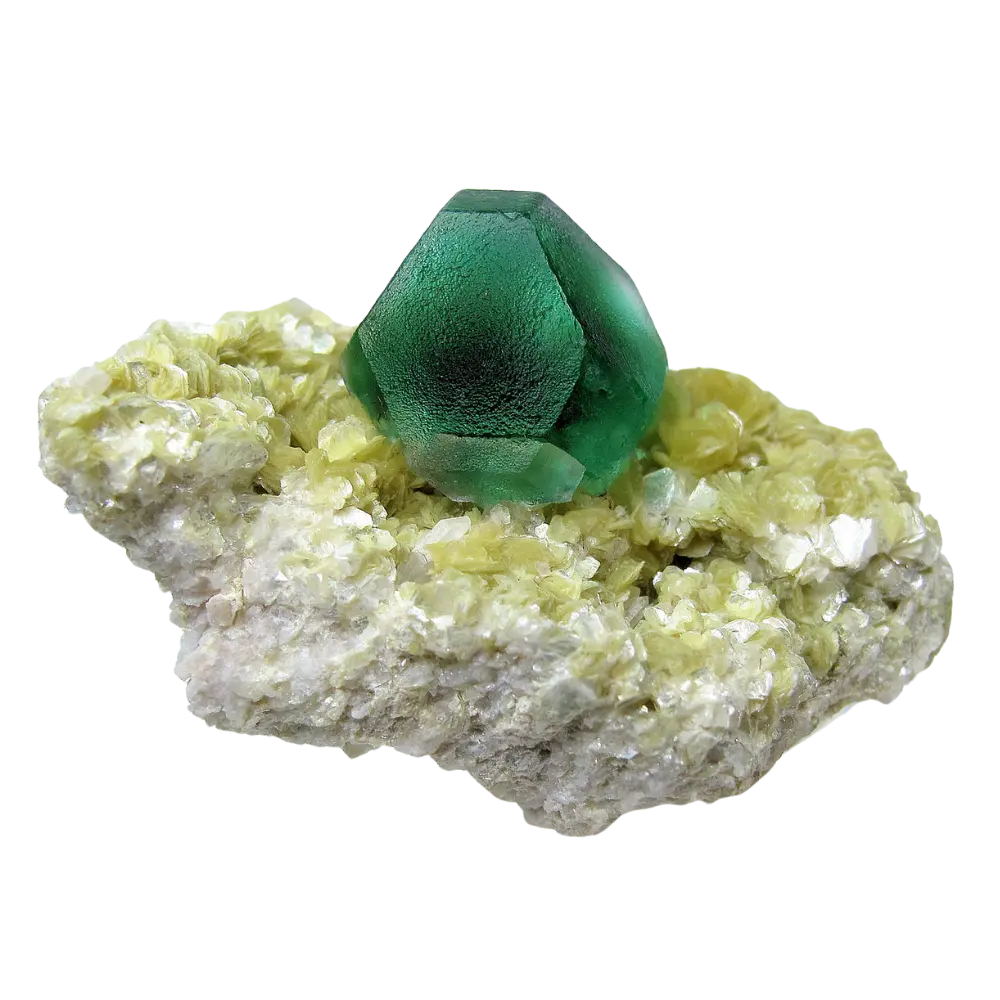
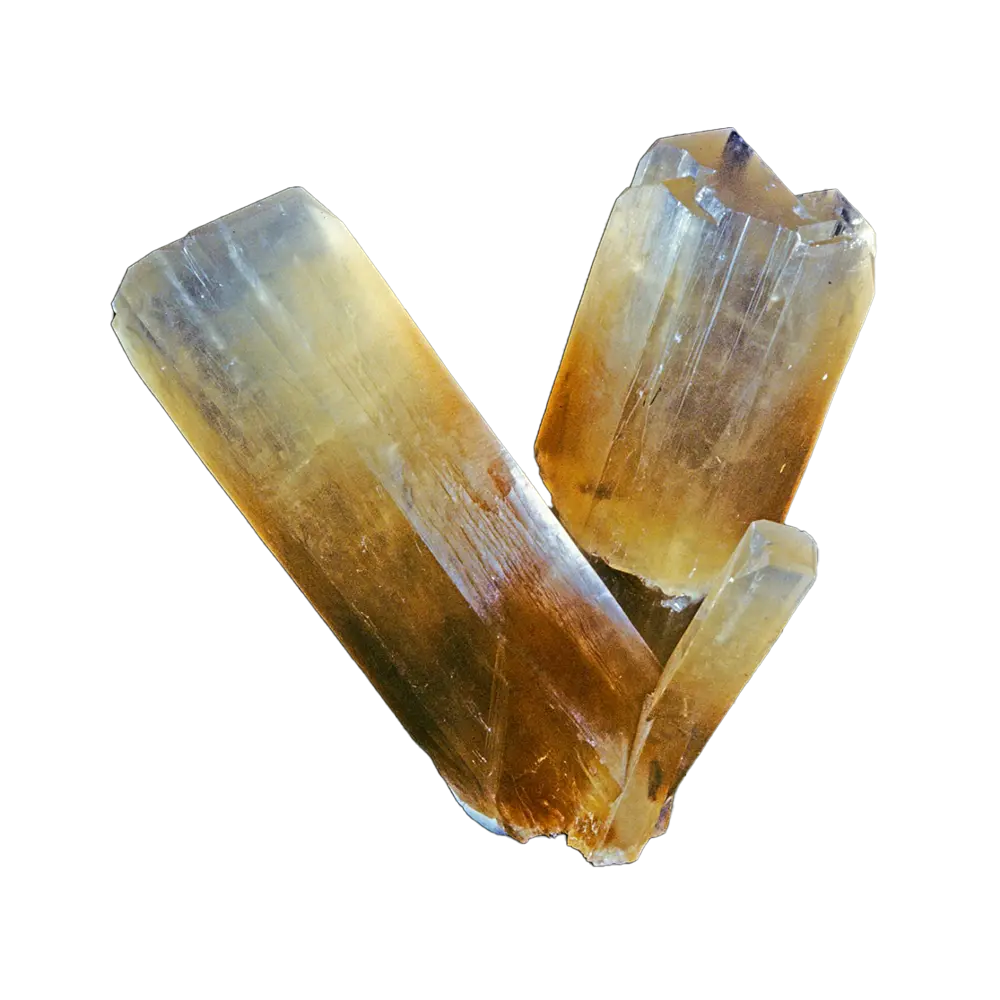
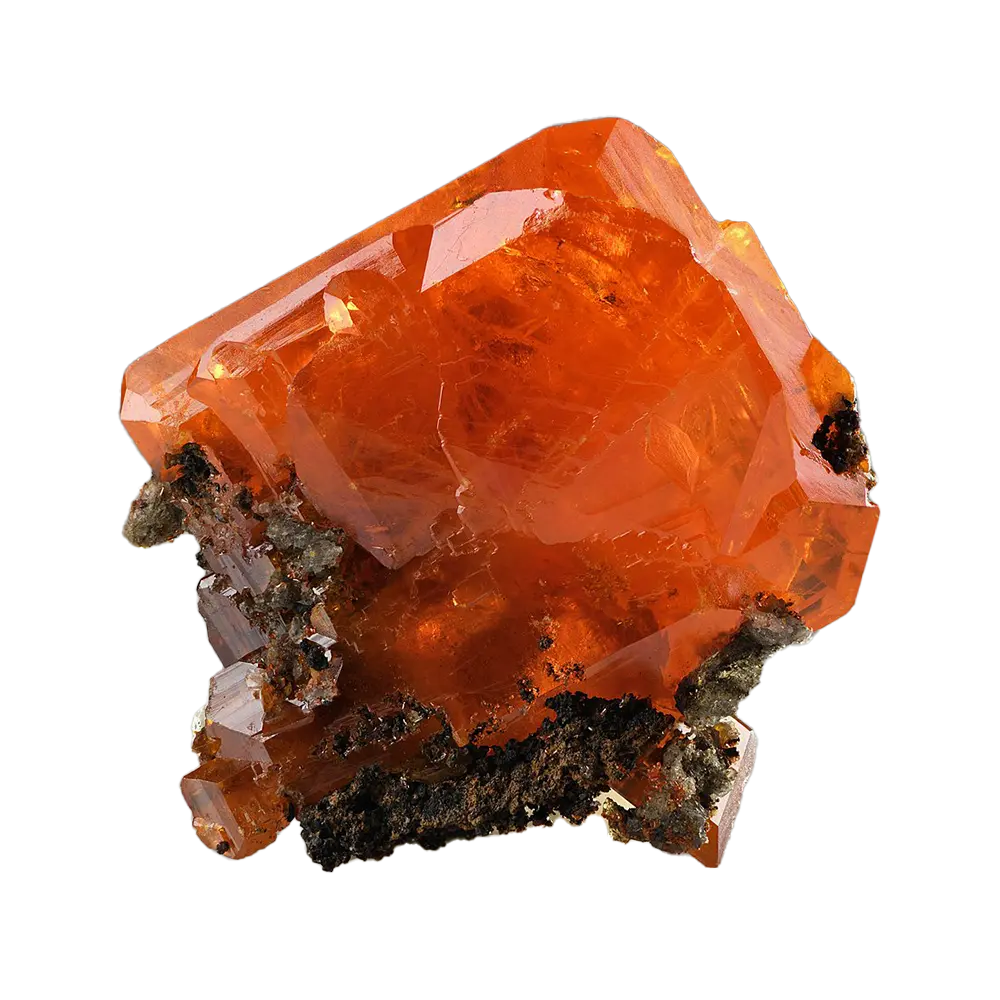
Fact Sheet:
– Chemical Composition: ZrSiO₄ (Zirconium Silicate)
– Hardness: 7.5 on the Mohs scale
– Crystal System: Tetragonal
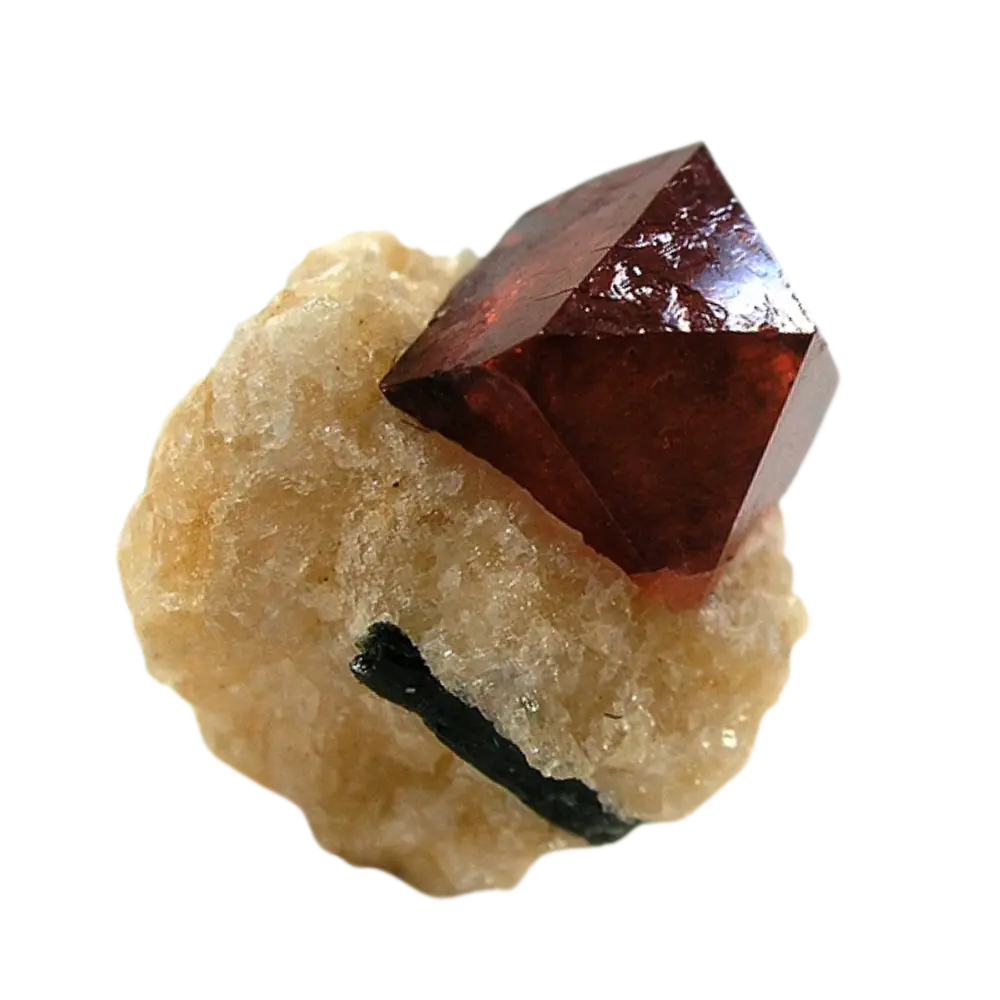
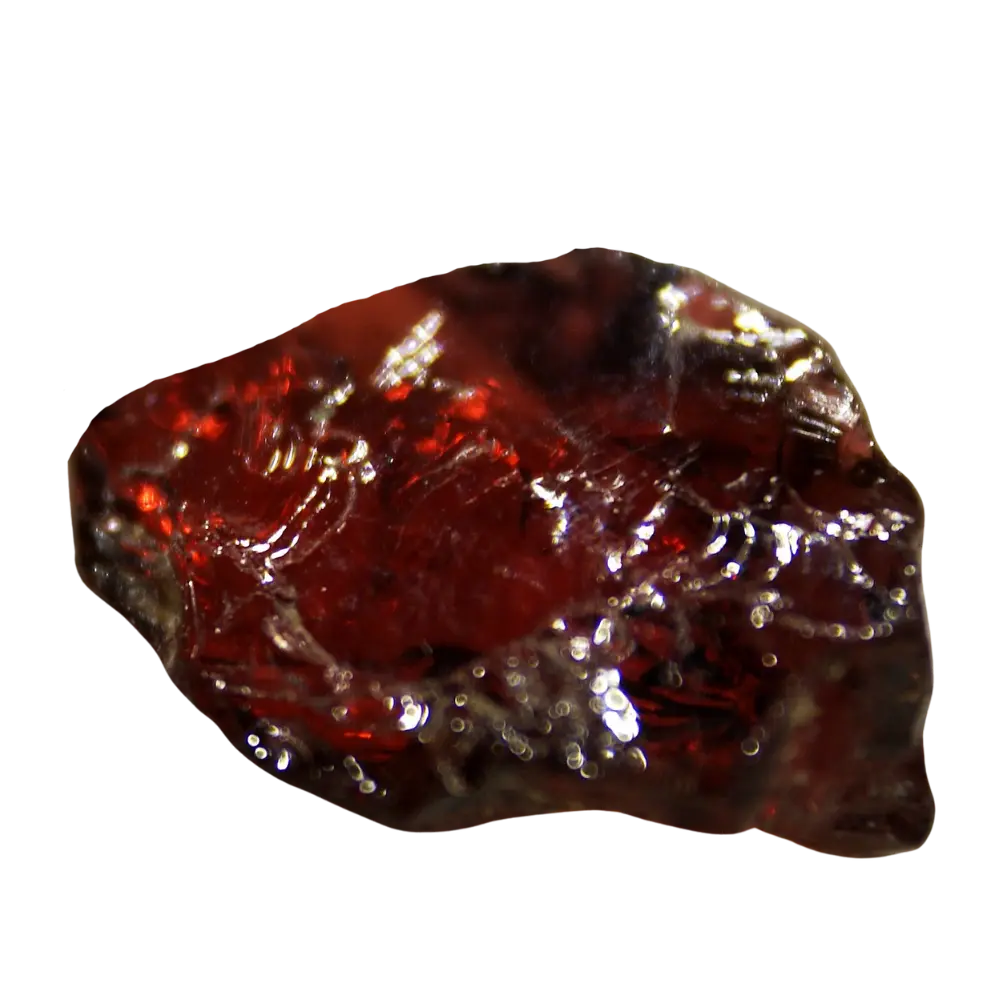
