Fact Sheet:
- Chemical Composition: Na₂B₄O₆(OH)₂·3H₂O (Hydrated Sodium Borate)
- Hardness: 2.5 to 3 on the Mohs scale
- Crystal System: Monoclinic
- Color Varieties: Colorless, white, pale yellow, or gray
- Major Localities: United States (California), Argentina, Turkey, and Russia
- Common Uses: Source of boron, used in glassmaking, detergents, ceramics, and as an insecticide
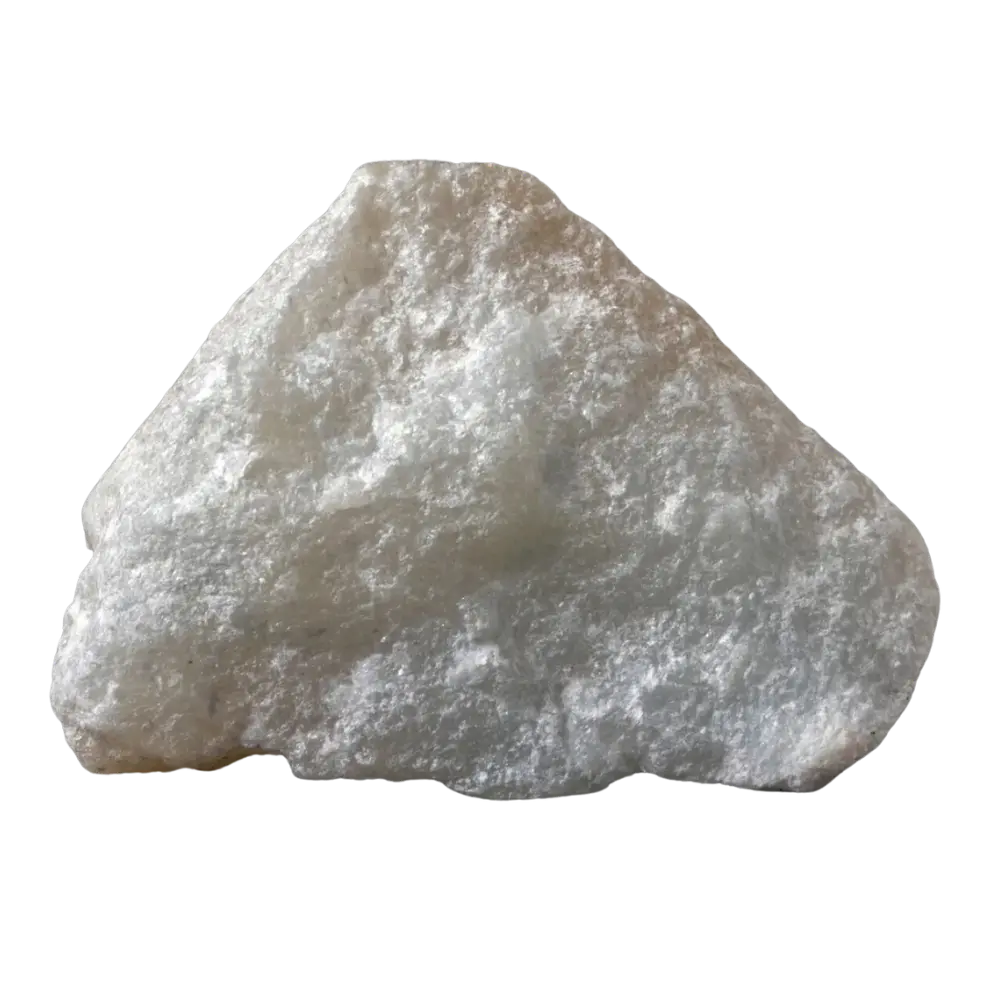
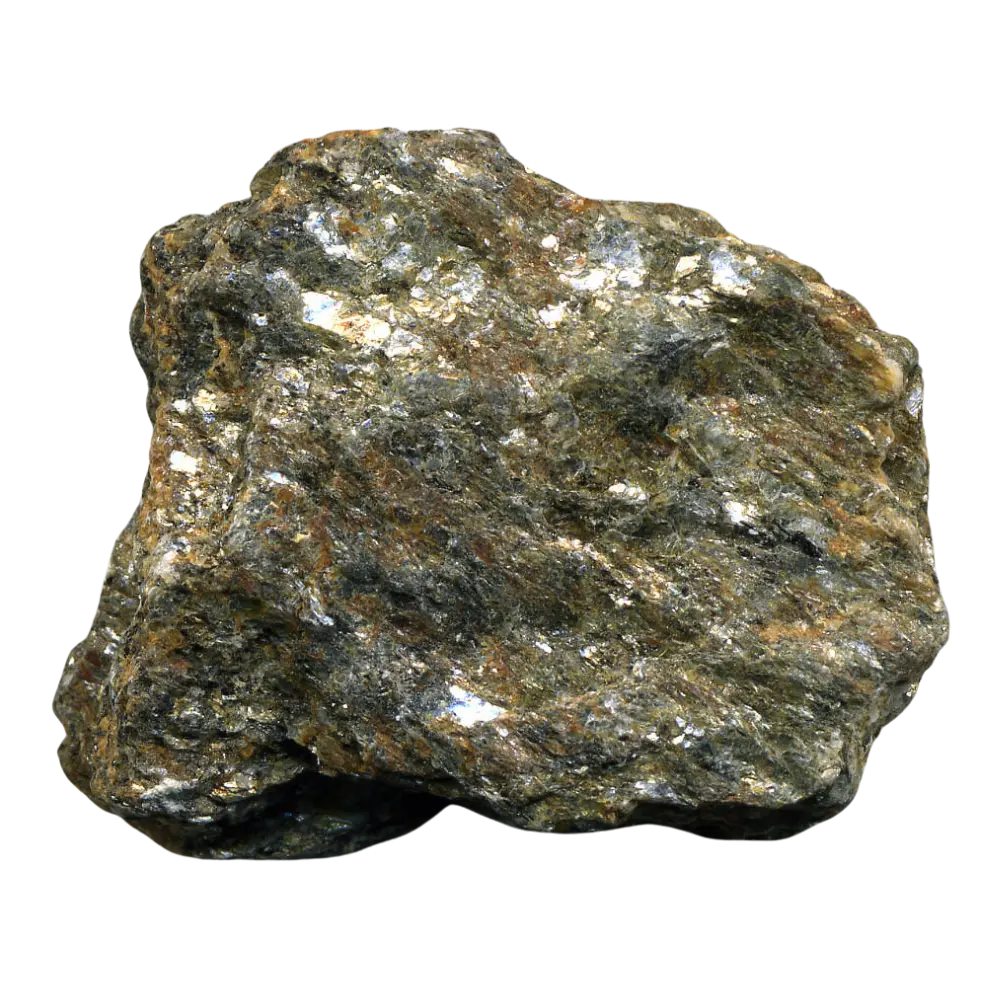
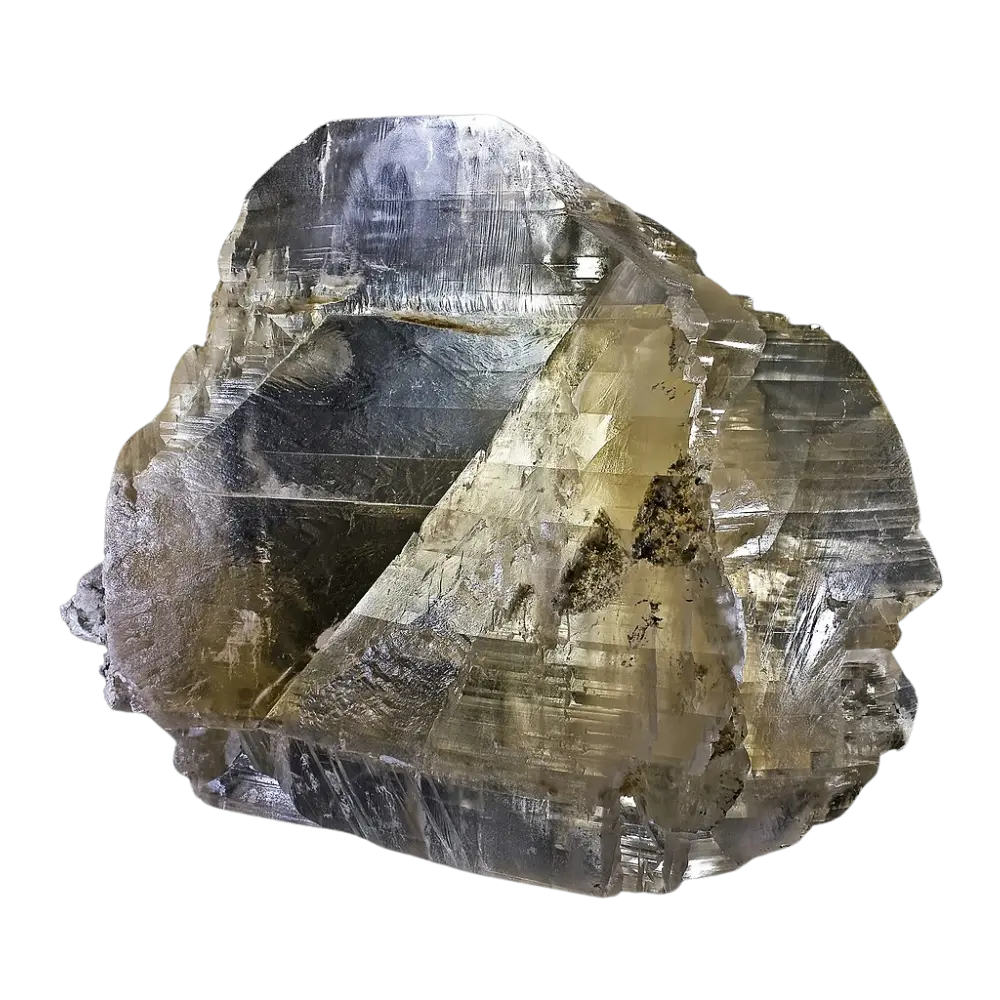
Introduction: Kernite is an important borate mineral, mainly valued for its high boron content, which makes it a key raw material in various industrial applications. Discovered in Kern County, California, after which it is named, kernite is primarily mined for its use in producing boron compounds, essential for glassmaking, agriculture, and detergents. With its pale color and relatively soft nature, kernite may not be as visually striking as some other minerals, but its economic importance is significant.
Formation: Kernite forms in arid regions where boron-rich water evaporates, leaving behind concentrated borate deposits. These deposits accumulate in ancient lakebeds or playa environments, where repeated cycles of evaporation lead to the crystallization of borate minerals like kernite. It is often associated with other borate minerals, such as borax and ulexite, which are also mined for boron.
