Fact Sheet:
– Chemical Composition: Mg₃Si₄O₁₀(OH)₂ (Magnesium Silicate Hydroxide)
– Hardness: 1 on the Mohs scale
– Crystal System: Monoclinic or triclinic
– Color Varieties: White, gray, green, brown, colorless
– Major Localities: United States, China, Brazil, India, and France
– Common Uses: Baby powder, cosmetics, ceramics, paint, paper, and plastics
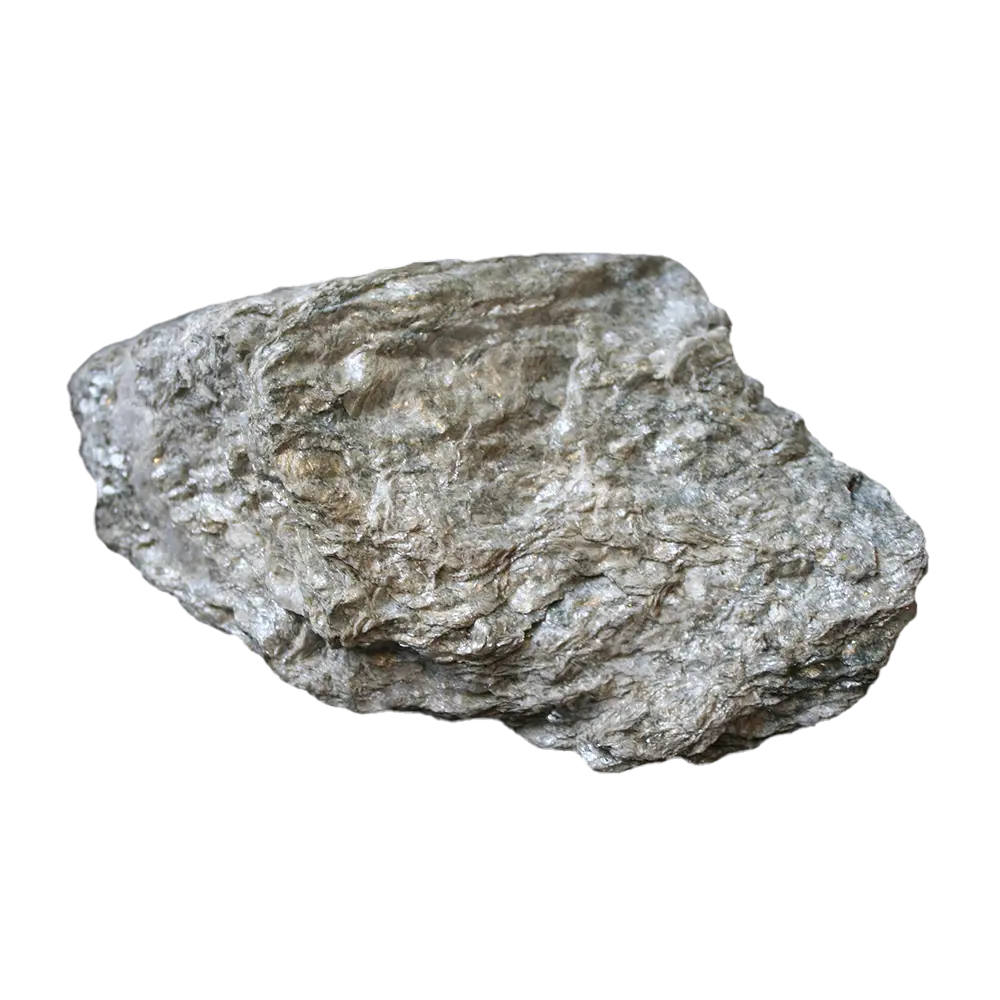
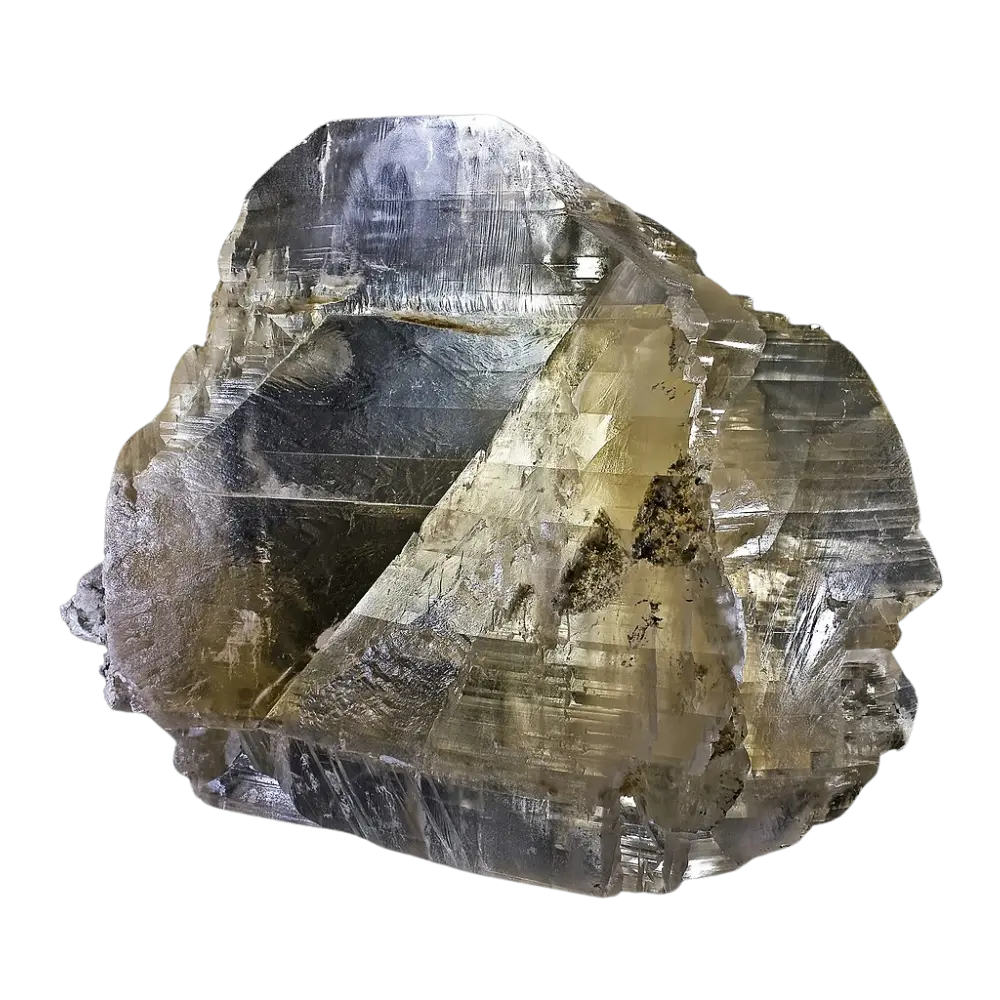
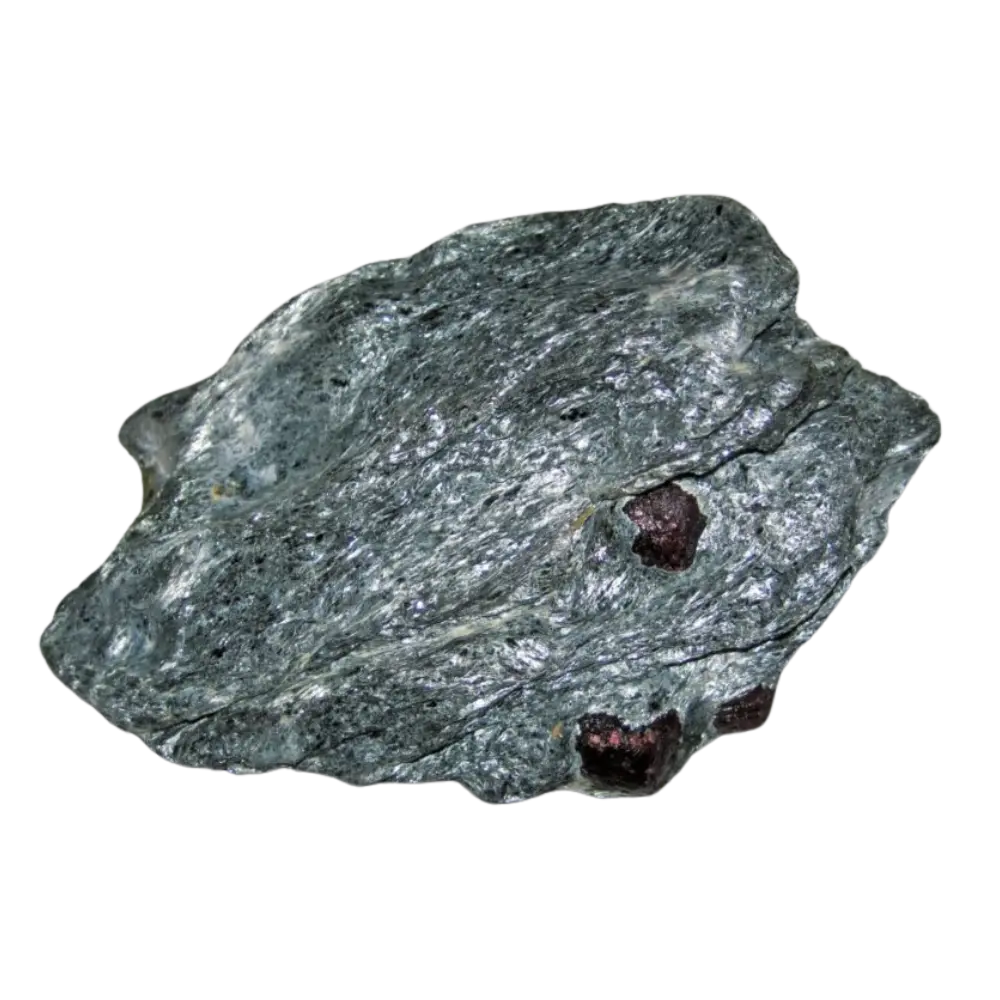
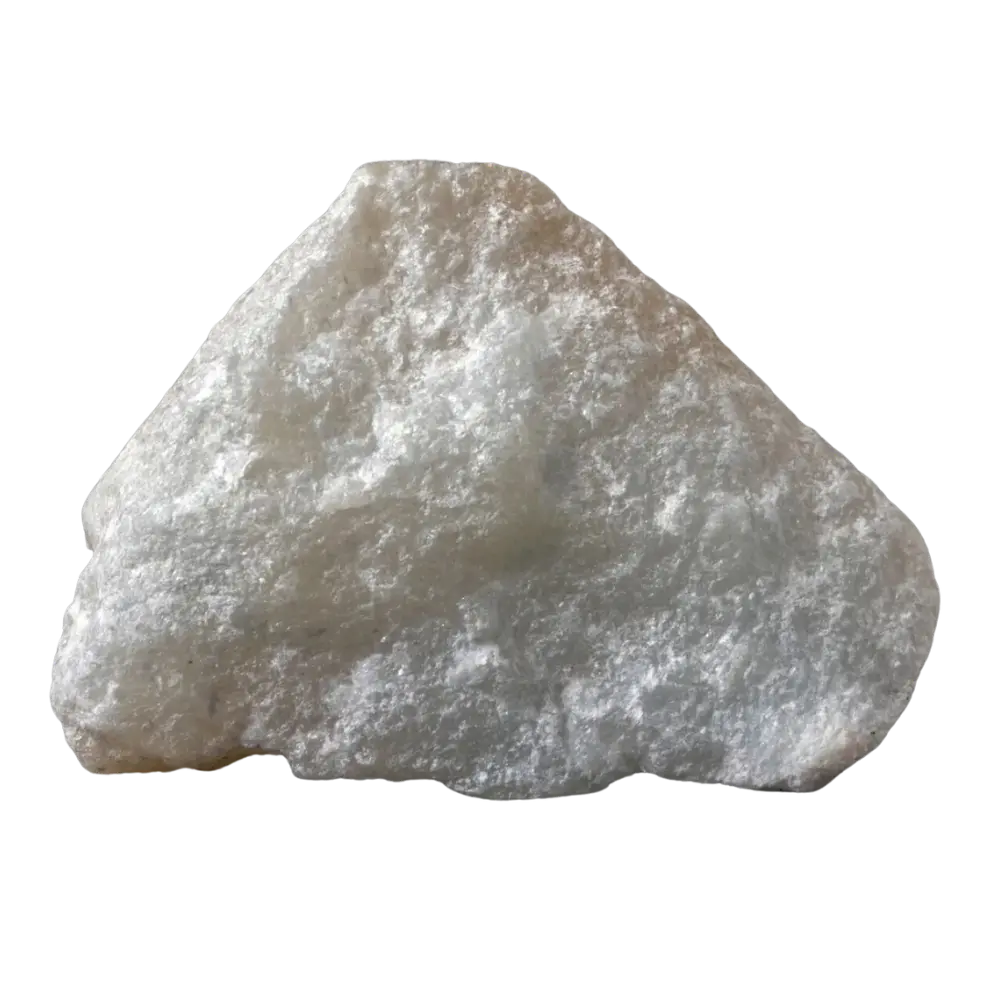
Introduction: Talc is the softest mineral known, ranking as 1 on the Mohs hardness scale. Its ability to be easily scratched by a fingernail and its greasy feel make it unique among minerals. Talc has been used by humans for millennia in various applications, from personal care products to industrial uses.
