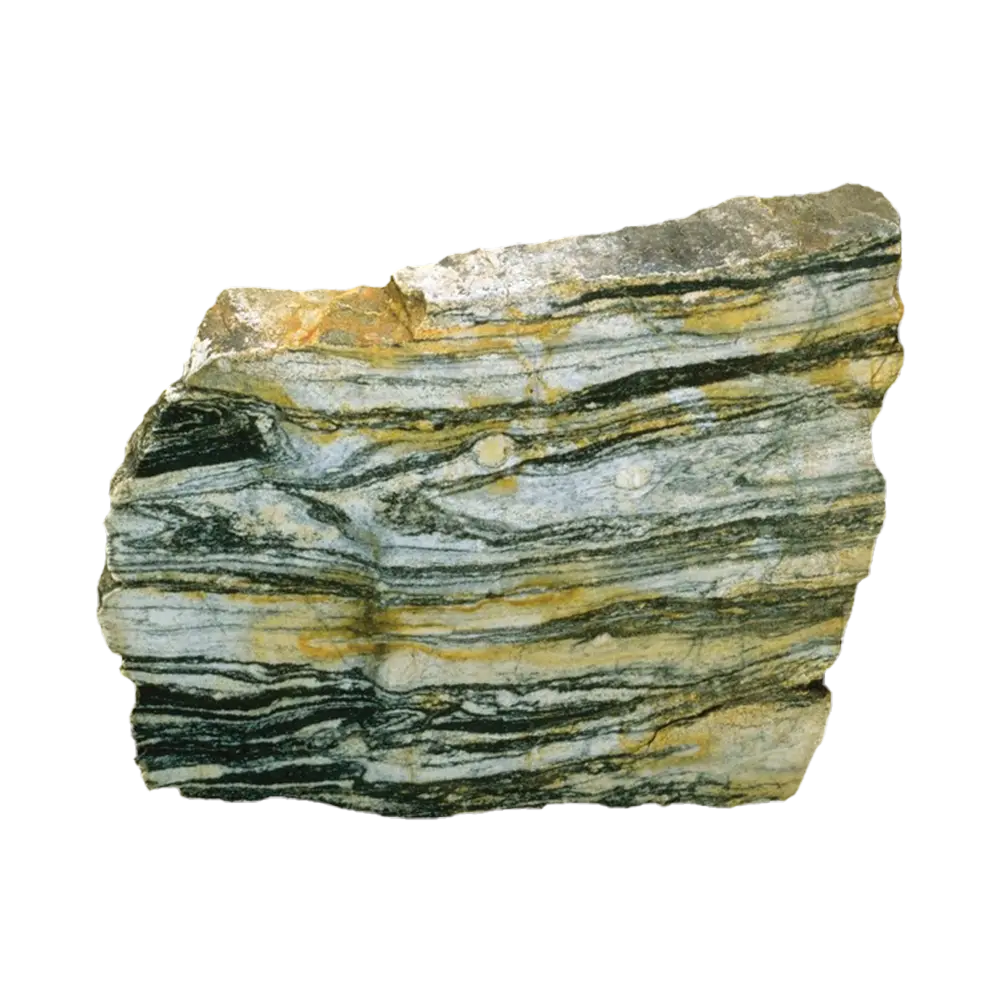
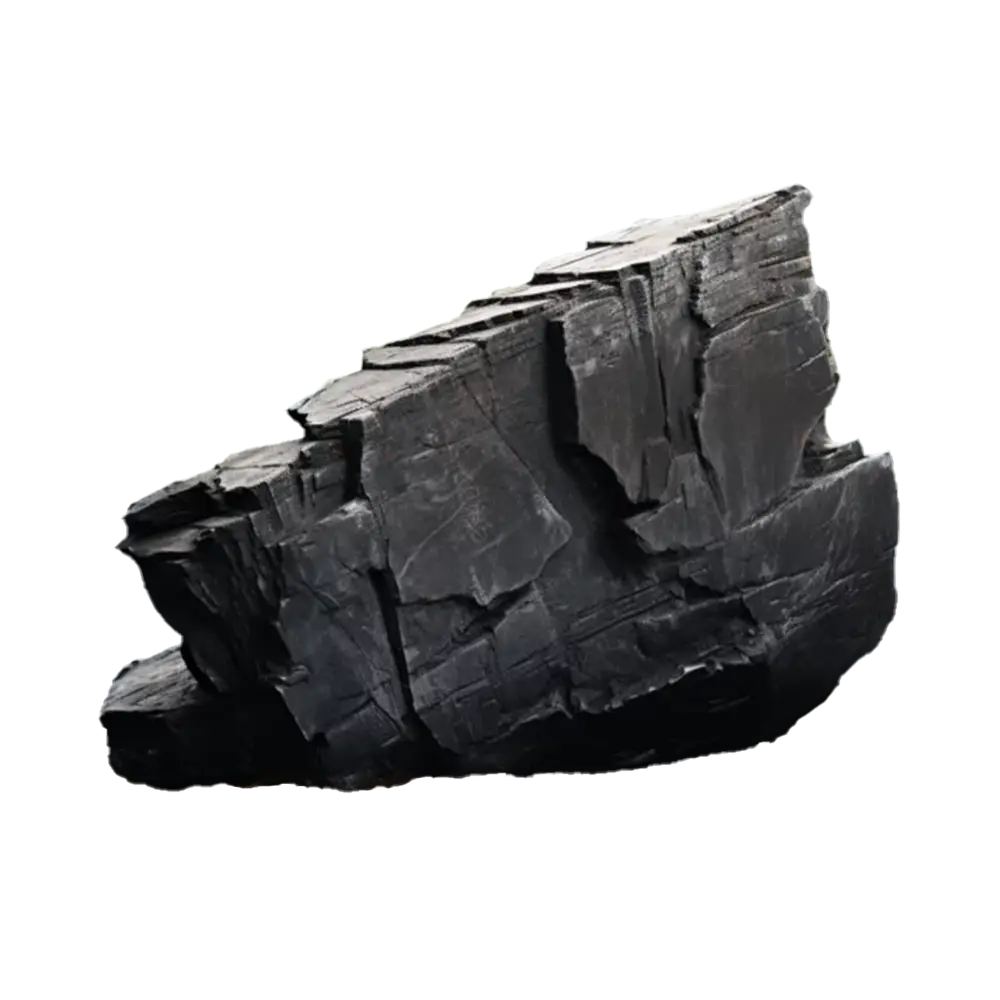
Fact Sheet:
- Chemical Composition: Primarily composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) in the form of calcite or dolomite
- Hardness: 3 to 5 on the Mohs scale (depending on composition)
- Crystal System: Metamorphic rock, non-foliated
- Color Varieties: White, pink, green, black, gray, brown, red, blue, and multicolored
- Major Localities: Italy, Greece, India, Turkey, China, and the United States
- Common Uses: Sculpture, architecture, flooring, countertops, and decorative stone
Introduction: Marble is one of the most beautiful and revered stones in human history, prized for its aesthetic appeal, durability, and workability. It is a metamorphic rock formed from the recrystallization of limestone or dolomite under extreme heat and pressure deep within the Earth’s crust. Marble has been used for millennia in architecture, sculpture, and decorative arts, with famous examples including the Parthenon in Athens, Michelangelo’s David, and the Taj Mahal. Today, it remains a favored material for countertops, flooring, and fine art, making marble an enduring symbol of elegance and sophistication.
Formation: Marble forms when limestone or dolomite undergoes metamorphism, a process in which the original rock is subjected to extreme heat and pressure, causing it to recrystallize. During this transformation, the calcite or dolomite grains in the rock grow and interlock, creating a denser, harder stone with a distinctive, often veined appearance. Marble typically forms in regions with tectonic activity, such as mountain-building zones, where the heat and pressure required for metamorphism are prevalent. The final appearance of the marble, including its color and patterning, is influenced by impurities such as iron oxides, graphite, clay, and other minerals present in the original limestone.
Types and Colors: Marble comes in a wide variety of colors and patterns, depending on the impurities and mineral content of the parent rock:
- White Marble: Pure marble with minimal impurities, known for its clean and classic appearance. Famous examples include Carrara marble from Italy and Thassos marble from Greece.
- Pink Marble: Contains traces of iron or manganese, giving it a soft, pink hue. It is often used in decorative architecture.
- Green Marble: Colored by the presence of serpentine or chlorite minerals, green marble is both rare and highly prized.
- Black Marble: Often contains graphite or organic matter, which gives it a deep, black color. It is frequently used in modern interior design.
