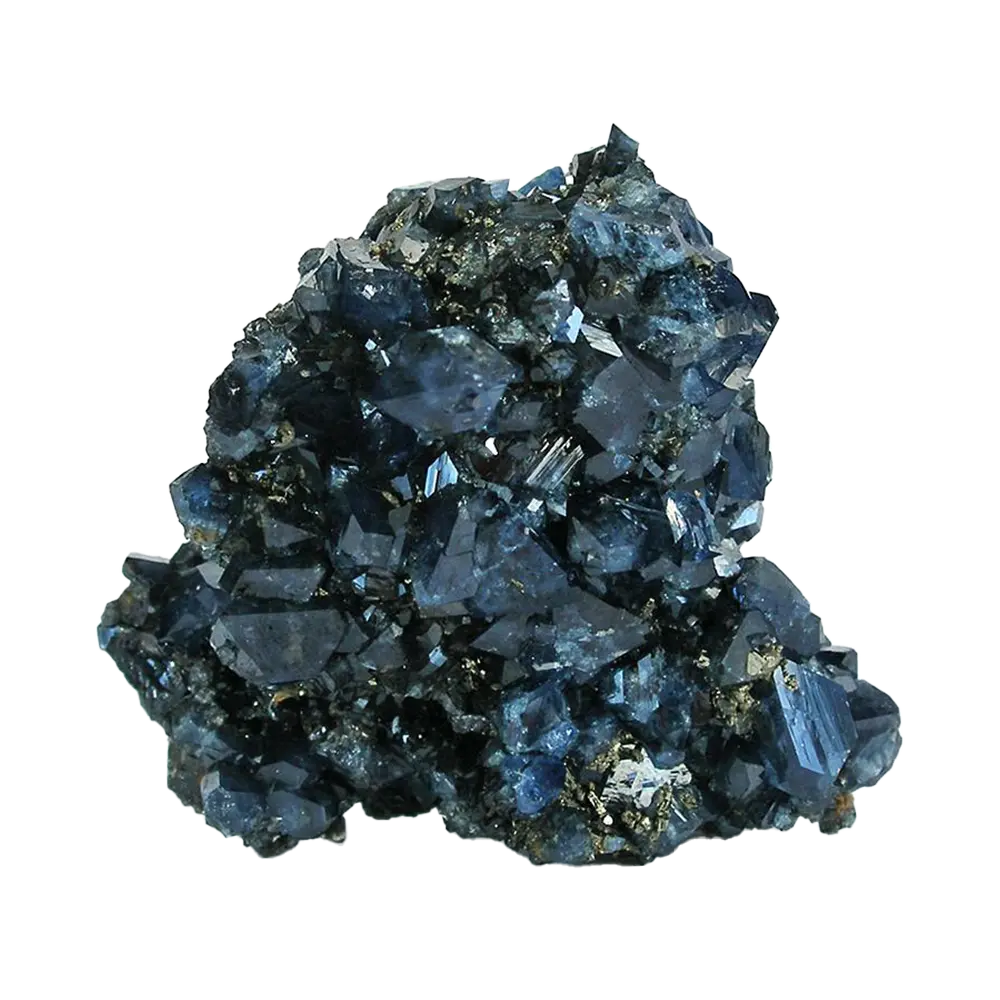
Fact Sheet:
- Chemical Composition: FeAsO₄·2H₂O (hydrated iron arsenate)
- Hardness: 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale
- Crystal System: Orthorhombic
- Color Varieties: Blue, green, gray, yellow, brown, and colorless
- Major Localities: Germany, United States, Canada, Namibia, Mexico, and Czech Republic
- Common Uses: Source of arsenic, collector’s mineral, and in environmental studies for arsenic containment
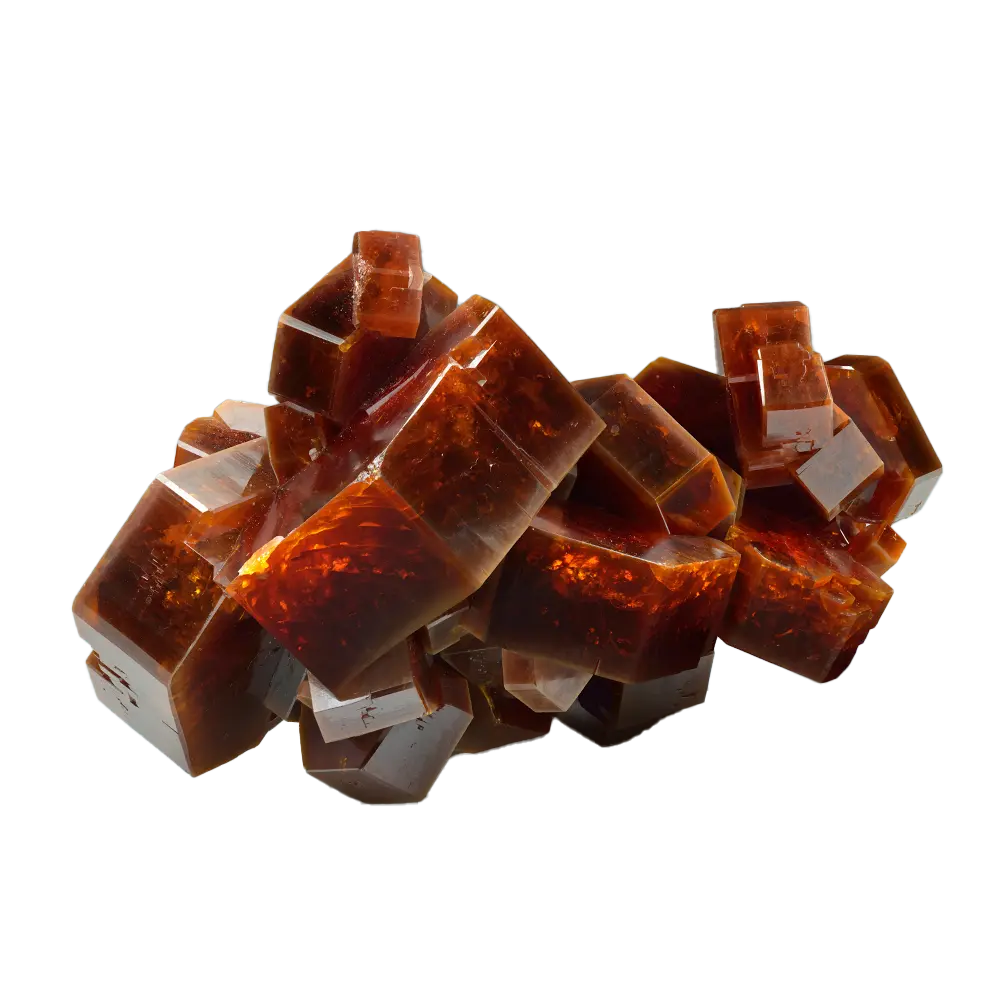
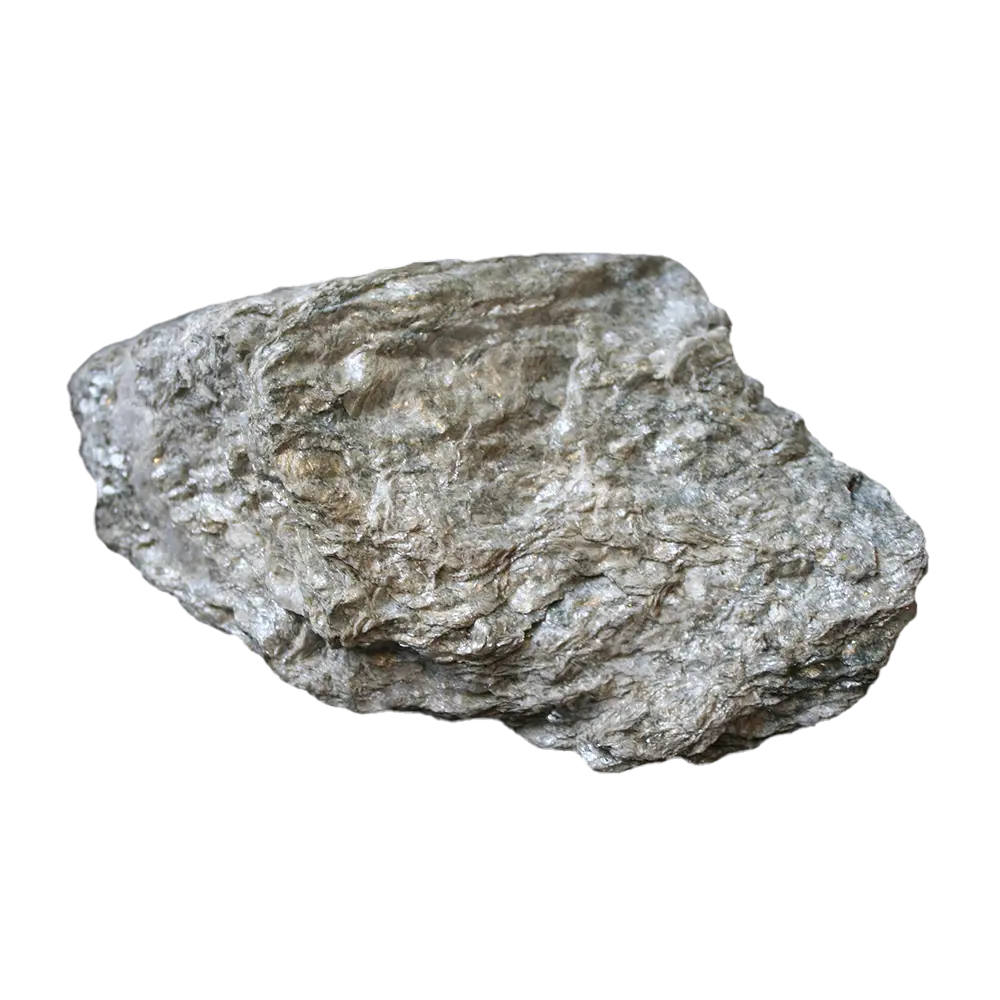
Introduction: Scorodite is a secondary mineral that forms from the oxidation of arsenic-rich minerals such as arsenopyrite. It is a hydrated iron arsenate, known for its beautiful crystals and striking colors, typically blue or green. Though scorodite is prized by mineral collectors for its vibrant