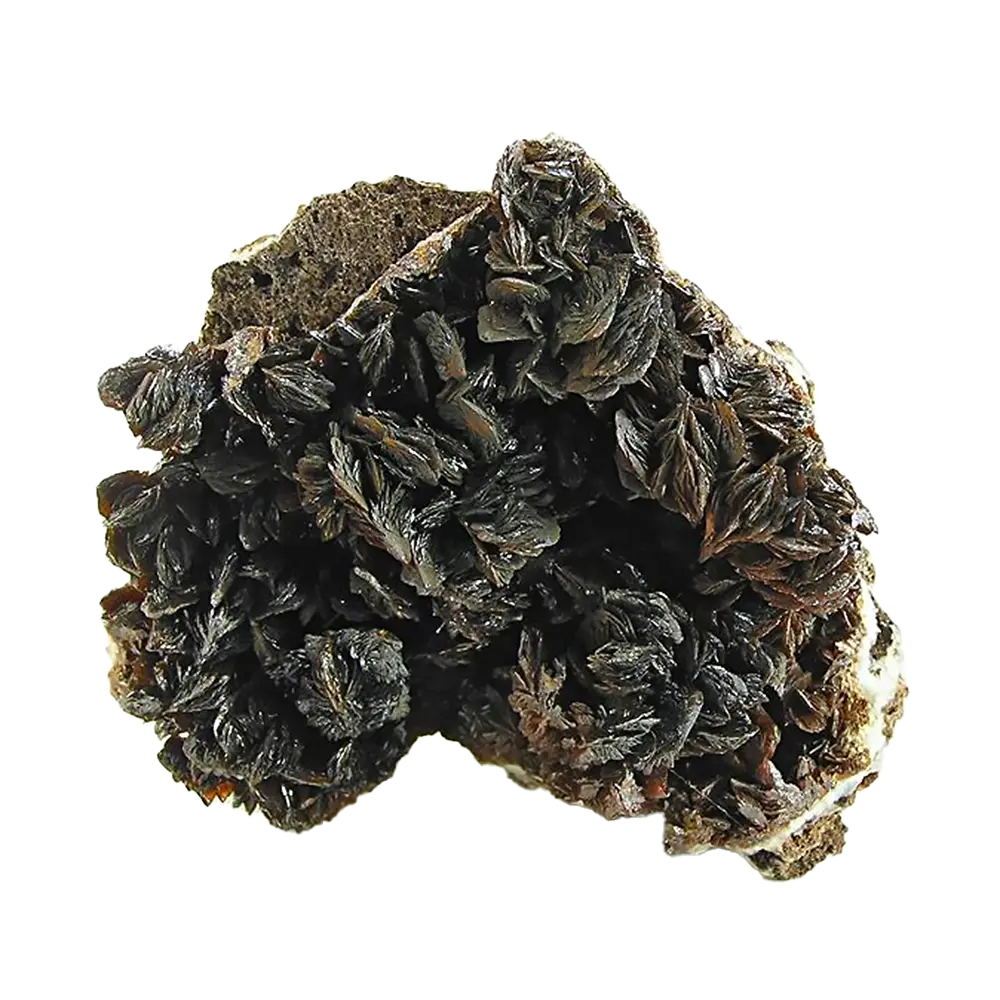
Fact Sheet:
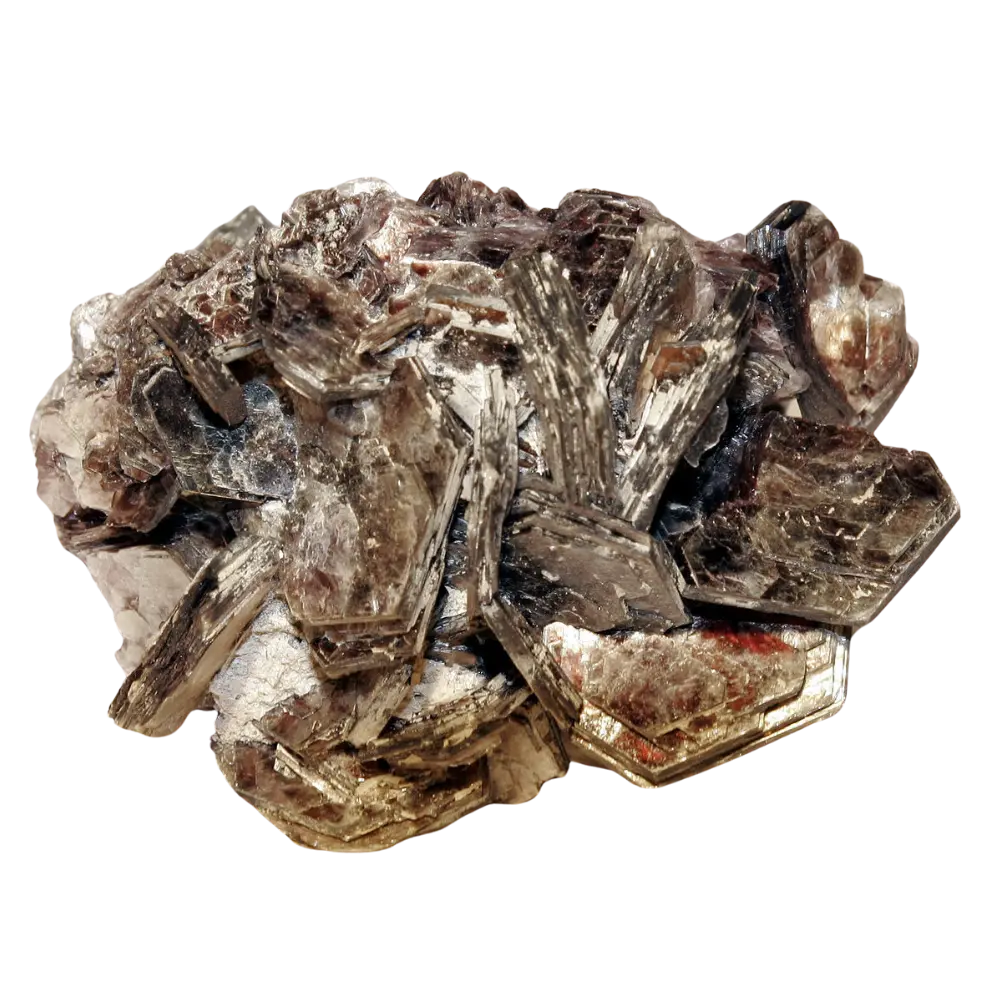
– Chemical Composition: A group of silicate minerals with varying compositions; common forms include muscovite (KAl₂(AlSi₃O₁₀)(OH)₂) and biotite (K(Mg,Fe)₃(AlSi₃O₁₀)(OH)₂)
– Hardness: 2.5 to 3 on the Mohs scale
– Crystal System: Monoclinic
– Color Varieties: Colorless, brown, green, yellow, purple, and black
– Major Localities: India, Russia, the United States, and Madagascar
