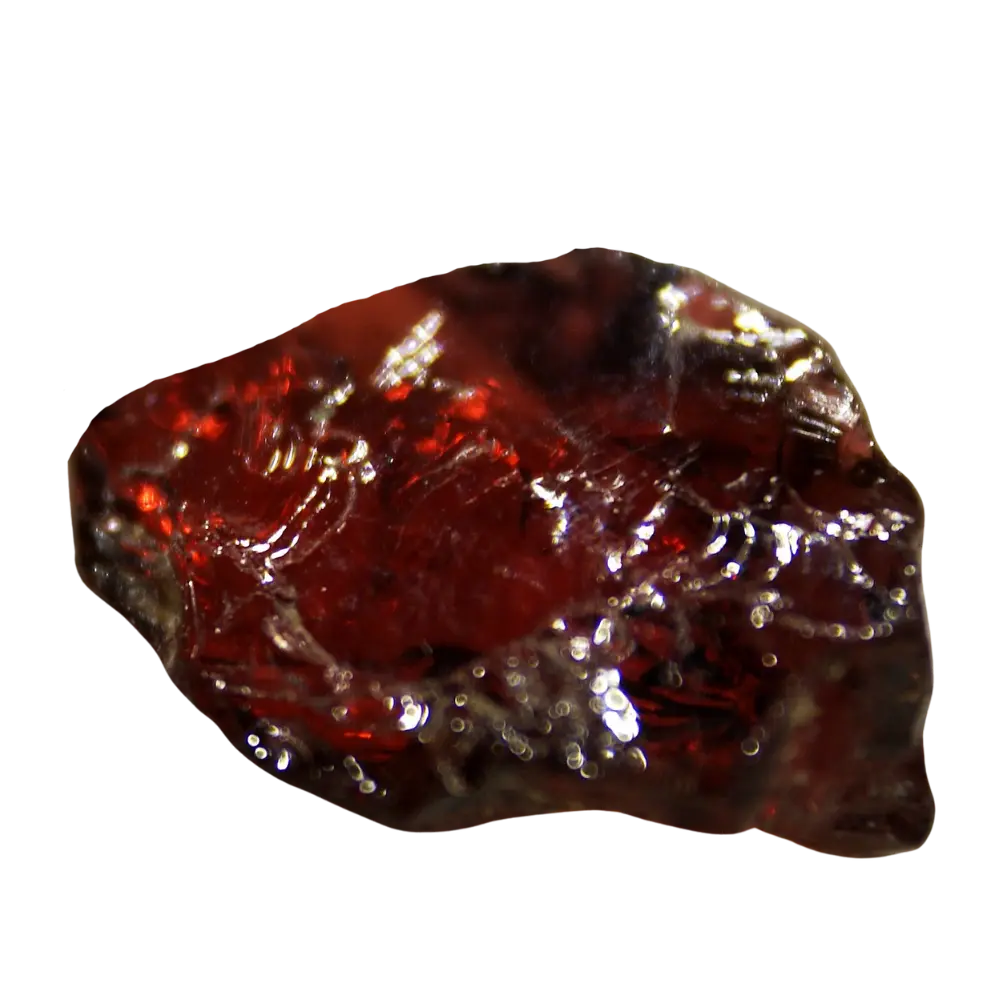
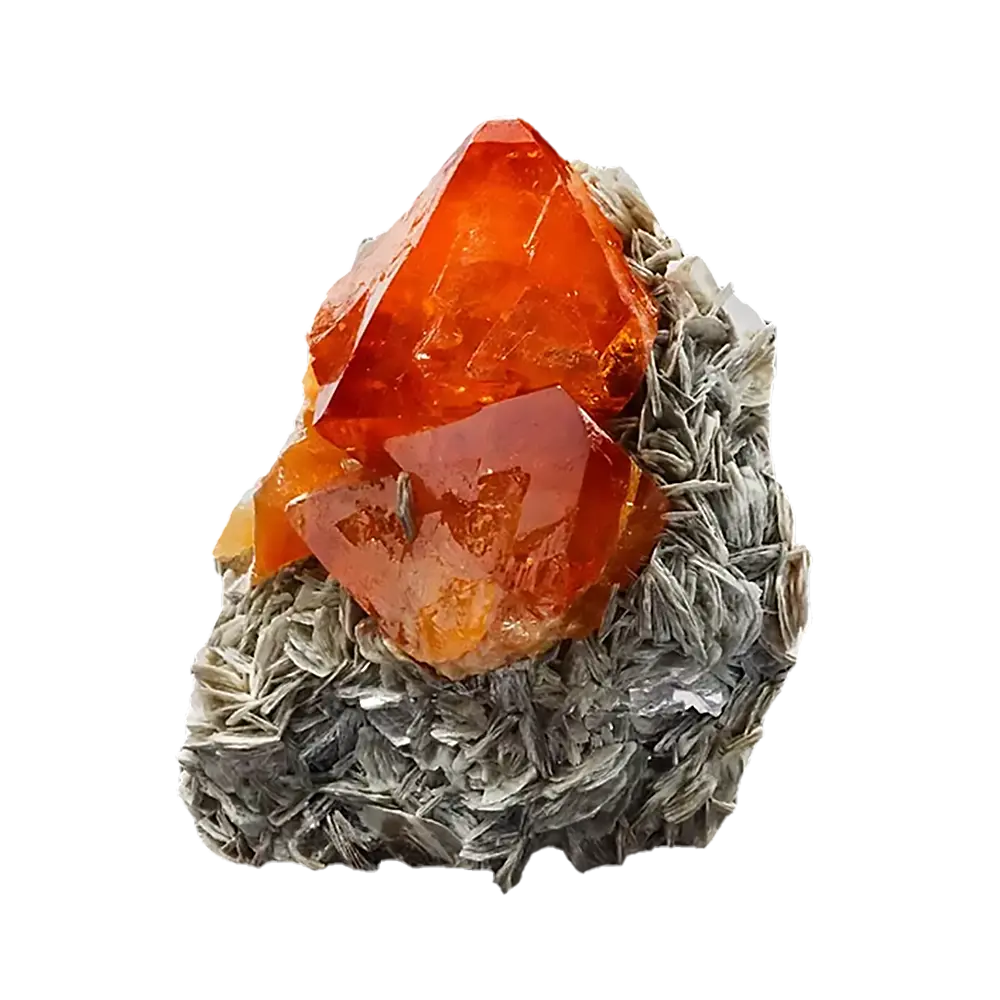
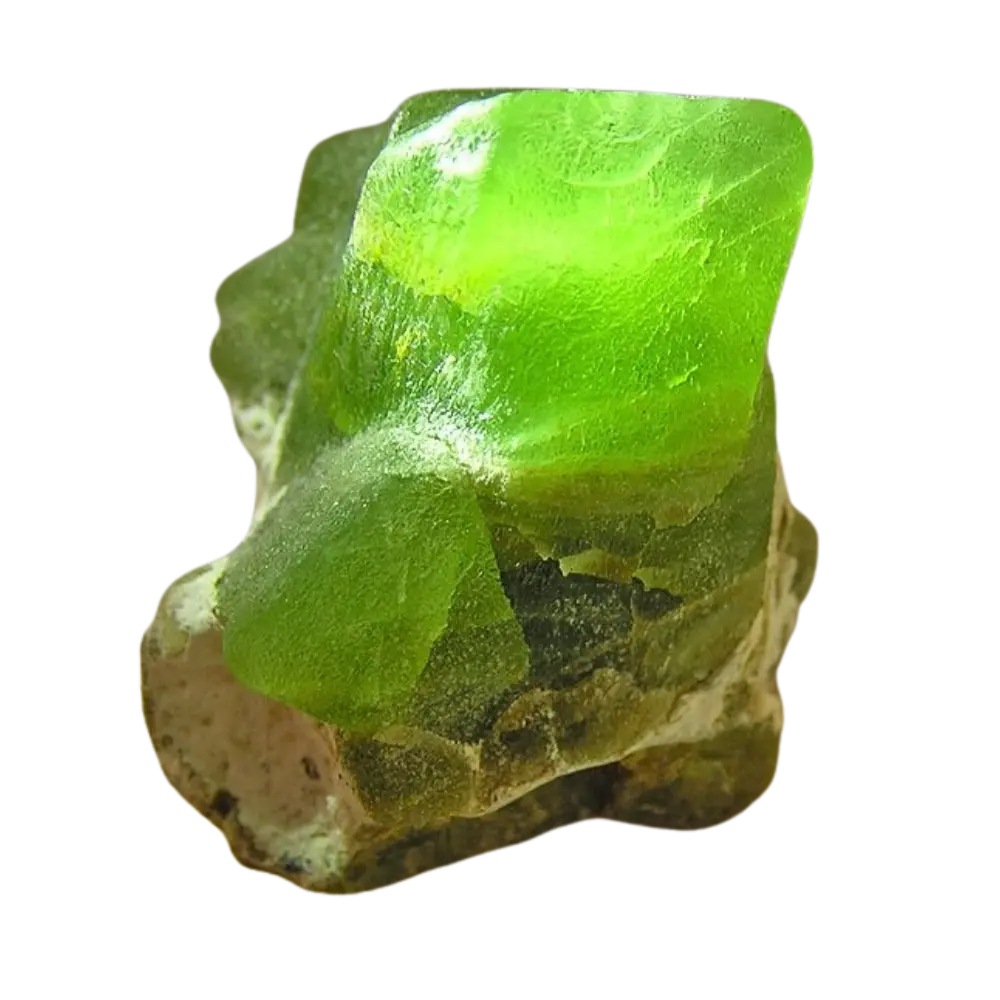
– Color Varieties: Red, green, yellow, orange, brown, purple, pink, black
– Major Localities: India, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, the United States, and Russia