hues and crystalline forms, it is also important in environmental studies due to its role in the containment of arsenic, a toxic element. Scorodite’s rarity, combined with its connection to arsenic management, makes it both a scientifically valuable and aesthetically appealing mineral.
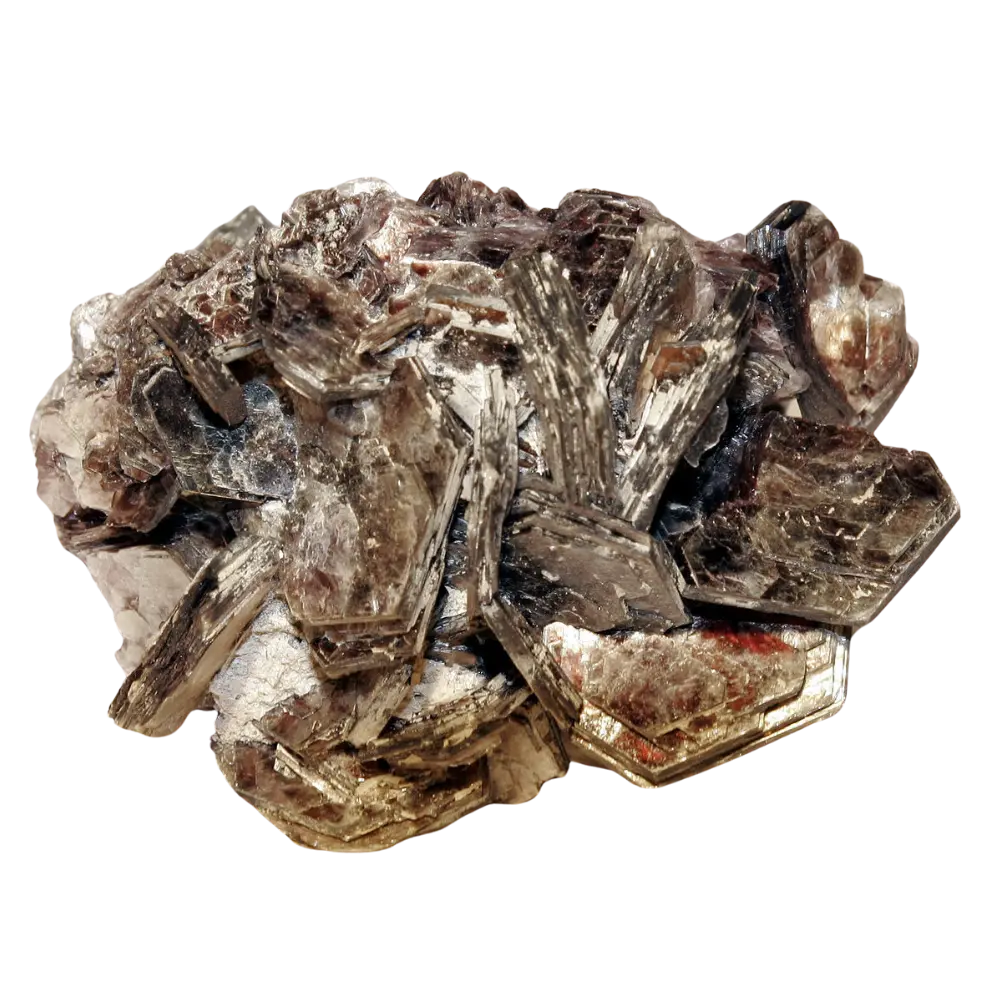
Formation: Scorodite forms as a secondary mineral in the oxidized zones of arsenic-bearing ore deposits. It typically develops through the chemical weathering of primary arsenic minerals such as arsenopyrite, realgar, or orpiment. The presence of iron and arsenic-rich solutions, combined with oxidizing conditions, leads to the precipitation of scorodite. This mineral is commonly found in hydrothermal veins, often in association with sulfides like galena and pyrite, as well as in weathered zones of lead, copper, and zinc deposits.