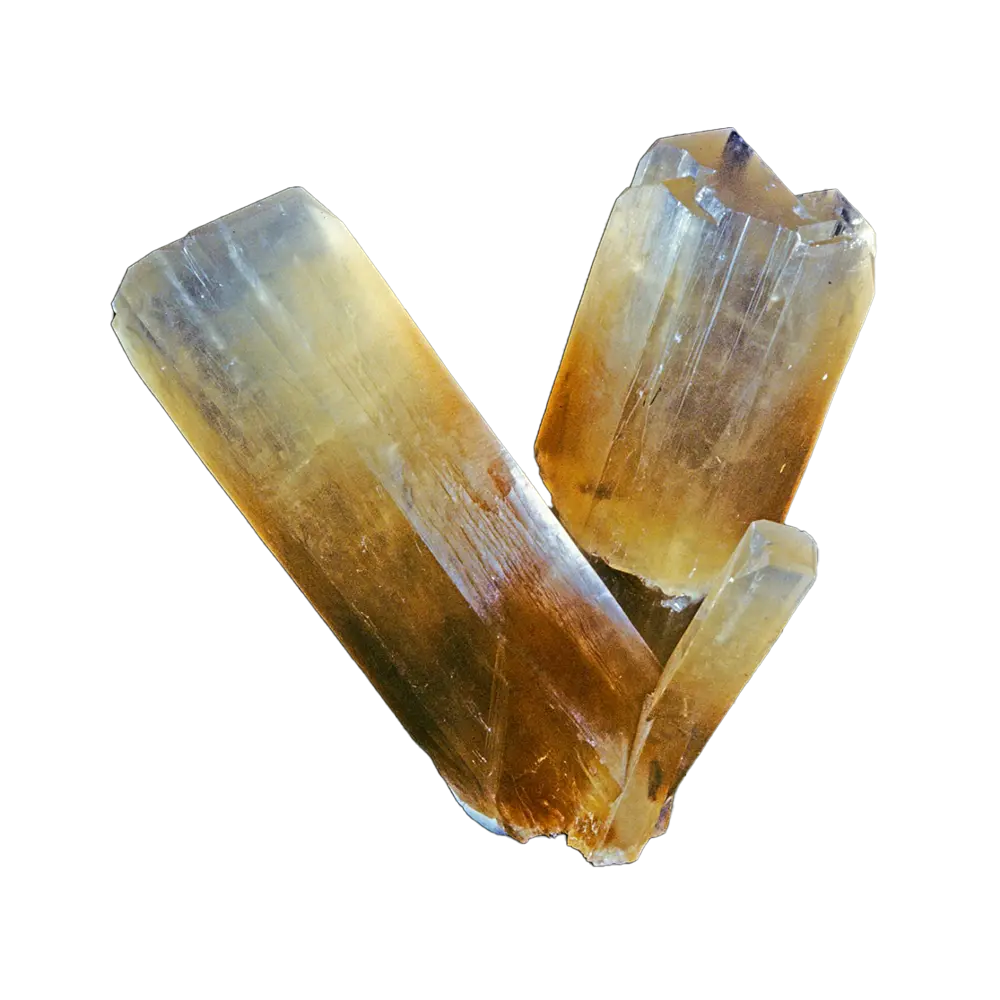
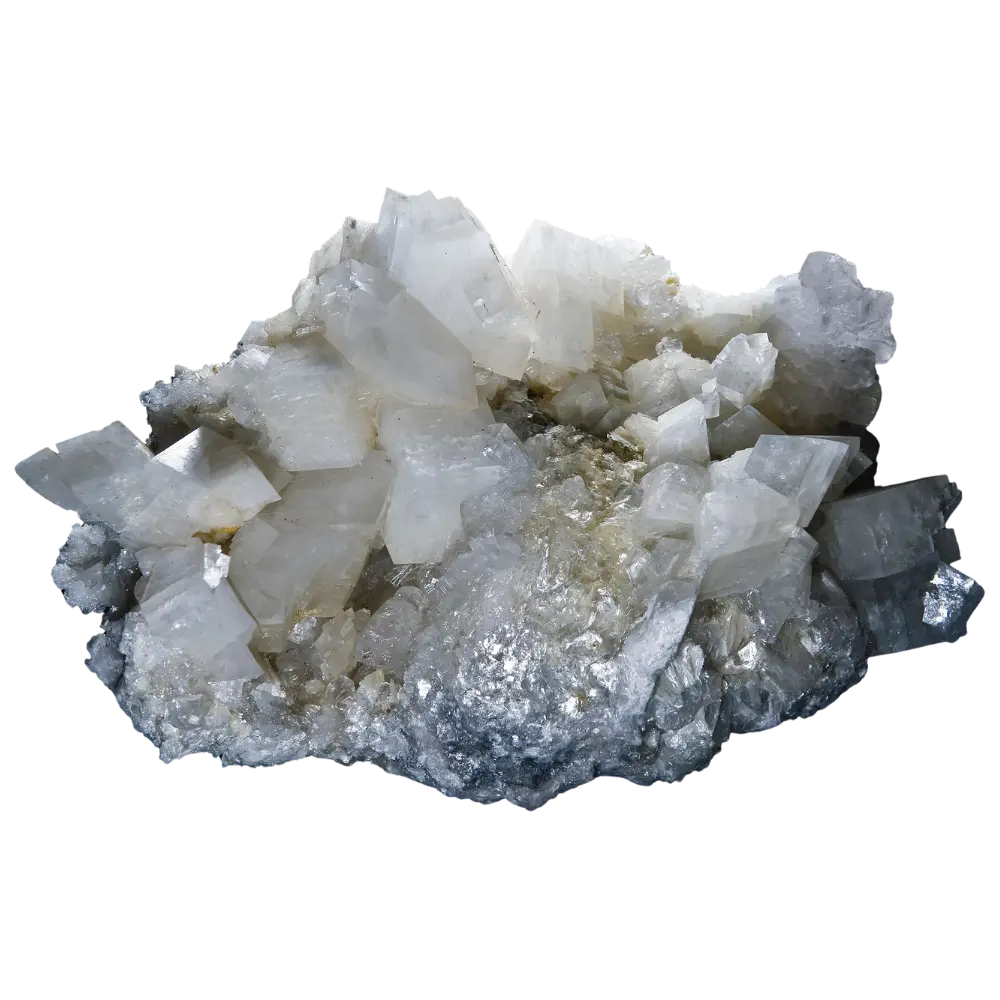
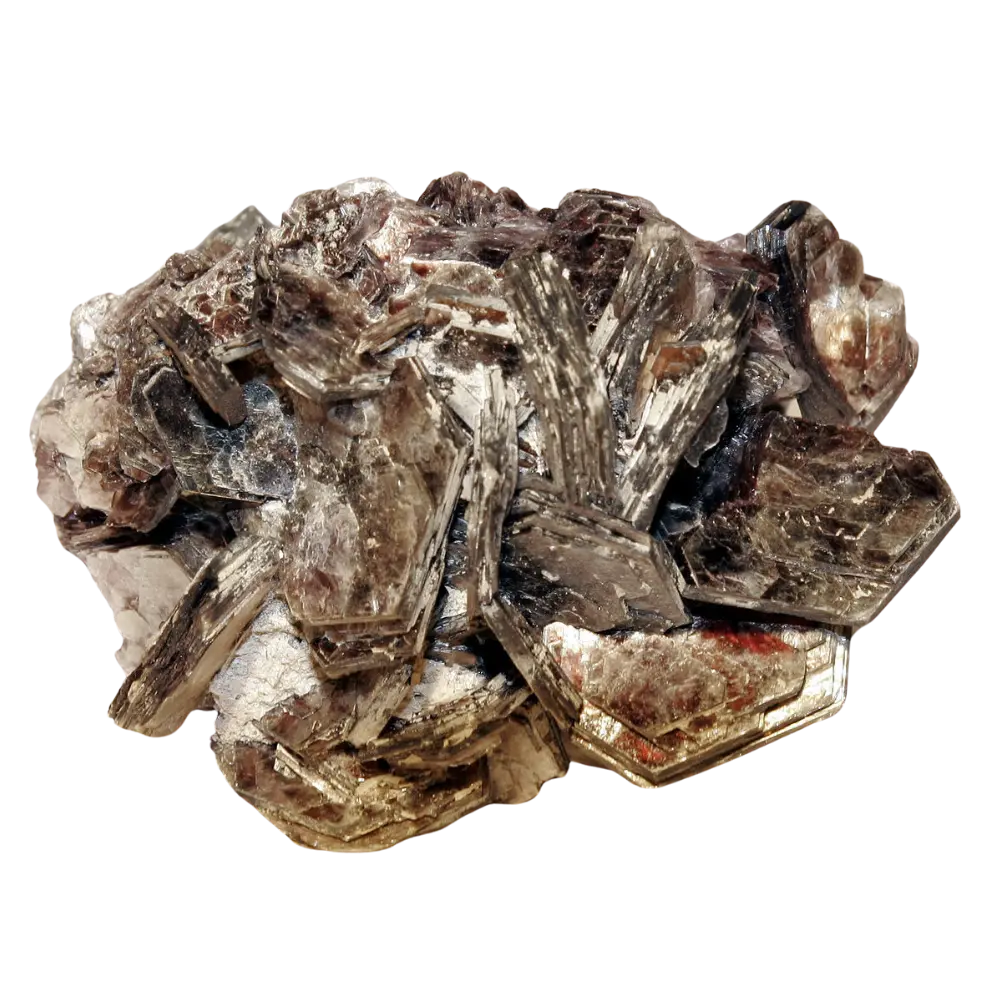
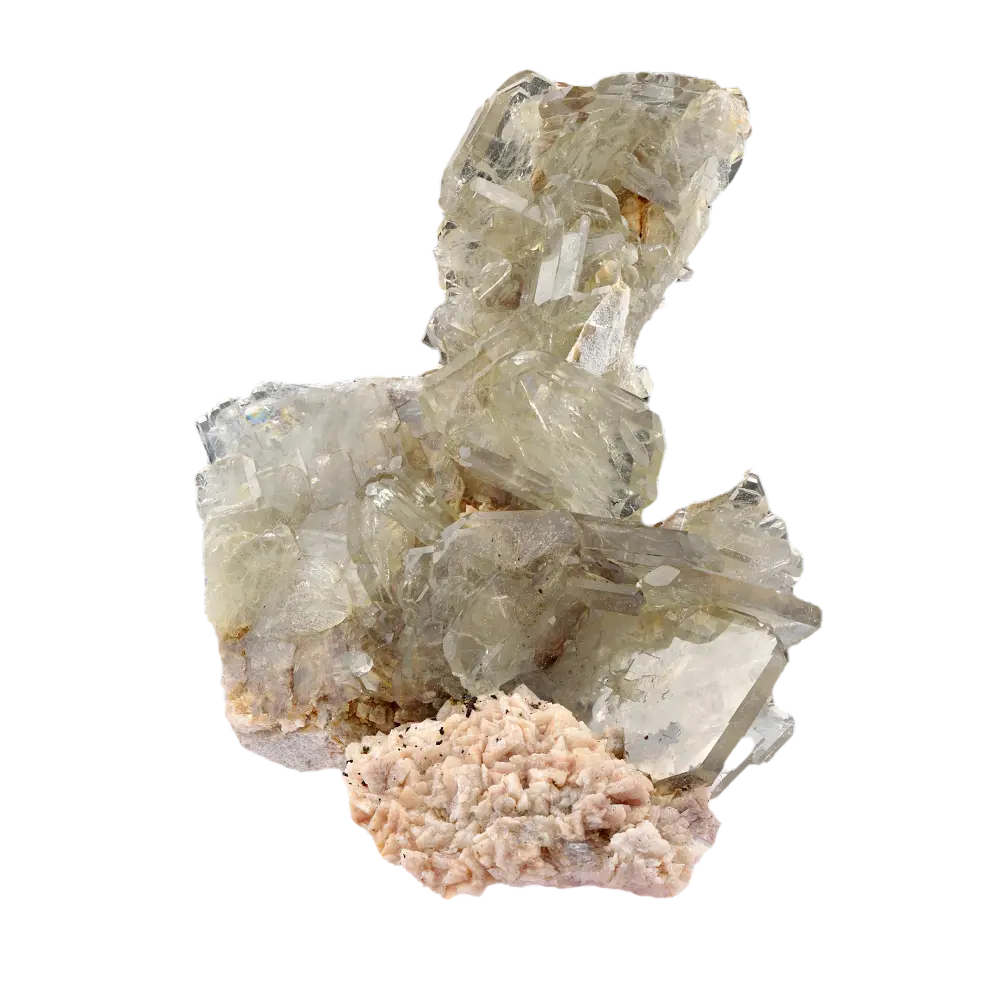
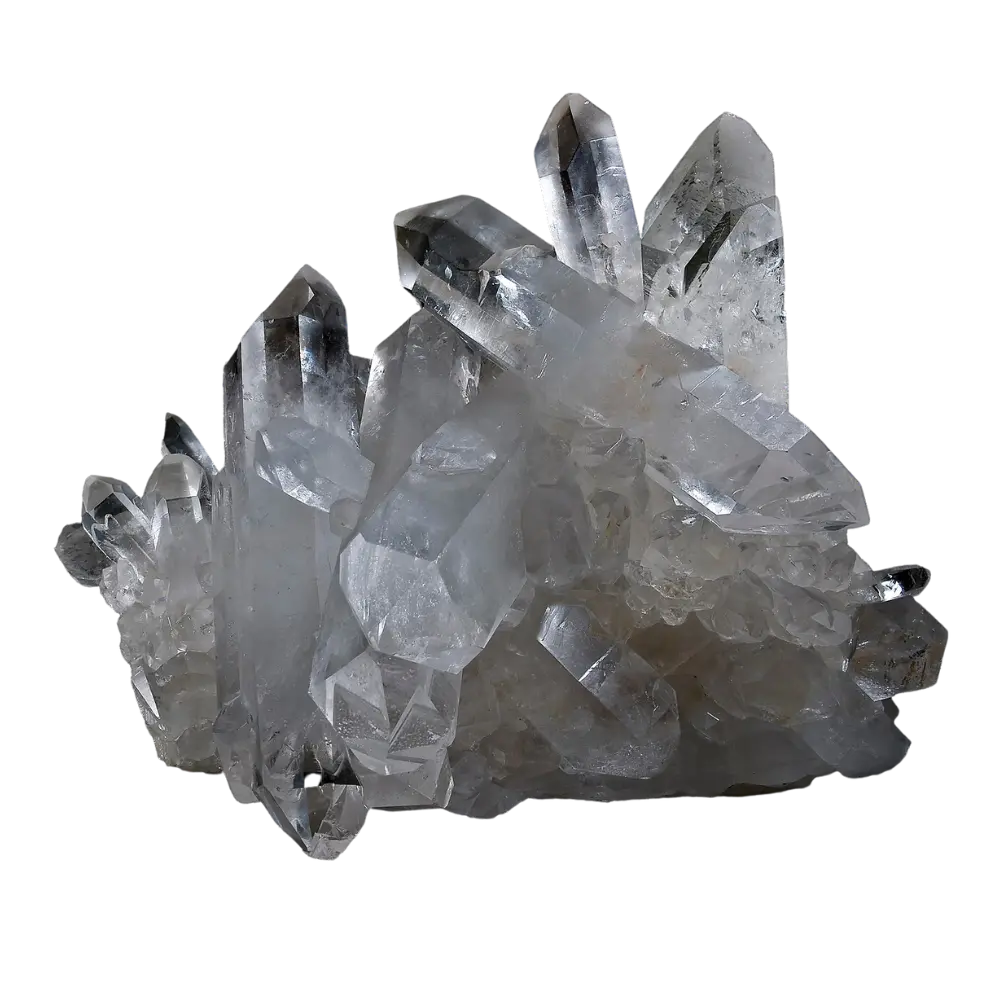
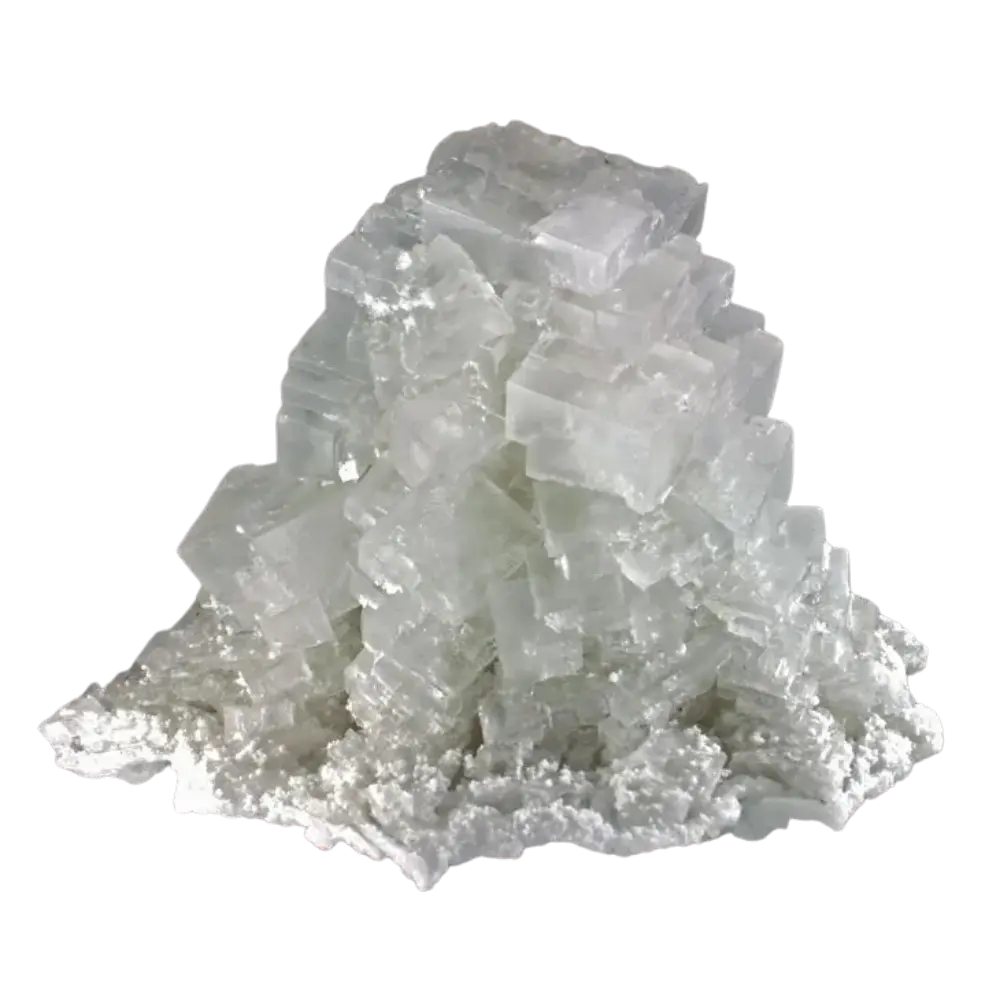
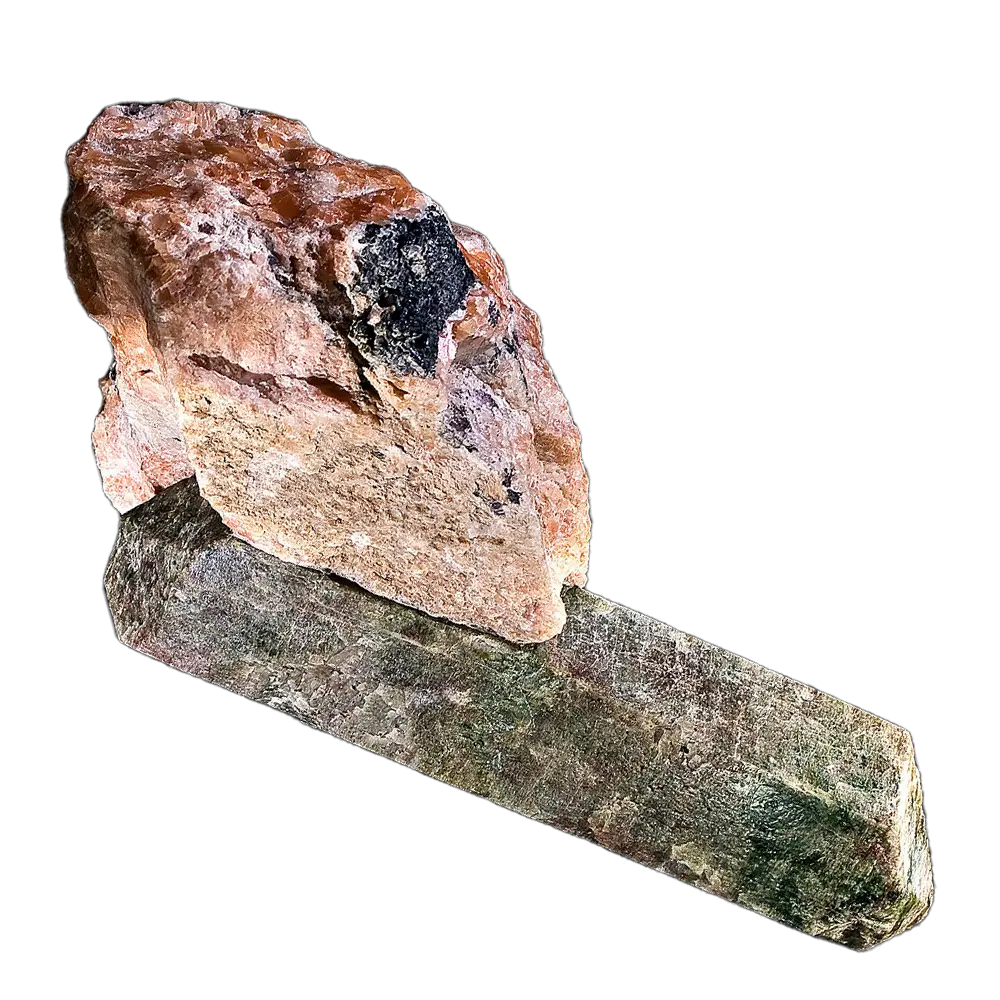
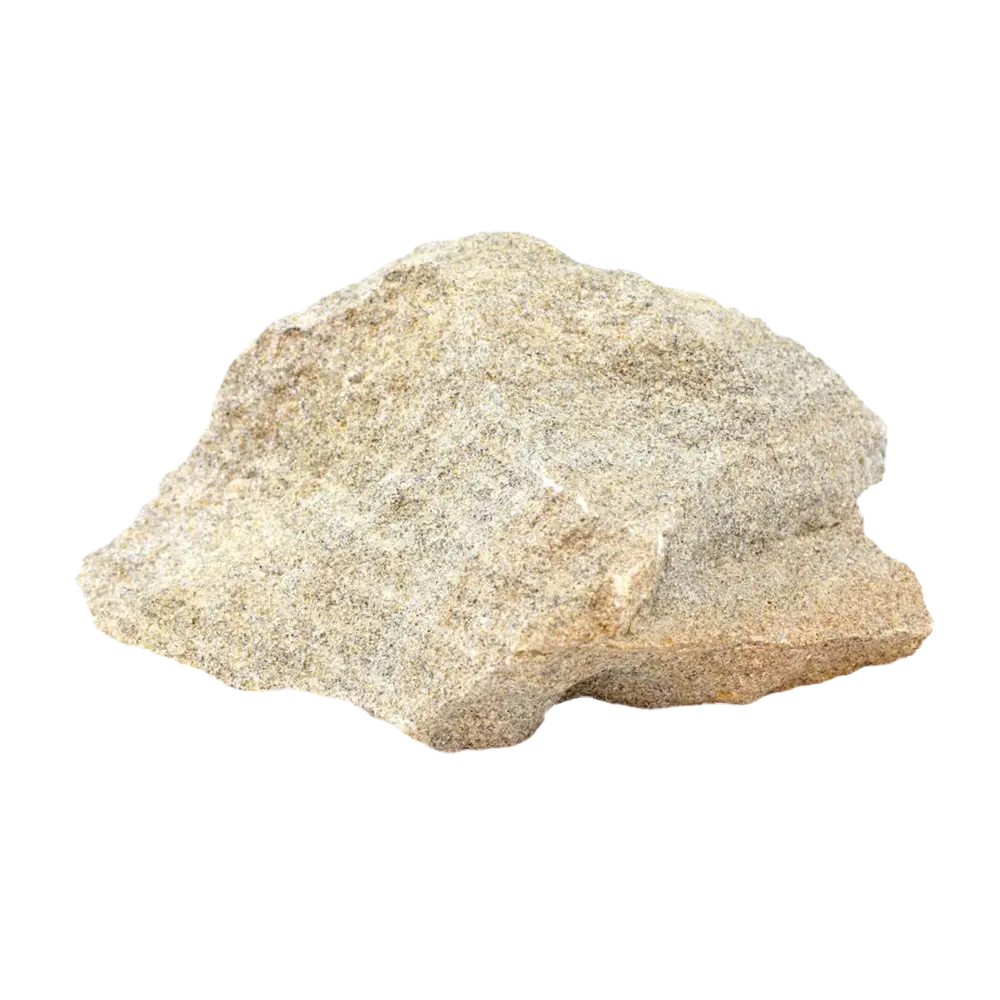
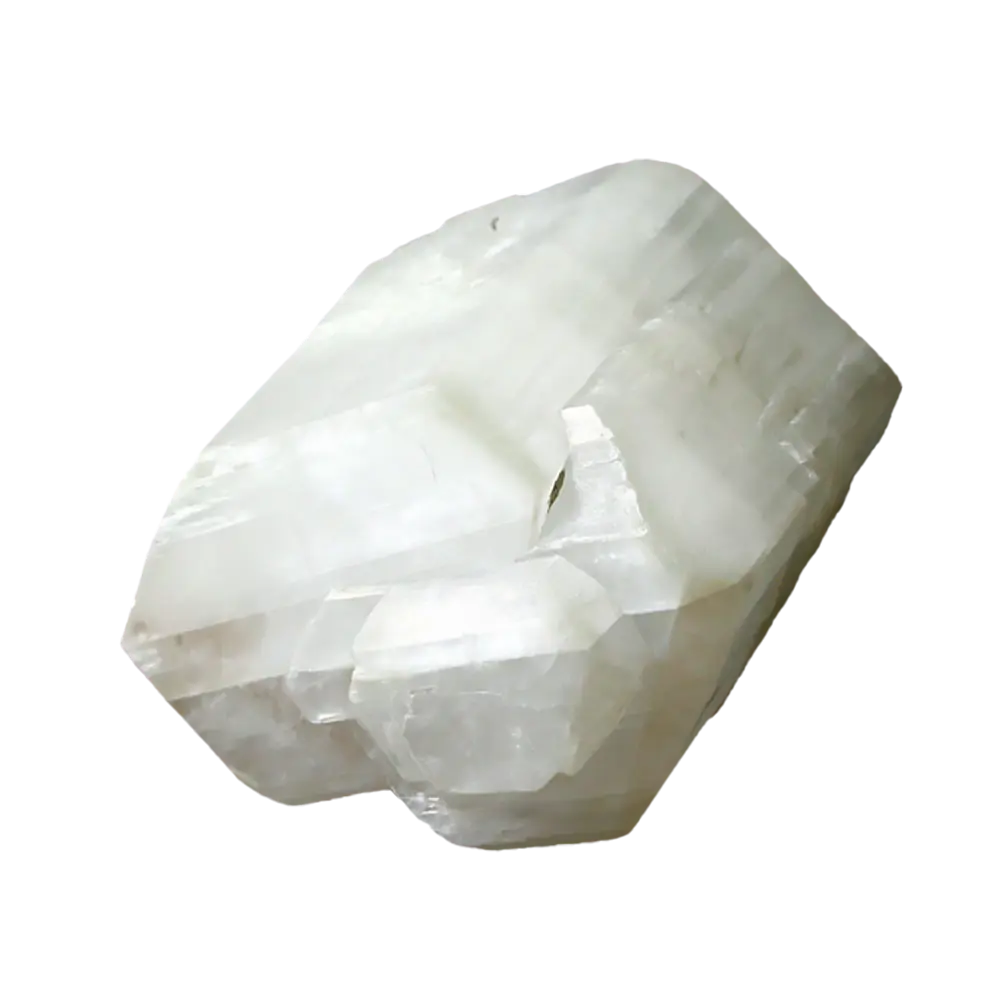
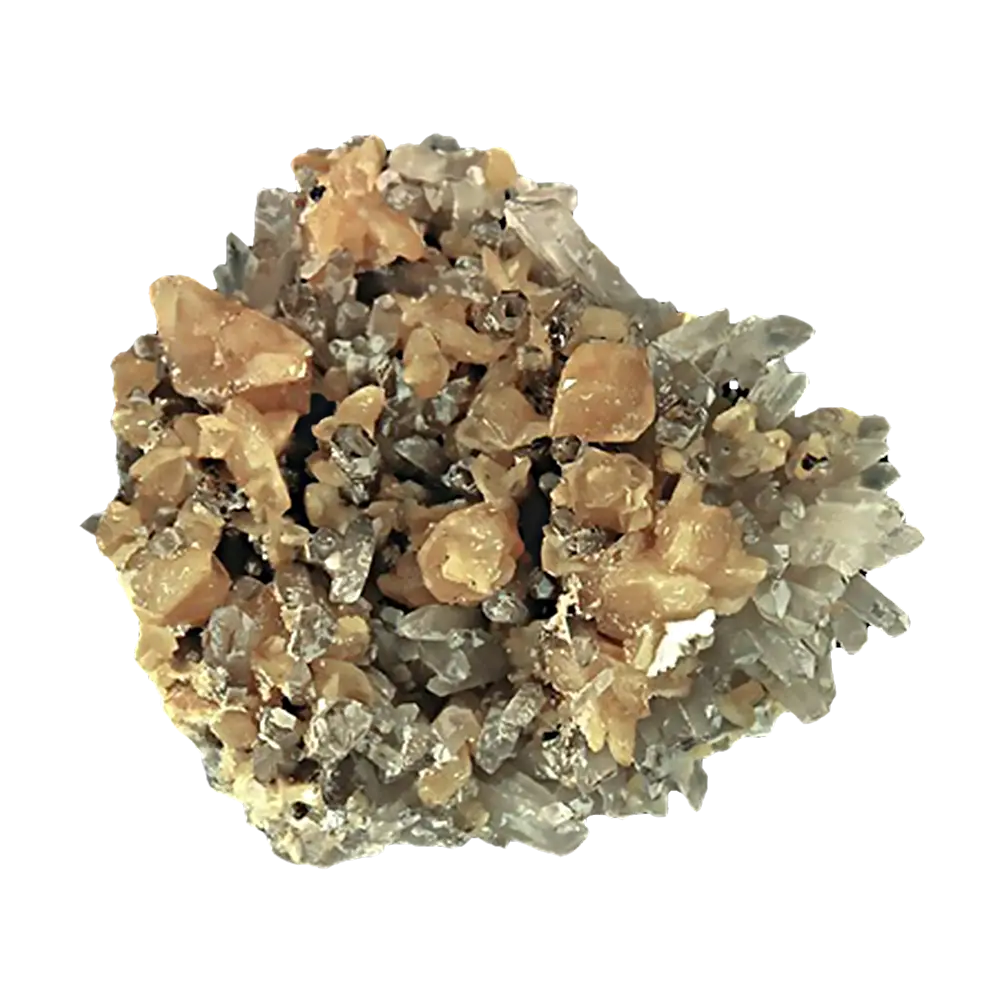