– Common Uses: Gemstones, abrasives, industrial applications
Introduction: Garnet is a diverse and widespread group of silicate minerals prized for its rich array of colors and durability. Known since ancient times, garnets have been used as gemstones and abrasives, playing a significant role in both decorative arts and industrial applications.
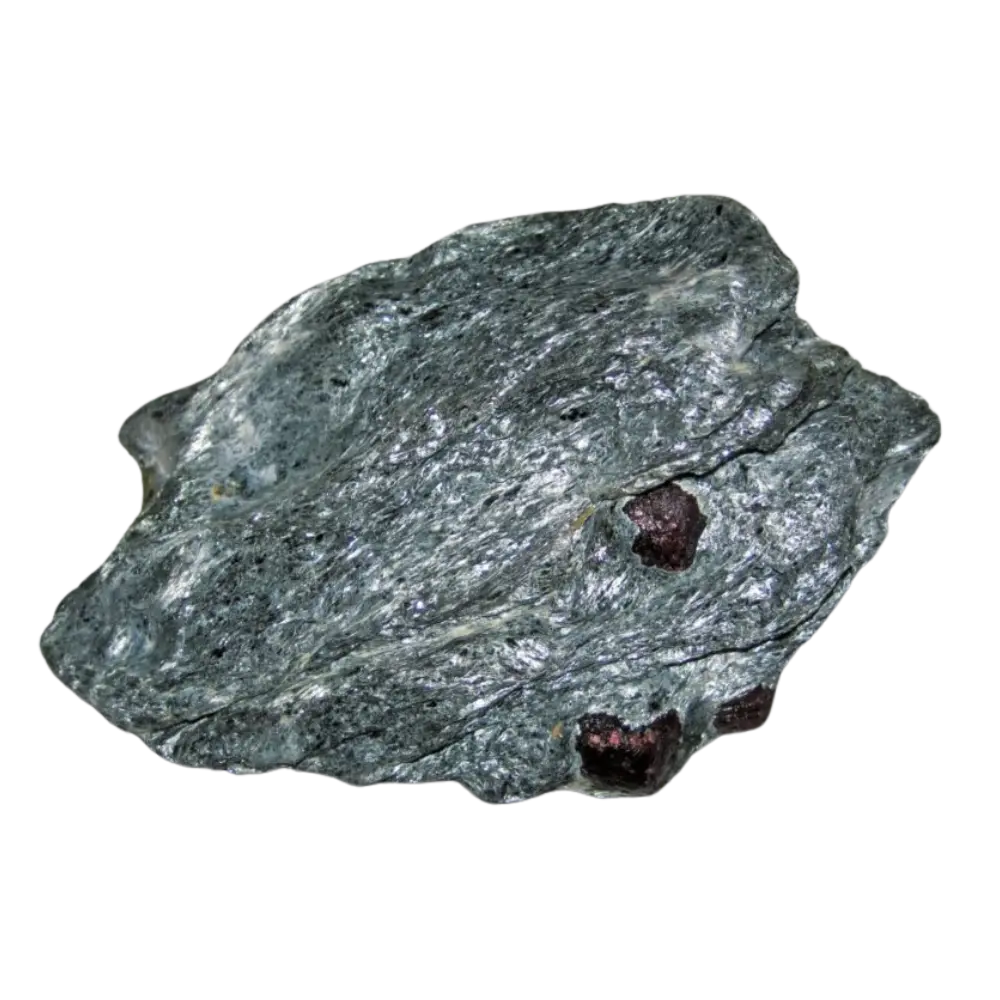
Formation: Garnets form under a variety of geological conditions, primarily in metamorphic rocks such as schist and gneiss, as well as in igneous rocks like granite. They can also be found in sedimentary rocks that have undergone high-pressure metamorphism. The formation of garnets depends