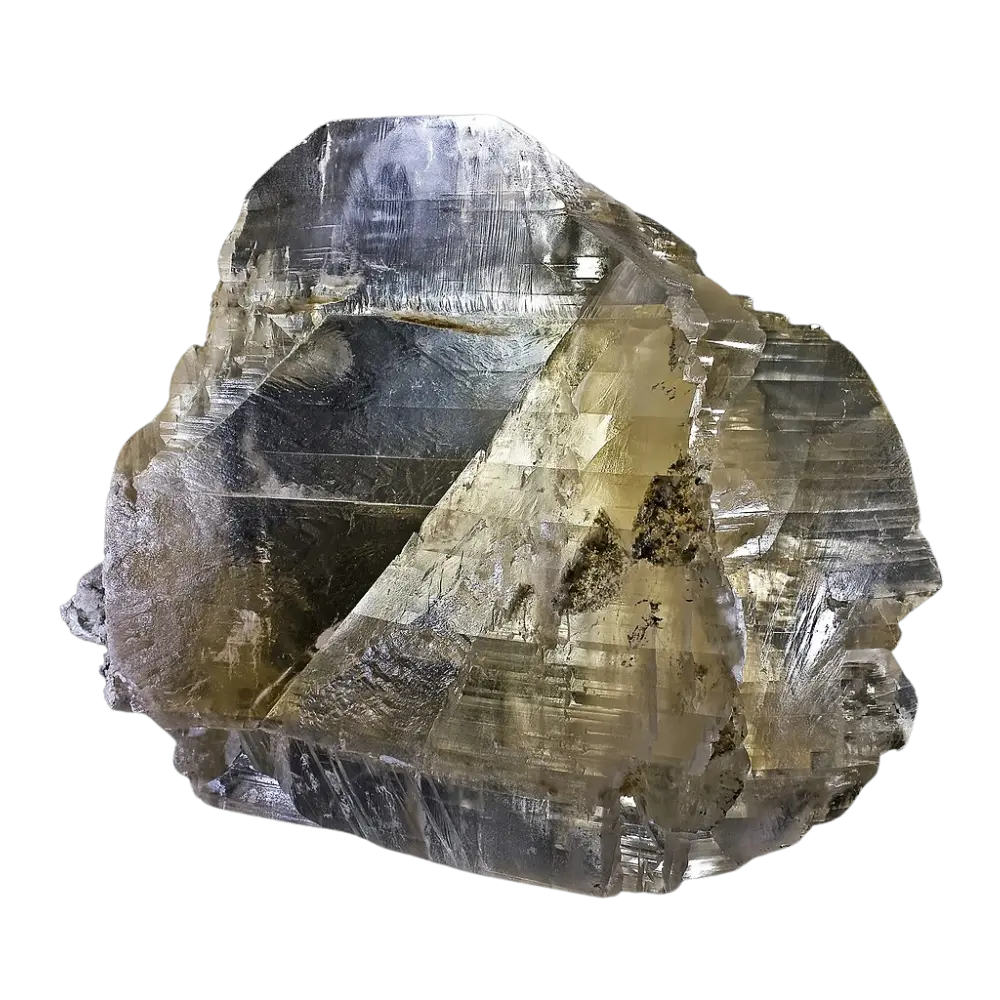
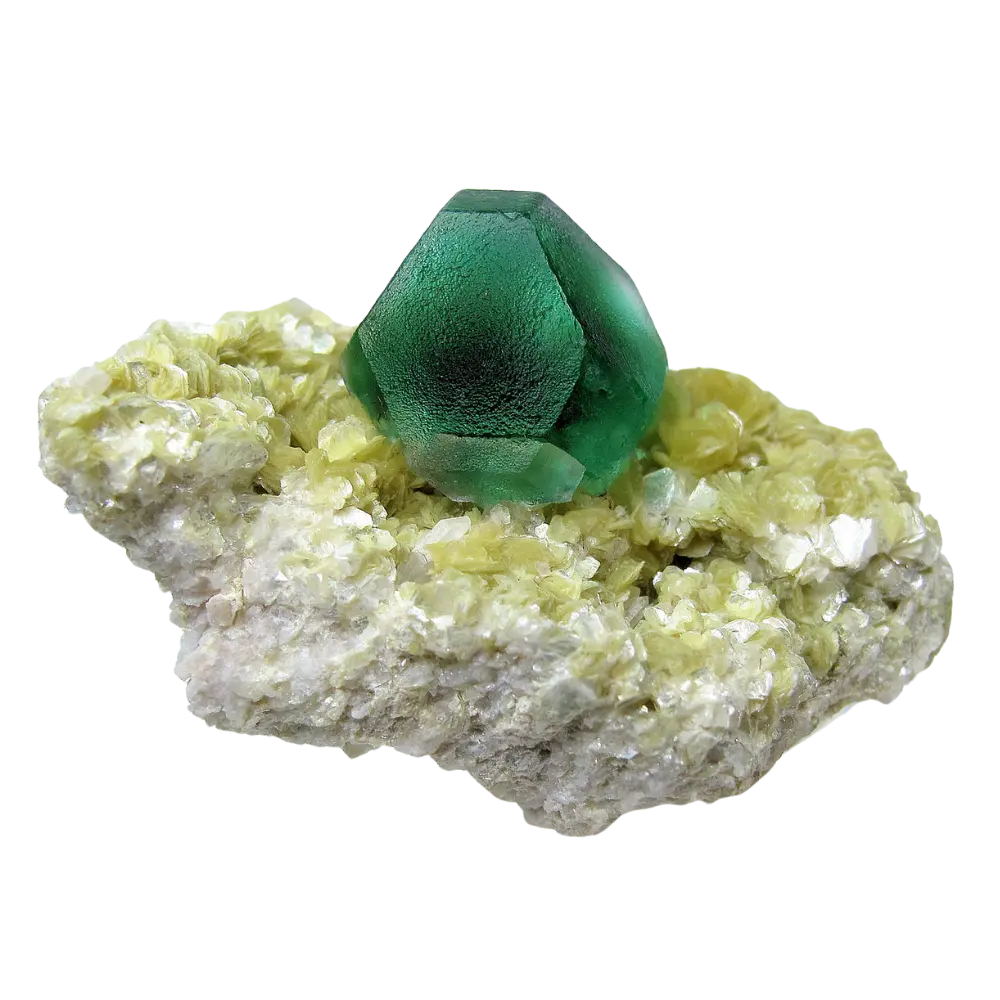
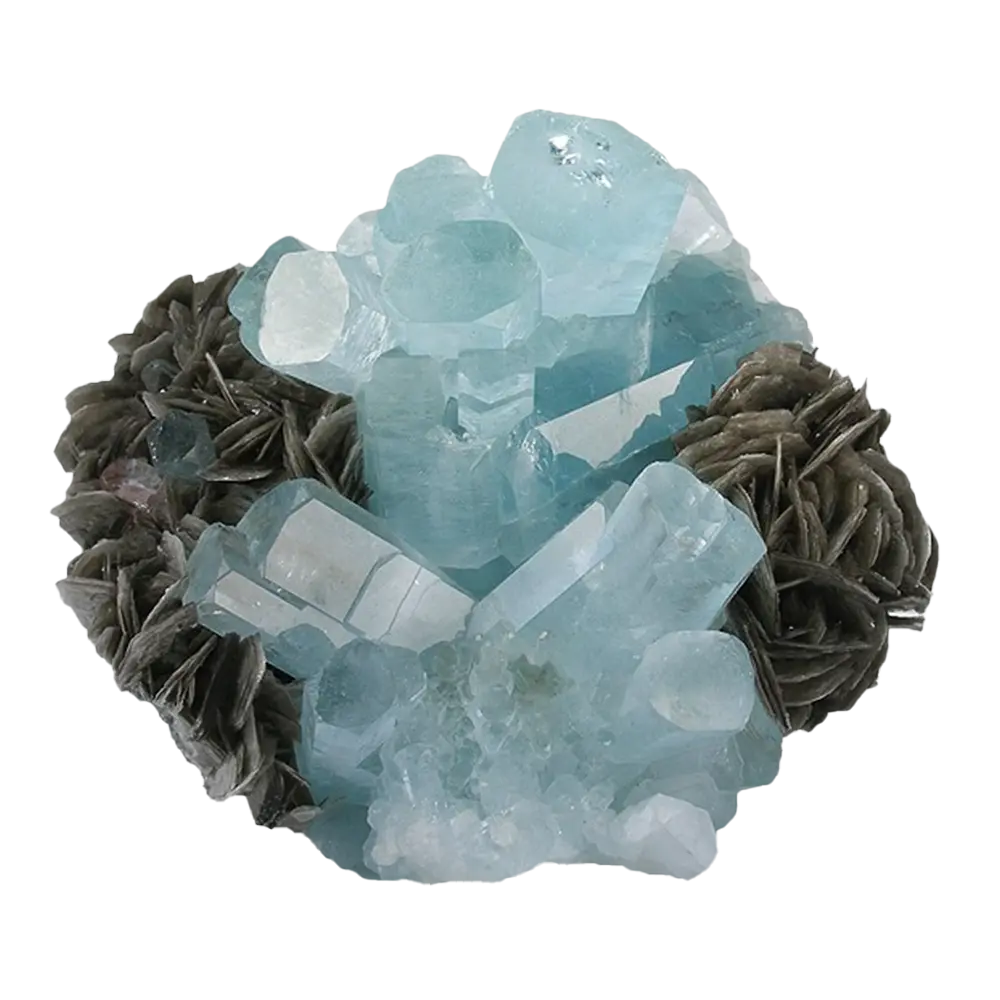
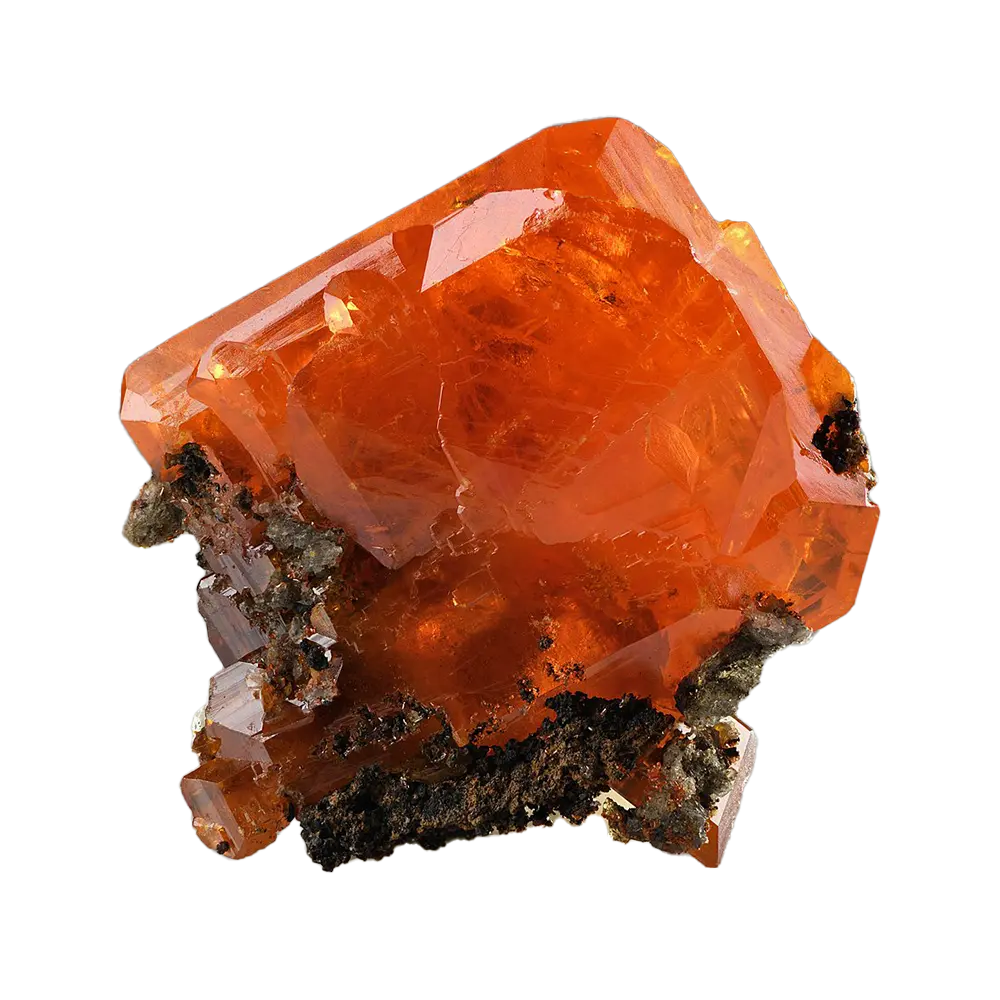
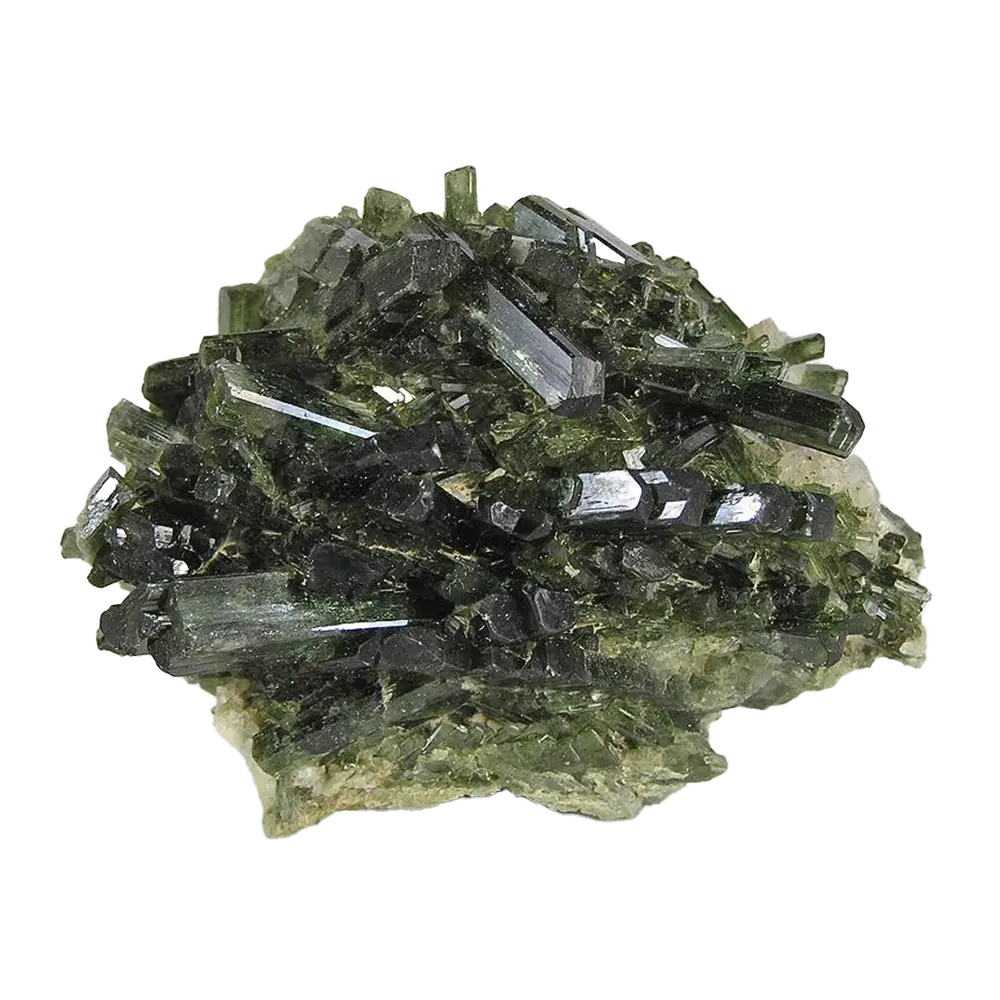