– Common Uses: Insulation, cosmetics, paints, and electronics
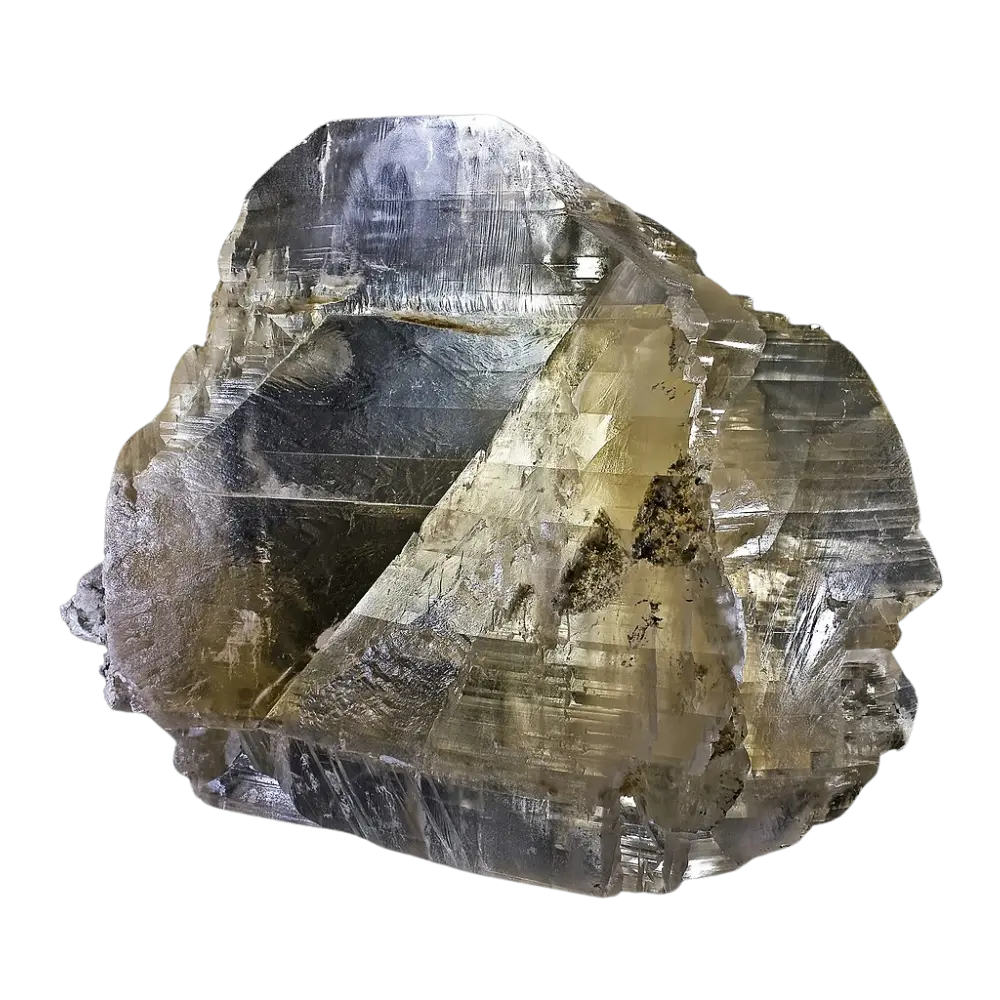
Introduction: Mica is a versatile and widespread group of minerals known for their distinctive layered structure and excellent cleavage properties, which allow them to be split into thin, flexible sheets. These minerals play a crucial role in various industrial applications, as well as in the creation of beauty products.