Formation: Talc forms through the metamorphism of magnesium-rich rocks, such as serpentine, pyroxenite, and amphibolite, in the presence of carbon dioxide and water. This process typically occurs at convergent plate boundaries where heat and pressure conditions favor the transformation of these rocks into talc.
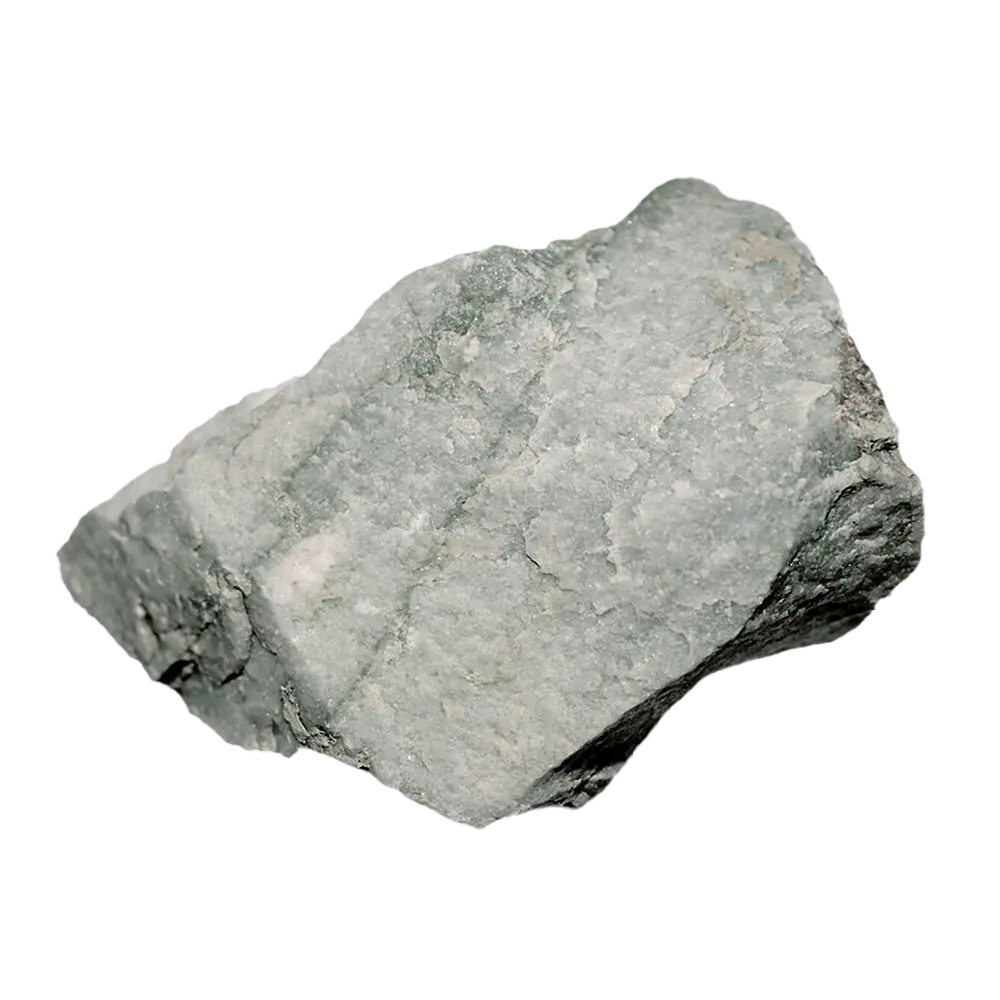
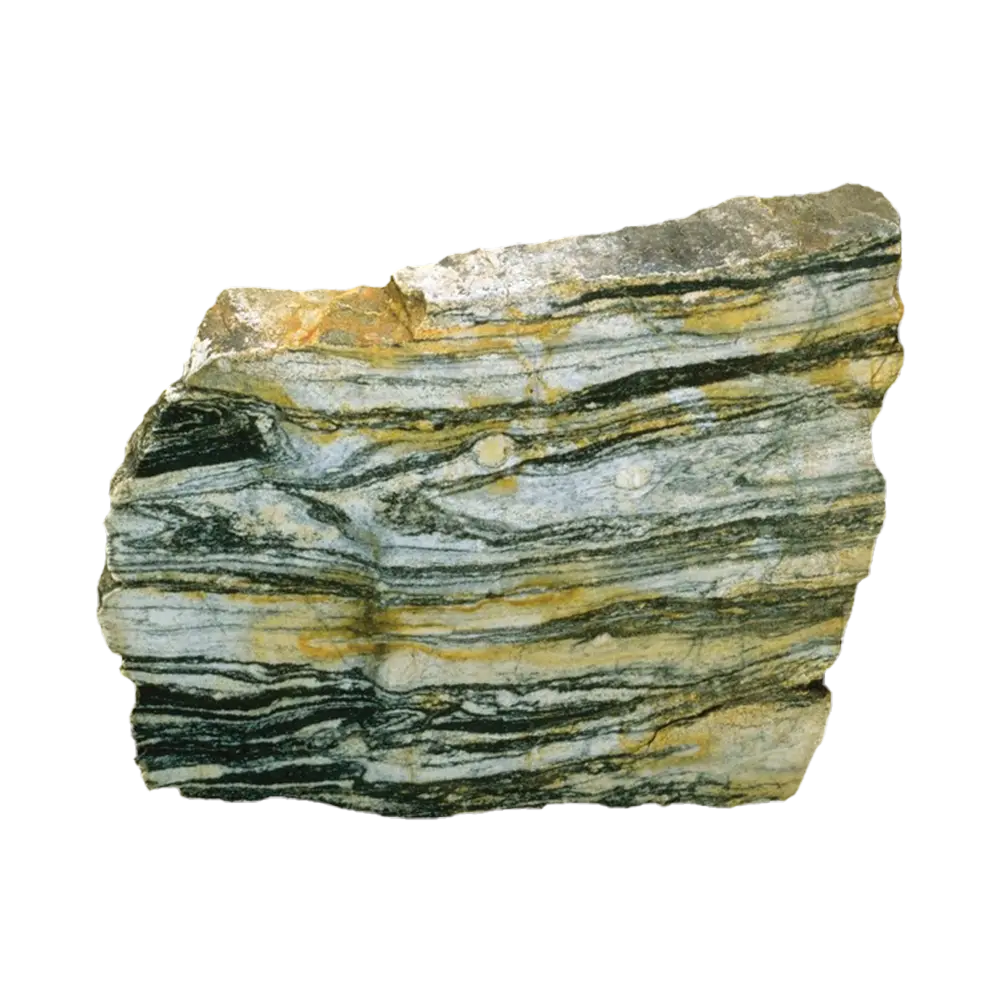
Types and Colors: Talc typically appears in various shades of white, gray, and green. The purest form, often used in cosmetics, is usually white or colorless. Talc can also contain minor impurities that give it different colors, such as brown or green.
Localities and Mining: Significant talc deposits are found in the United States (notably in Montana, Texas, and Vermont), China, Brazil, India, and France. These countries have extensive mining operations that extract talc for various uses, from cosmetics to industrial applications.
Applications: Talc’s softness, chemical inertness, and hydrophobic properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications:
– Cosmetics and Personal Care: Talc is widely used in baby powder, face powders, and other cosmetic products due to its ability to absorb moisture and provide a silky texture.
– Ceramics: Talc is used in the manufacture of ceramics to improve thermal shock resistance and glaze adherence.
– Paint and Coatings: Talc is used as a filler to improve the paint’s smoothness and to control gloss.
– Paper: Talc is added to paper to enhance its printability and reduce surface friction.
– Plastics: Talc is used as a reinforcing filler in plastics to improve mechanical properties and thermal resistance.