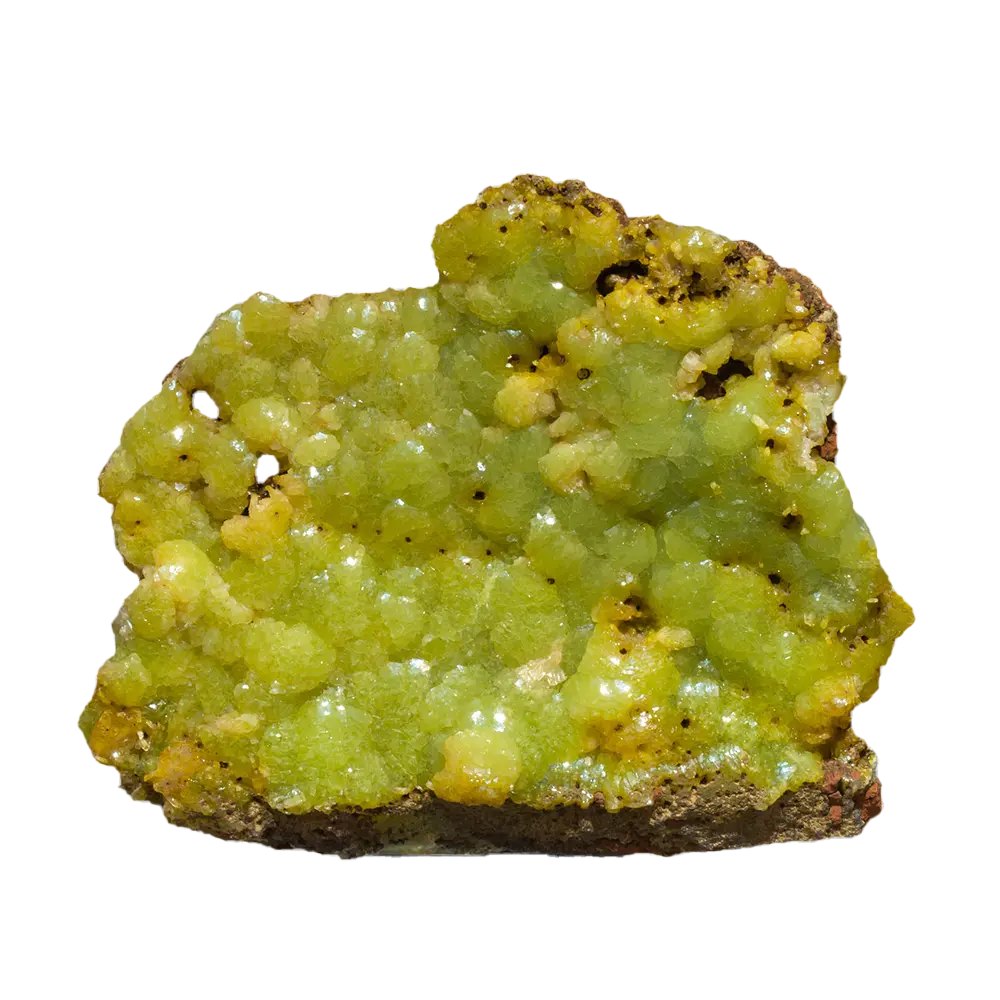
Types and Colors: Scorodite is known for its beautiful range of colors, which vary depending on the exact chemical composition and environmental conditions:
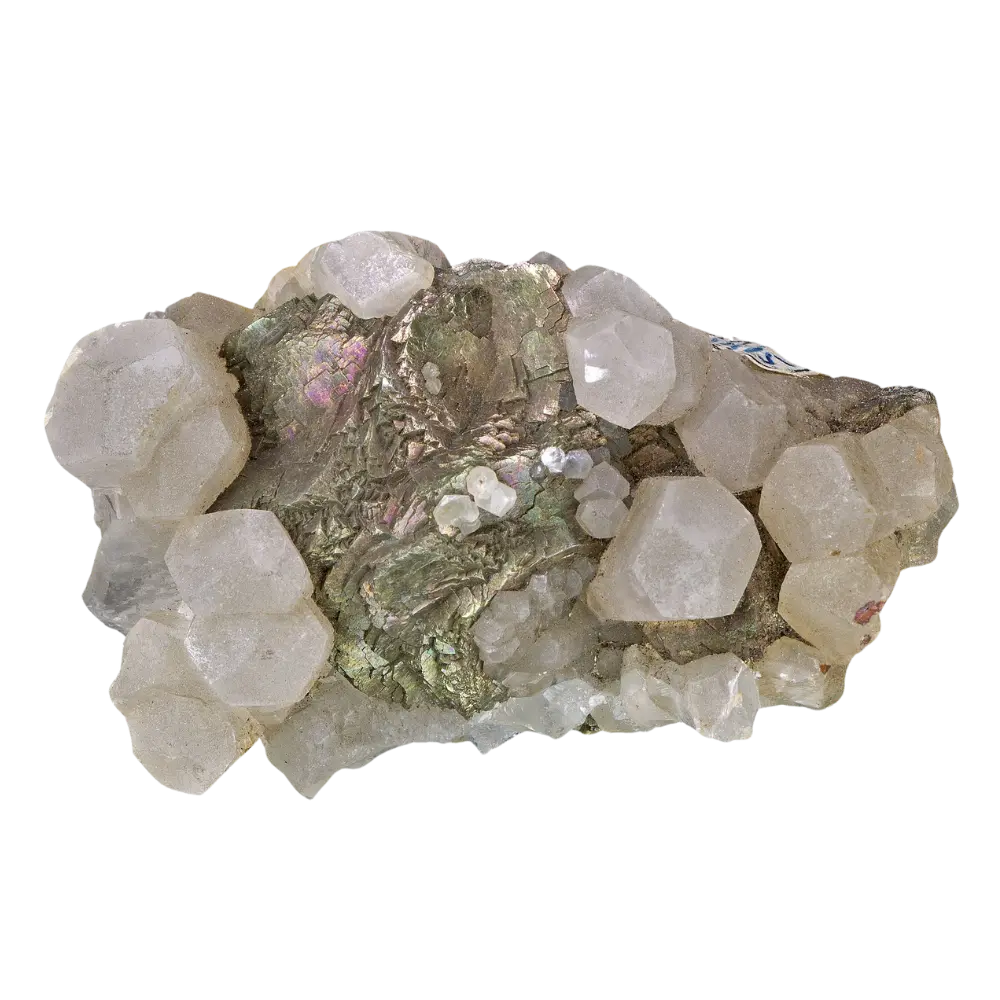
- Blue Scorodite: The most sought-after form of scorodite, which displays vivid blue to blue-green colors, often due to the presence of trace elements or structural defects.