on the chemical composition of the surrounding rocks and the temperature and pressure conditions.
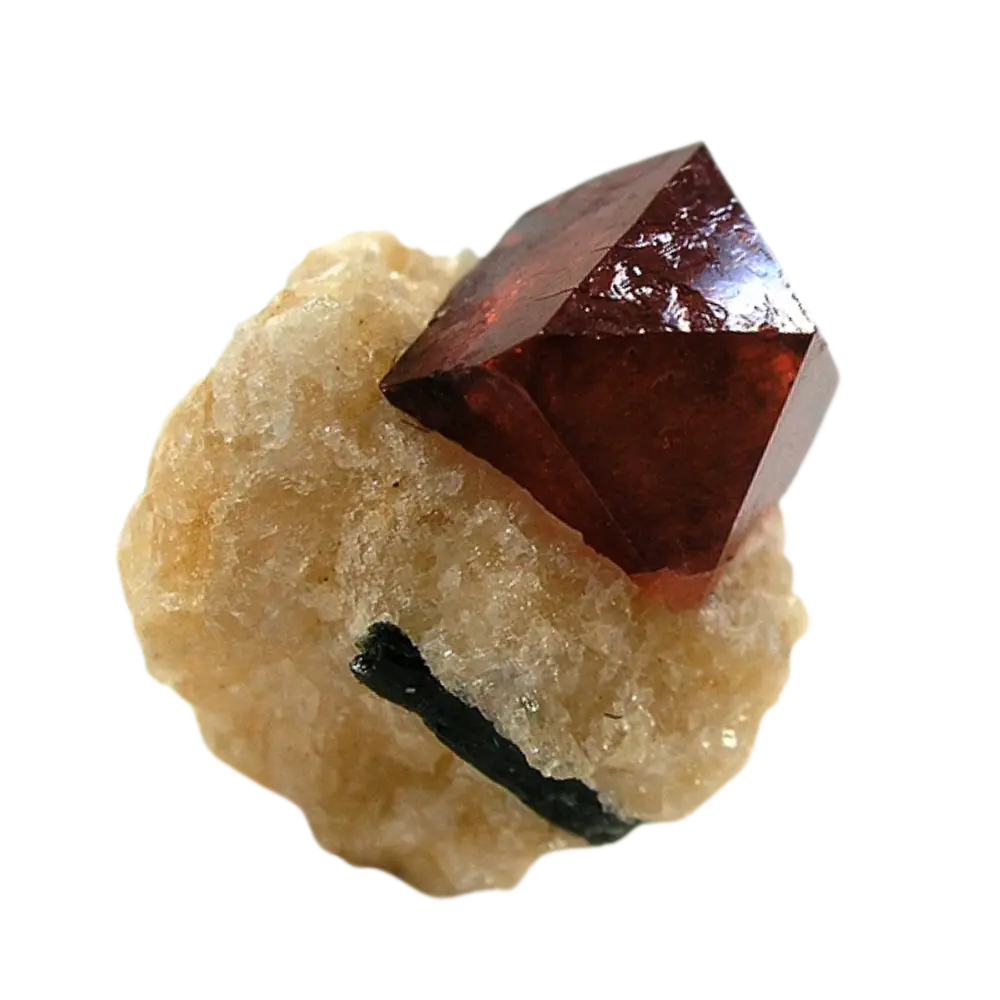
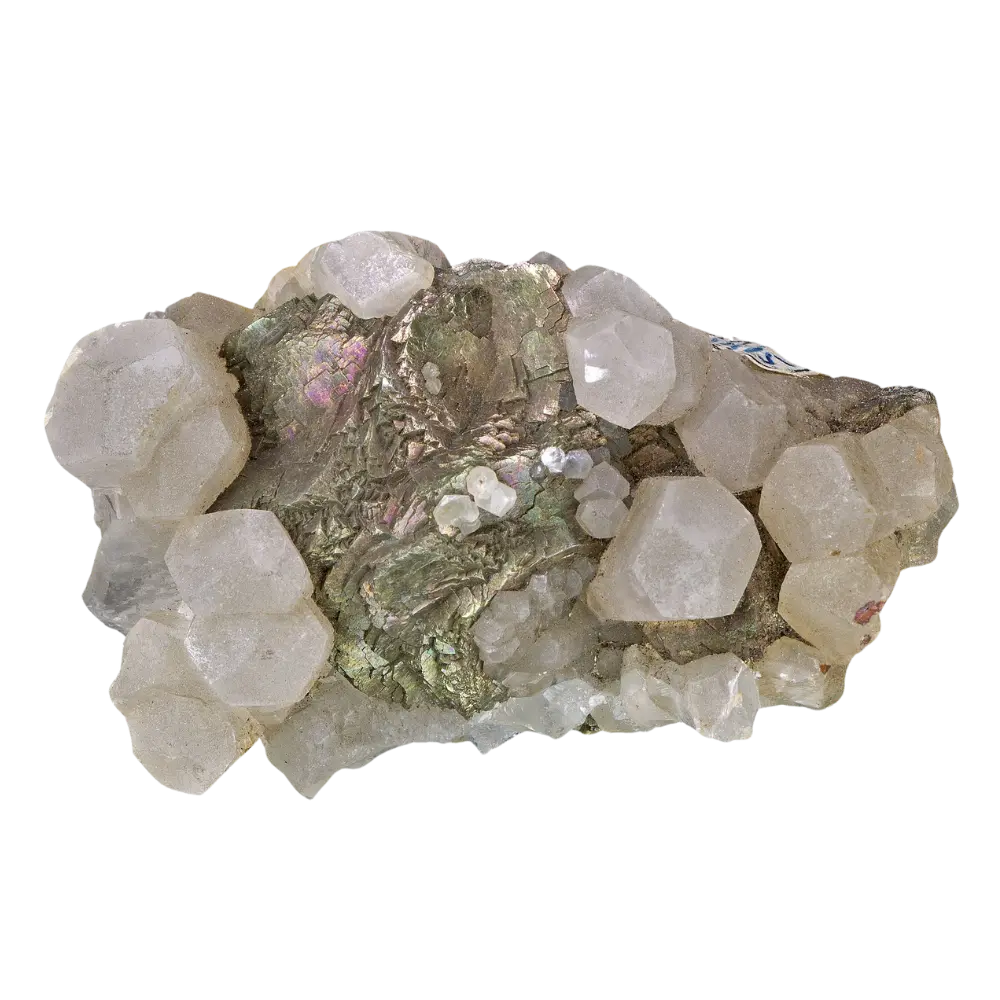
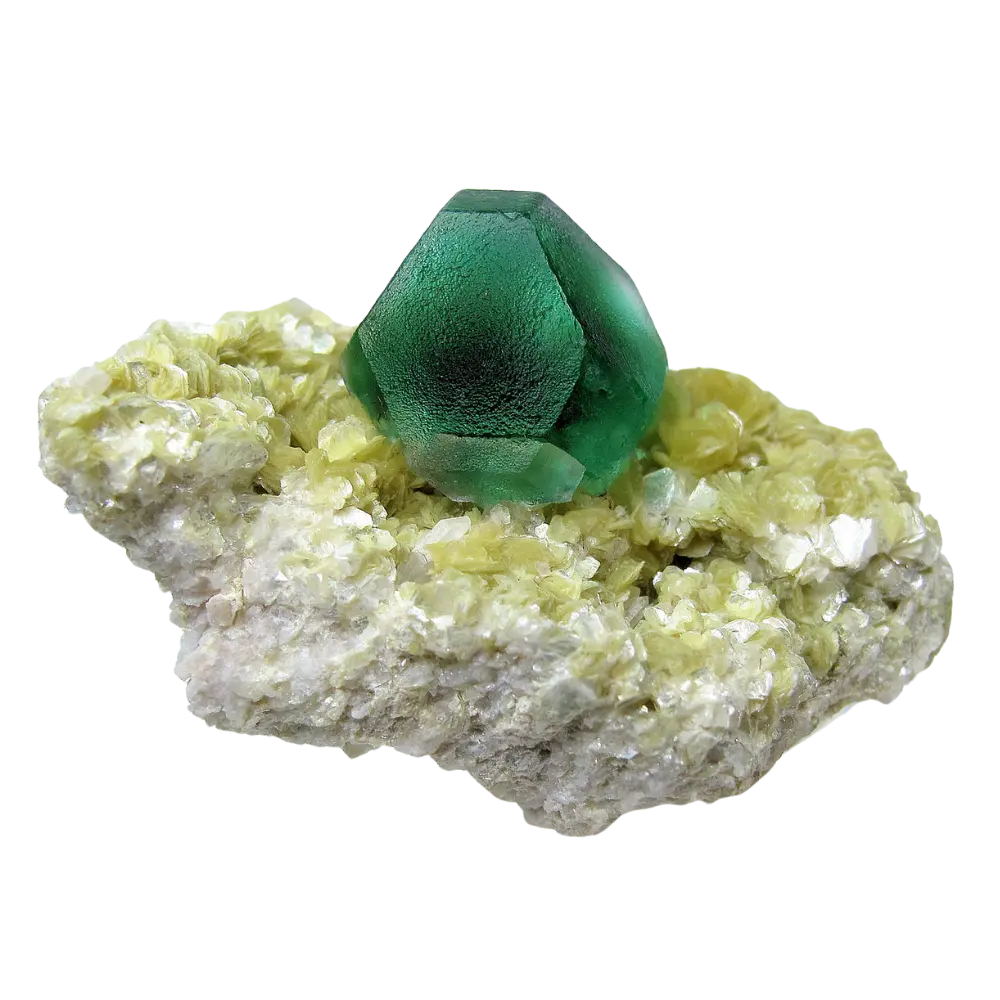
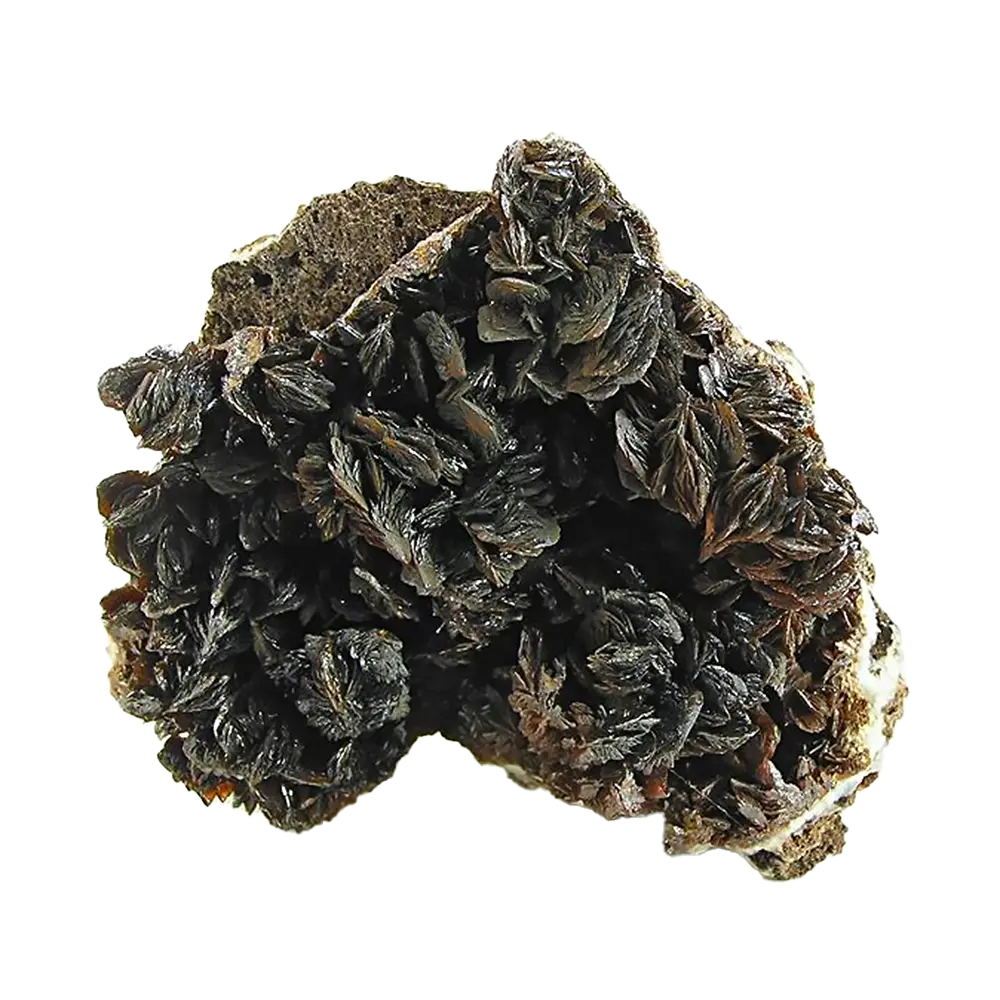
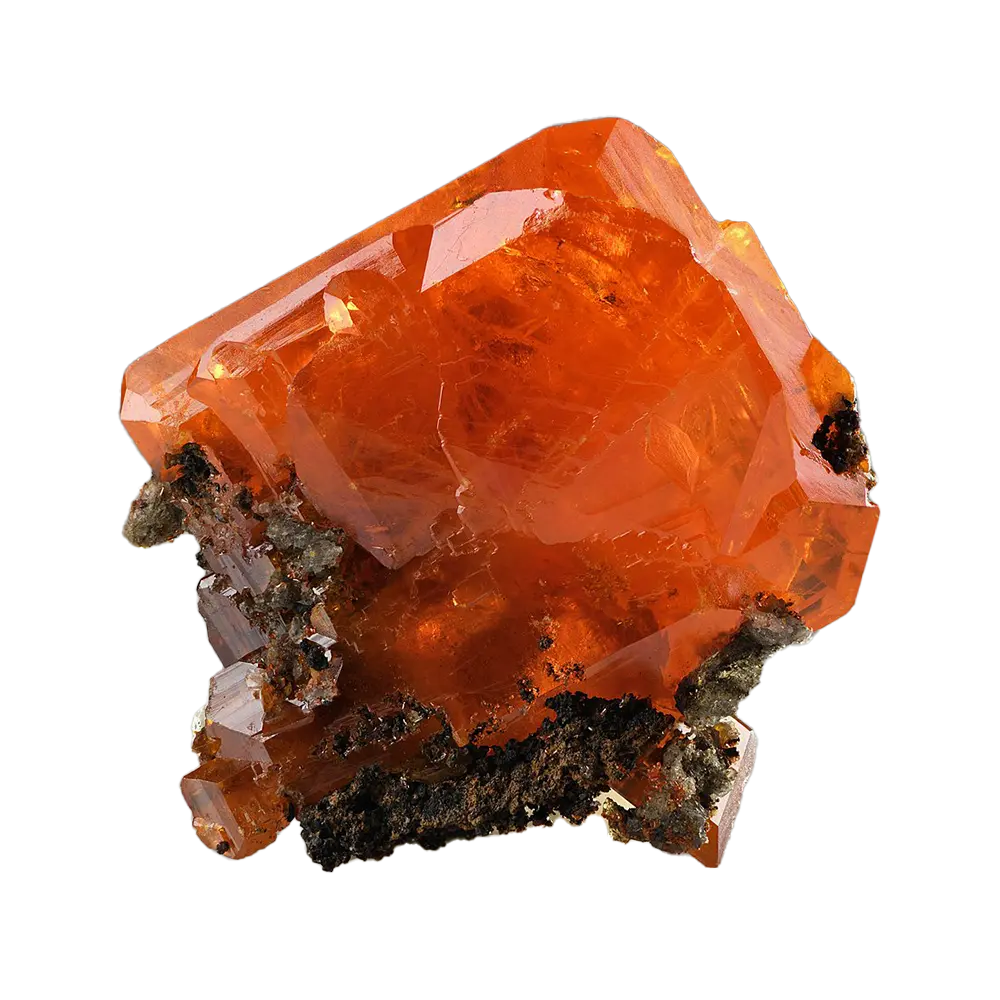
Types and Colors: Garnets come in several different types, each with its unique chemical composition and color:
– Almandine: Typically red to brownish-red, common in metamorphic rocks.
– Pyrope: Deep red to black, often used in jewelry.
– Spessartine: Orange to reddish-brown, found in granite pegmatites.
– Grossular: Green, yellow, or brown, found in skarns and contact metamorphosed limestones.
– Andradite: Yellow-green to black, includes demantoid (green) and topazolite (yellow).
– Uvarovite: Bright green, the rarest type of garnet, found in chromite deposits.
Localities and Mining: Significant garnet deposits are found in India (Rajasthan), Madagascar, Sri Lanka, the United States (Idaho and Arizona), and Russia (Ural Mountains). These countries mine garnet for both gemstone and industrial uses, with high-quality specimens often used in jewelry.
Applications: Garnet’s durability and varying hardness make it suitable for numerous applications:
– Gemstones: Garnets are popular in jewelry for their wide range of colors and brilliant luster.
– Abrasives: Garnet is used in waterjet cutting, sandblasting, and as an abrasive in sanding belts and disks due to its hardness and toughness.
– Industrial Applications: Garnet is used as a filtration medium in water purification and as a component in abrasive powders and papers.