Types and Colors: Kernite is typically colorless to white but may appear pale yellow or gray due to impurities. It has a glassy or silky luster and forms in elongated prismatic crystals or fibrous masses. The crystals are typically transparent to translucent, giving kernite a distinctive appearance, although it is not typically used as a gemstone.
Localities and Mining: Kernite is found in several arid regions around the world, with the most famous deposits located in California:
- United States (California): Kernite was first discovered in Kern County, in the Boron mining district. This region is one of the world’s largest sources of borate minerals, particularly in the Rio Tinto Boron Mine.
- Argentina: Large borate deposits are also found in Jujuy Province, where kernite is mined alongside other borates.
- Turkey: Turkey is a major producer of borate minerals, and although borax is more prevalent, kernite is also found in borate-rich areas like the Eskişehir Province.
- Russia: Borate deposits, including kernite, occur in several parts of Russia, contributing to the country’s industrial boron production.
Applications: Kernite is primarily used as a source of boron, which has a wide range of applications:
- Glassmaking: Boron compounds, derived from kernite, are used in the production of borosilicate glass, which is highly resistant to heat and chemical corrosion. This type of glass is used in laboratory equipment, cookware (such as Pyrex), and electronic displays.
- Detergents: Boron compounds from kernite are key ingredients in laundry detergents and household cleaners, where they help boost cleaning power.
- Ceramics and Enamels: Boron compounds lower the melting point of silica in ceramics and glass enamels, making them easier to produce and improving the durability of the final product.
- Agriculture: Boron is an essential micronutrient for plants, and kernite-derived borates are used in fertilizers to correct boron deficiencies in soils.
- Insecticides: Boron compounds are used as natural insecticides and herbicides, providing an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic chemicals.