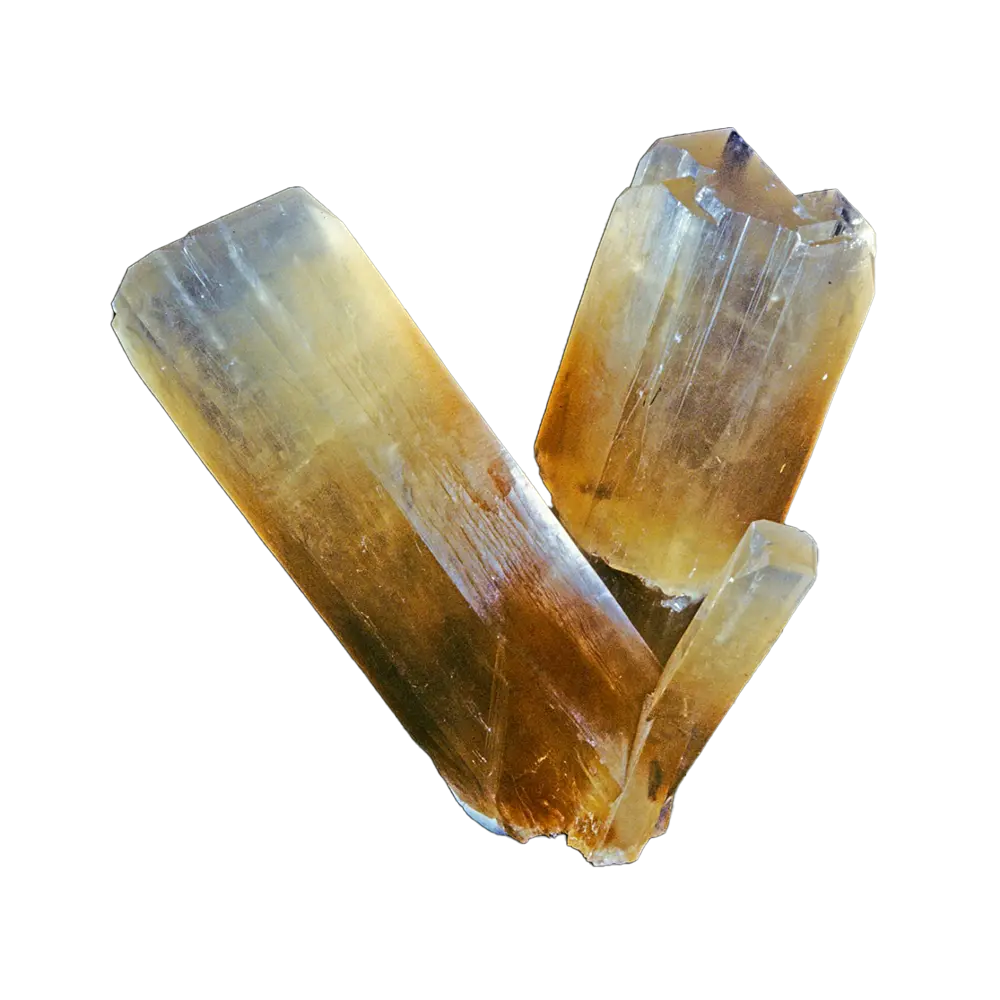
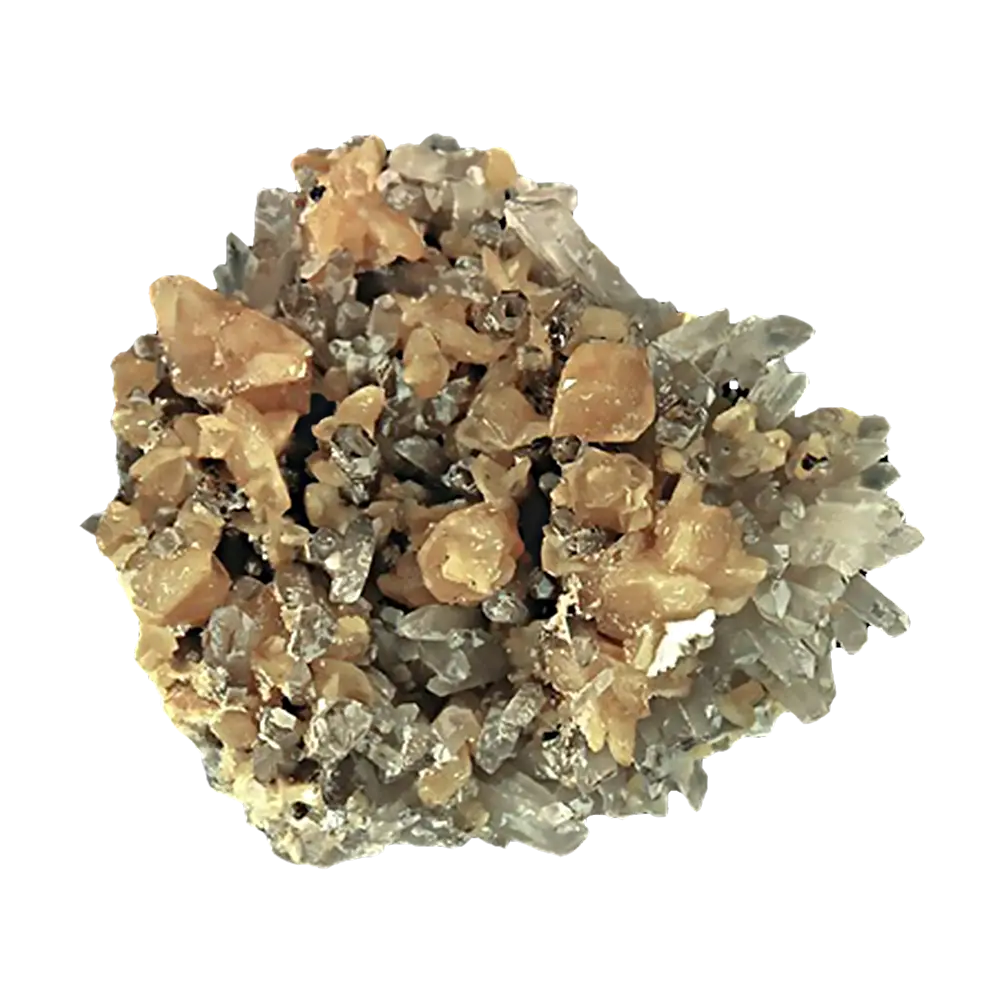
- Green and Yellow Scorodite: Less common but still highly attractive, these colors can result from iron oxidation states or the incorporation of other elements.