- Multicolored Marble: Often found with striking veins of contrasting colors, caused by various mineral impurities. These patterns make each piece of marble unique and highly sought after in luxury design.
Localities and Mining: Significant marble deposits are found in many parts of the world, with a few regions being especially well-known for their high-quality marble:
- Italy: The Carrara region of Italy is world-famous for its white Carrara marble, which has been used since Roman times in sculptures and buildings.
- Greece: The island of Thassos is renowned for its pure white marble, used in ancient Greek temples and statues.
- India: The Makrana marble from Rajasthan was used to construct the iconic Taj Mahal. India is also a leading exporter of green and pink marble.
- Turkey: Known for its high-quality marbles, Turkey produces a variety of colors, including beige, white, and black marble, making it a major player in the global marble market.
- United States: Significant deposits of marble are found in Vermont, Georgia, and Colorado. The Yule Marble Quarry in Colorado is famous for providing marble used in the Lincoln Memorial and the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier.
- China: China is one of the largest producers of marble, offering a wide range of colors and types, particularly for the export market.
Applications: Marble has been used for thousands of years in architecture, art, and interior design. Its elegance and durability make it suitable for various applications:
- Sculpture: Marble has long been a preferred material for sculptors due to its softness and fine grain, which allow for detailed carving. Famous sculptures like Michelangelo’s David and the Venus de Milo were made from marble.
- Architecture: Marble is widely used in buildings, especially in columns, flooring, and cladding, where its beauty and durability are highly valued. Many ancient and modern monuments, such as the Parthenon and the U.S. Capitol Building, feature marble prominently.
- Countertops and Flooring: In contemporary design, marble is used extensively in countertops, tiles, and flooring, lending a luxurious and timeless look to kitchens, bathrooms, and other interior spaces.
- Decorative Stone: Marble’s natural veining and color variations make it a popular choice for decorative features like fireplaces, tabletops, and wall coverings.
- Monuments: Many historical monuments, gravestones, and memorials are made from marble due to its ability to withstand weathering and maintain its beauty over time.