Formation: Mica minerals form in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary environments. They crystallize from molten rock as it cools, typically forming in the late stages of crystallization in pegmatites. Metamorphic rocks such as schist and gneiss are also rich in mica due to the reformation of minerals under high pressure and temperature.
Types and Colors:
– Muscovite: Usually colorless or pale-colored; commonly used in the electrical and electronics industry.
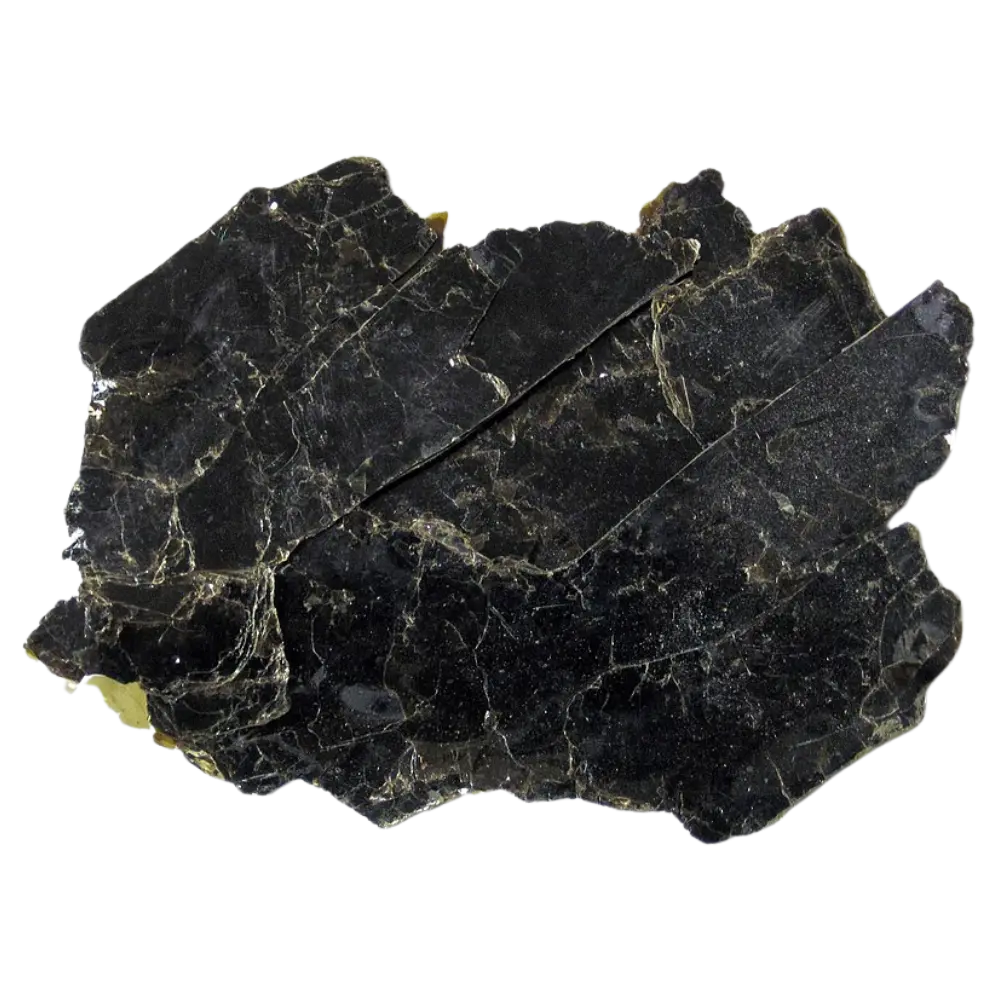
– Biotite: Dark brown to black; often found in granite and other igneous rocks.
– Phlogopite: Typically brown to greenish-brown; used in industrial applications where high heat resistance is required.
– Lepidolite: Purple or pink; contains lithium and is used in the manufacture of lithium batteries and as a gemstone.
Localities and Mining: Significant mica deposits are found in India (the largest producer), Madagascar, Russia, and parts of the United States. These countries mine large quantities of mica, which are then processed for various industrial and commercial uses.
Applications: Mica is valued for its electrical insulating properties, heat resistance, and ability to be split into thin sheets. It is widely used in the electronics industry, in the manufacture of paints and coatings, as a filler in plastics and rubber, and in cosmetics for its shimmering quality.
Sources and further reading
http://www.minsocam.org/msa/collectors_corner/arc/mica.htm
https://mrdata.usgs.gov/mineral-resources/mica.html
https://www.gsi.gov.in/webcenter/portal/OCBIS/pageQuickLinks/pageFour