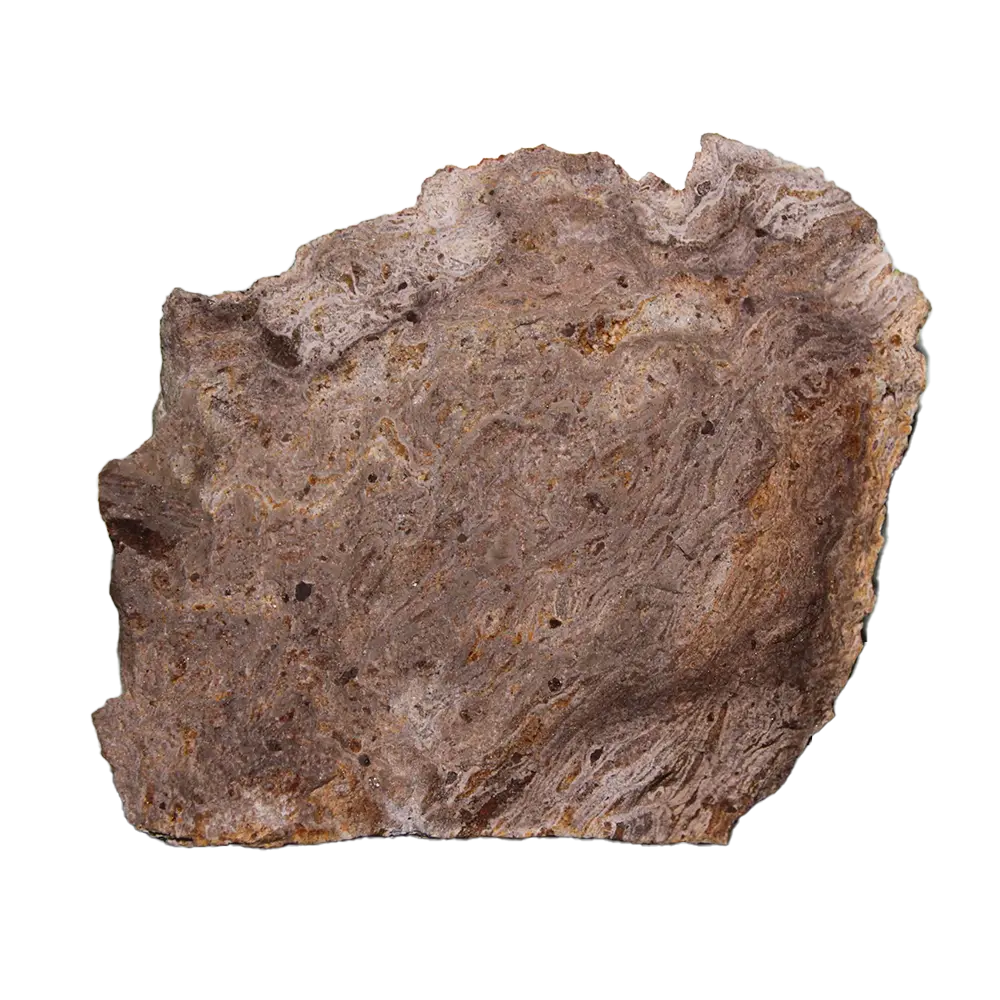
- Brown and Gray Scorodite: These forms are often associated with weathered deposits and typically occur in less visually striking specimens.