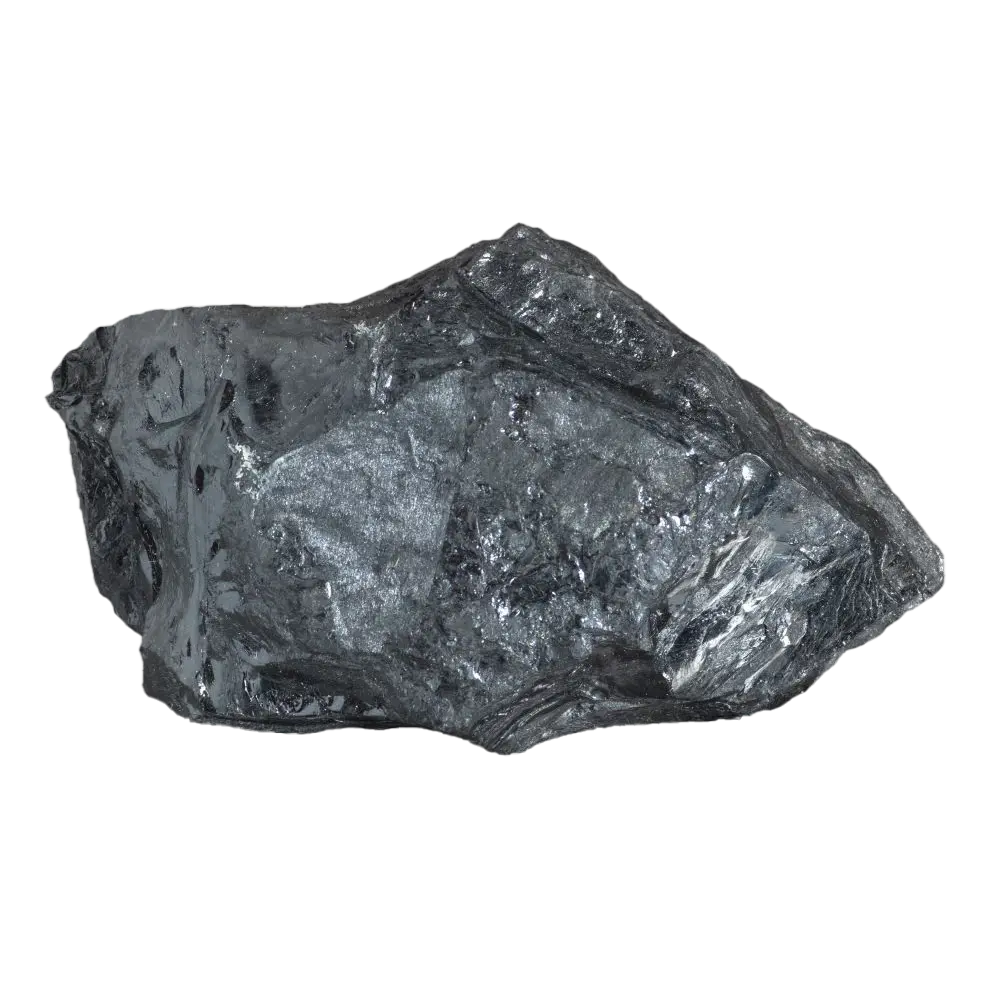
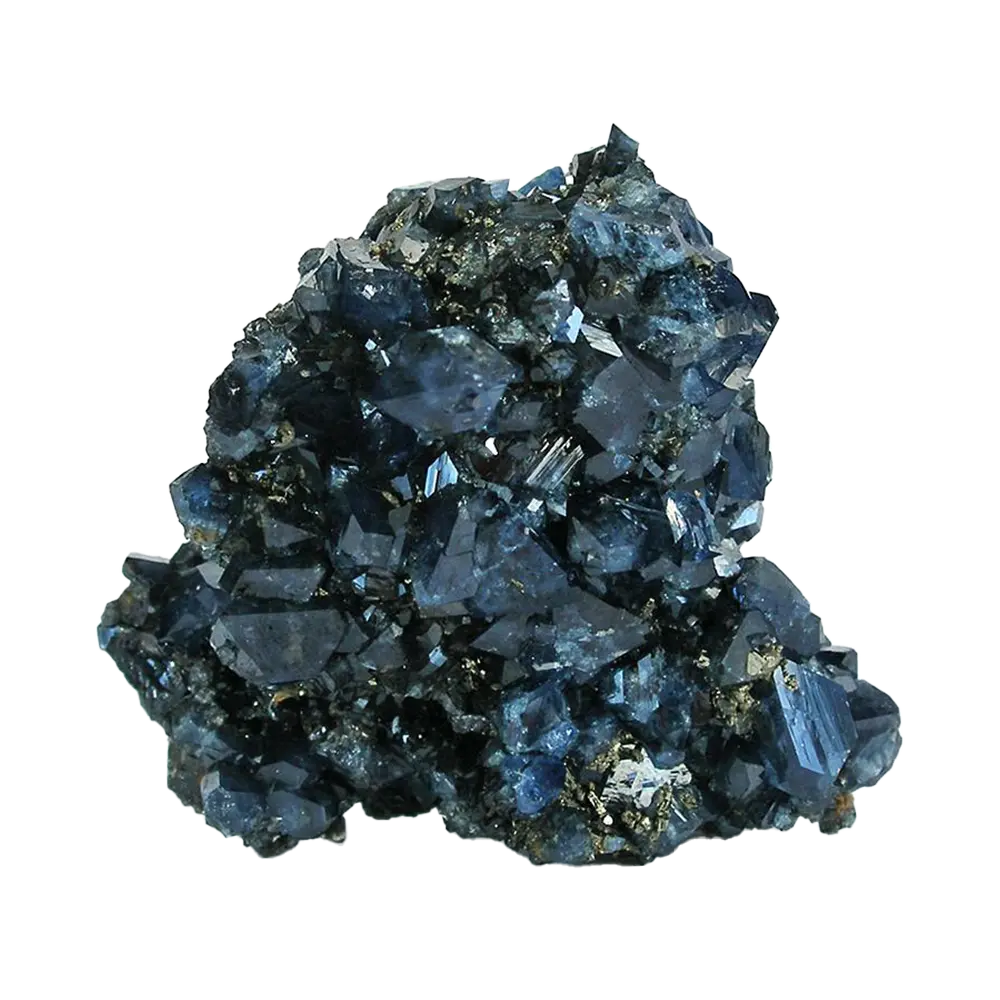
– Color Varieties: Colorless, yellow, red, brown, green, blue
– Major Localities: Australia, Sri Lanka, Brazil, Russia, and the United States
– Common Uses: Gemstones, geochronology, ceramics, and refractory materials
Introduction: Zircon is a remarkable mineral known for its brilliant luster, diverse color range, and significant role in geological studies. Often used as a gemstone, zircon is also a vital tool for scientists studying the Earth’s history, as it can contain traces of uranium and thorium, making it useful for radiometric dating.
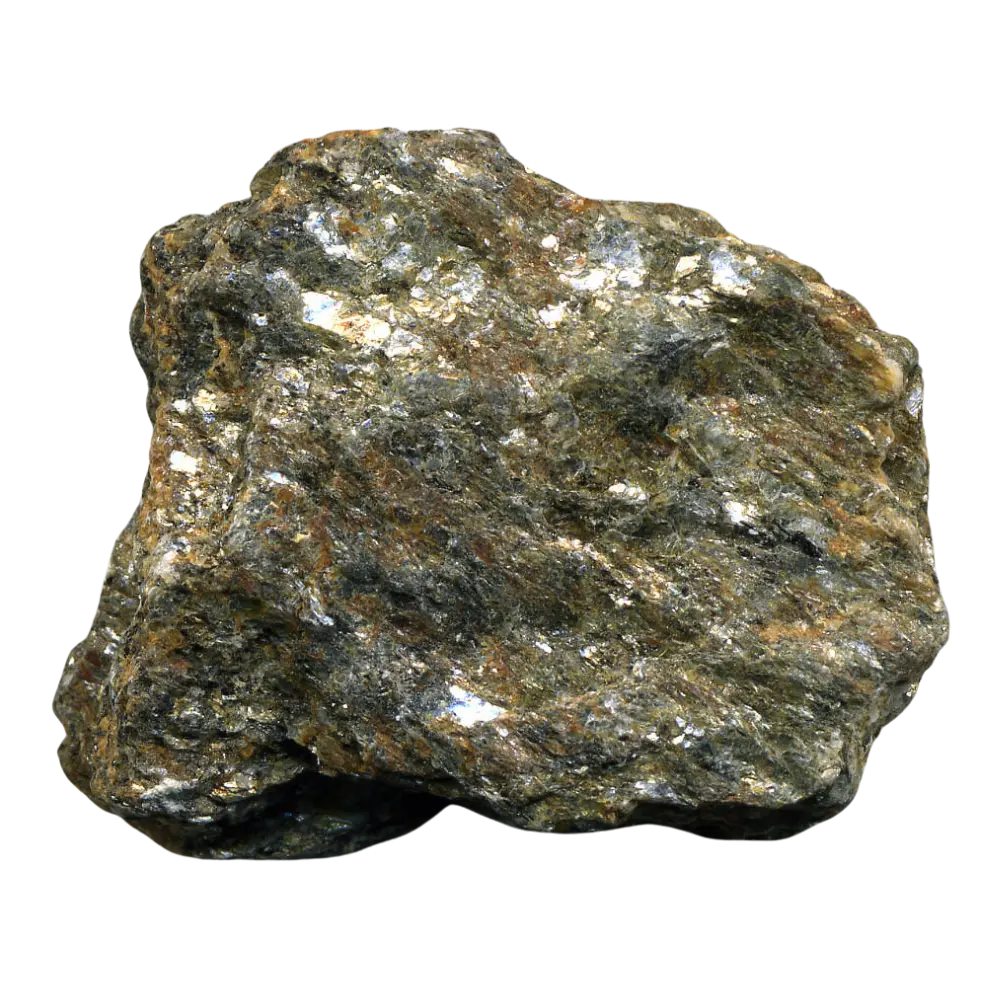
Formation: Zircon forms in igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. It crystallizes from magma or lava and is resistant to weathering and erosion, making it common in sedimentary deposits. Zircon’s durability and resistance to chemical alteration allow it to survive geological processes, providing a record of the Earth’s crust formation.
Types and Colors: Zircon typically appears in a wide range of colors, influenced by trace elements:
– Colorless Zircon: Often heat-treated to achieve the prized “blue zircon” used in jewelry.
– Yellow to Red Zircon: Known as hyacinth, found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
– Brown to Green Zircon: Found in various geological environments, used for geochronology.
Localities and Mining: Significant zircon deposits are found in Australia (notably the Harts Range and Northern Territory), Sri Lanka, Brazil, Russia, and the United States. Australia is the leading producer of zircon, with extensive mining operations extracting it for both industrial and gem-quality uses.
Applications: Zircon has several important applications:
– Gemstones: Zircon is used in jewelry for its brilliance and wide range of colors. Heat-treated blue zircon is particularly popular.
– Geochronology: Zircon crystals are used in radiometric dating to determine the age of rocks and geological events, providing insights into the Earth’s history.
– Ceramics and Refractories: Zircon is used in the manufacture of ceramics and as a refractory material due to its high melting point and chemical stability.
– Industrial Uses: Zirconium extracted from zircon is used in various industrial applications, including in nuclear reactors and as an abrasive.