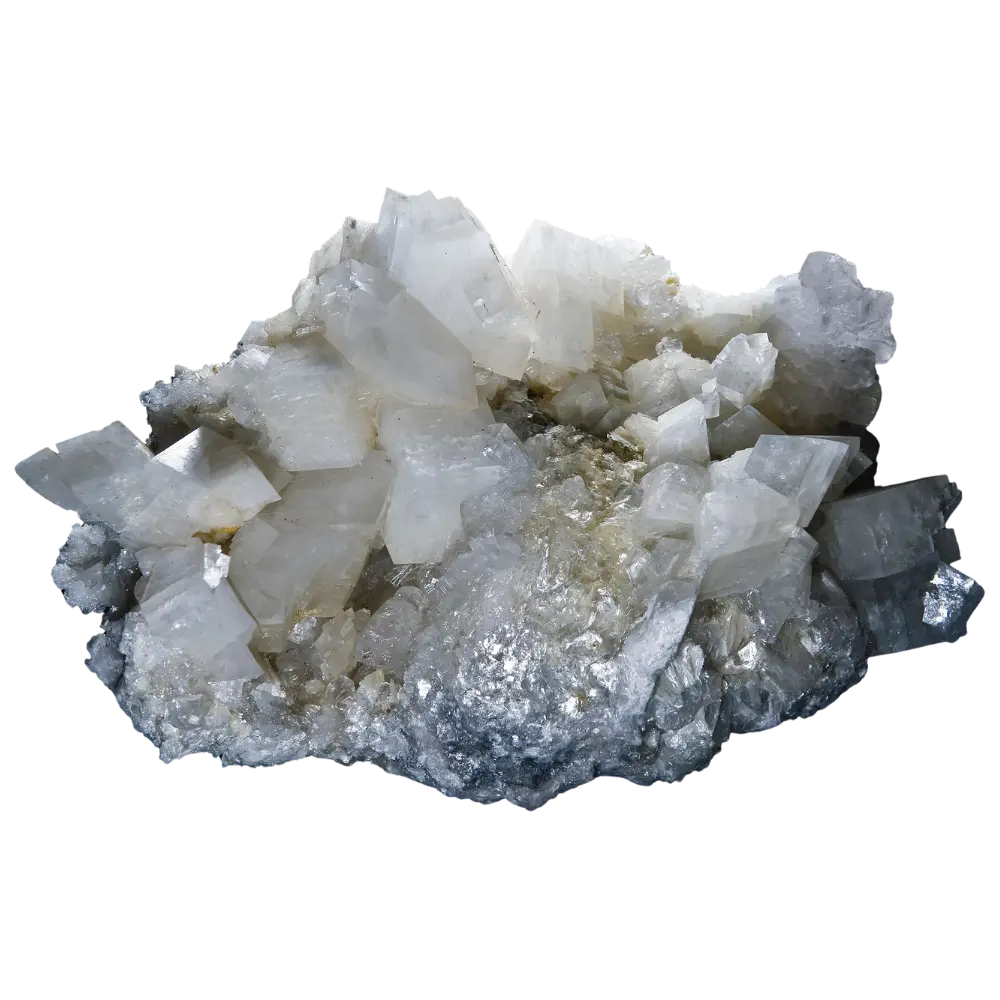
- Colorless Scorodite: Rare but can form under specific environmental conditions, usually in fine crystal structures.
In addition to its color, scorodite is often noted for its brilliant luster, ranging from vitreous (glassy) to sub-metallic, making it an eye-catching mineral for collectors.
Localities and Occurrence: Scorodite is found in several key localities around the world, particularly in regions with significant arsenic-rich deposits:
- Germany: Scorodite was first discovered in Saxony, Germany, in the Freiberg mining district. It remains a significant locality for well-formed specimens.
- United States: In the U.S., scorodite is found in several states, including Arizona, Nevada, and Montana, where it occurs in oxidized arsenic-bearing deposits.
- Canada: The Yukon and other parts of Canada have yielded notable scorodite specimens, often associated with gold and arsenic mineralization.
- Namibia: Scorodite occurs in the famous Tsumeb Mine, where it is found alongside a variety of secondary minerals formed in the oxidized zones of polymetallic deposits.
- Mexico: Mexican scorodite specimens, particularly from the Ojuela Mine, are well-known for their vibrant colors and well-formed crystals.
- Czech Republic: Historic mining districts in the Czech Republic have produced fine scorodite specimens, often associated with arsenopyrite and other arsenic minerals.
Applications: Though scorodite is not commonly used industrially, it has significant roles in several fields:
- Arsenic Source: Scorodite can serve as a minor ore of arsenic, although most arsenic is extracted from other minerals like arsenopyrite. Arsenic has various industrial applications, including in semiconductors, pesticides, and wood preservatives.
- Collector’s Mineral: Due to its vibrant color and well-formed crystals, scorodite is highly sought after by mineral collectors. Blue scorodite crystals, in particular, are considered some of the most beautiful in the mineral world.
- Environmental Significance: Scorodite plays a crucial role in the stabilization of arsenic in mine tailings and waste. As a naturally occurring arsenic compound, scorodite is stable under certain environmental conditions, and research has focused on its potential for arsenic containment and remediation in contaminated soils and water systems. This makes it valuable in environmental studies and mining waste management.